Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Miura, Yasufumi*; Suzuki, Kenji*; Morooka, Satoshi; Shobu, Takahisa
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 8(1), p.1_1 - 1_14, 2024/03
Suzuki, Kenji*; Miura, Yasufumi*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Toyokawa, Hidenori*; Saji, Choji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Morooka, Satoshi
Zairyo, 72(4), p.316 - 323, 2023/04
Suzuki, Kenji*; Kura, Komoe*; Miura, Yasufumi*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Toyokawa, Hidenori*; Saji, Choji*; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Shobu, Takahisa
Zairyo, 71(12), p.1005 - 1012, 2022/12
This paper describes a stress measurement from a welded part of an austenitic stainless steel using synchrotron X-rays. Difficulty measuring the X-ray stress of the welded part is caused by the broadening of the diffraction spot in the radial and circumferential directions. The bending strains of the rectangular bar made of the welded part were measured using synchrotron white X-rays and the double exposure method. To improve the energy resolution, monochromatic synchrotron X-ray of 70 keV was used. The diffraction pattern showed the sharp arc like a pattern from texture material. The diffraction profile was obtained from the integral of the diffraction intensity in the direction of the circumference. The diffraction angle was determined using the double exposure method. As a result, the distribution of the residual stresses of the welded part could be measured.
Kumagai, Tomohisa*; Miura, Yasufumi*; Miura, Naoki*; Marie, S.*; Almahdi, R.*; Mano, Akihiro; Li, Y.; Katsuyama, Jinya; Wada, Yoshitaka*; Hwang, J.-H.*; et al.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(1), p.011509_1 - 011509_18, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:20.34(Engineering, Mechanical)To predict fracture behavior for ductile materials, some ductile fracture simulation methods different from classical approaches have been investigated based on appropriate models of ductile fracture. For the future use of the methods to overcome restrictions of classical approaches, the applicability to the actual components is of concern. In this study, two benchmark problems on the fracture tests supposing actual components were provided to investigate prediction ability of simulation methods containing parameter decisions. One was the circumferentially through-wall and surface cracked pipes subjected to monotonic bending, and the other was the circumferentially through-wall cracked pipes subjected to cyclic bending. Participants predicted the ductile crack propagation behavior by their own approaches, including FEM employed GTN yielding function with void ratio criterion, are FEM employed GTN yielding function, FEM with fracture strain or energy criterion modified by stress triaxiality, XFEM with J or delta J criterion, FEM with stress triaxiality and plastic strain based ductile crack propagation using FEM, and elastic-plastic peridynamics. Both the deformation and the crack propagation behaviors for monotonic bending were well reproduced, while few participants reproduced those for cyclic bending. To reproduce pipe deformation and fracture behaviors, most of groups needed parameters which were determined toreproduce pipe deformation and fracture behaviors in benchmark problems themselves and it is still difficult to reproduce them by using parameters only from basic materials tests.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Shirai, Nobutoshi; Miura, Yasushi; Tachibana, Ikuya; Omori, Satoru; Wake, Junichi; Fukuda, Kazuhito; Nakano, Takafumi; Nagasato, Yoshihiko
JAEA-Technology 2016-007, 951 Pages, 2016/07
The periodic safety review of TRP is to confirm the safety activities and get effective additional measures the facility safety and its reliability. We implemented 4 items; for (1) evaluation of safety activity implementation, we confirmed we are adequately expanding its safety activities by the necessary documents and schemes. For (2) evaluation of status of safety activities reflecting the latest technical knowledges, we confirmed we reflect latest knowledges for improvement of safety and reliability. For (3) technical evaluation about aging degradation, we can keep the safety of the facilities important to safety and the sea discharge line, under assumption of the present maintenance, because of "focuses for aging degradation". For (4) planning measures about a 10-years-plan that the operator shall implement to keep the facility condition, by the technical evaluation, we found no additional safety plans into maintenance strategies.
Yamamoto, Masato*; Onizawa, Kunio; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Ogawa, Takuya*; Mabuchi, Yasuhiro*; Valo, M.*; Lambrecht, M.*; Viehrig, H.-W.*; Miura, Naoki*; Soneda, Naoki*
Small Specimen Test Techniques; 6th Volume (ASTM STP 1576), p.53 - 69, 2015/05
In order to ensure the robustness of the Master Curve technique, round-robin tests were performed using 0.16 inch-thick Mini-CT specimens by different investigators to see if consistent 
 values can be obtained. All the specimens used were machined and pre-cracked by one fabricator from unique Japanese RPV material. Seven institutes participated in this exercise, and obtained valid
values can be obtained. All the specimens used were machined and pre-cracked by one fabricator from unique Japanese RPV material. Seven institutes participated in this exercise, and obtained valid 
 values according to the ASTM E1921 standard. The scatter of
values according to the ASTM E1921 standard. The scatter of 
 values obtained was well within the uncertainty range defined in the standard, indicating the robustness of the Mini-CT specimen test technique. Throughout this activity, we could obtain 182
values obtained was well within the uncertainty range defined in the standard, indicating the robustness of the Mini-CT specimen test technique. Throughout this activity, we could obtain 182 
 for a single material. We investigated the statistics of this large database, and found that there is no remarkable difference not only in the
for a single material. We investigated the statistics of this large database, and found that there is no remarkable difference not only in the 
 values but also in the fracture toughness distribution between the Mini-CT specimen and the standard size 1T-C(T) specimen results.
values but also in the fracture toughness distribution between the Mini-CT specimen and the standard size 1T-C(T) specimen results.
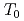 under various selections of temperature conditions
under various selections of temperature conditionsYamamoto, Masato*; Kimura, Akihiko*; Onizawa, Kunio; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Ogawa, Takuya*; Mabuchi, Yasuhiro*; Viehrig, H.-W.*; Miura, Naoki*; Soneda, Naoki*
Proceedings of 2014 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2014) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2014/07
The Master Curve (MC) approach for the fracture toughness reference temperature To is expected to be a powerful tool to ensure the reliability of long-term used RPV steels. In order to get sufficient number of data for the MC approach related to the present surveillance program for RPVs, the use of miniature specimens is important. The test technique for the miniature specimens (Mini-CT) of 4 mm thick had been verified the basic applicability of MC approach by means of Mini-CT for the determination of fracture toughness of typical Japanese RPV steels. A round robin (RR) program was organized to assure the robustness of the technique. As the third step of RR program, blinded tests were carried out. Precise material information was not provided to the participants. From the results obtained, the scatter range in 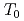 was within the acceptable scatter range specified in the testing standard. The selection of testing temperature seems to give limited effect like that in larger specimens.
was within the acceptable scatter range specified in the testing standard. The selection of testing temperature seems to give limited effect like that in larger specimens.
Yamamoto, Masato*; Onizawa, Kunio; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Ogawa, Takuya*; Mabuchi, Yasuhiro*; Miura, Naoki*
Proceedings of 2013 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2013) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/07
Master Curve (MC) approach for the fracture toughness evaluation is expected to be a powerful tool to assess the structural integrity of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs). In order to get sufficient number of reliable data by the MC approach from used specimens of surveillance tests for RPVs, the use of miniature specimens is necessary. For this purpose, a round robin test program on the miniature compact tension specimens (Mini-CT) of 4 mm thick for the MC approach was launched with the participation of academia, industries and a research institute in Japan. The program aims to verify the reliability of experimental data from Mini-CT, and to pick out technical issues to be solved. As the second step of this program, the effect of loading rate (d /d
/d ) was evaluated based on enlarged database. Despite of the difference in d
) was evaluated based on enlarged database. Despite of the difference in d /d
/d , no specific difference in scatter band of
, no specific difference in scatter band of 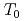 was found in d
was found in d /d
/d -
- 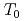 relationships. D
relationships. D /d
/d seems not to be sensitive on scatter band of To in the present results.
seems not to be sensitive on scatter band of To in the present results.
Ishiyama, Koichi; Kimura, Takashi; Miura, Yasushi; Yamaguchi, Katsuhiro*; Kabuki, Toshihide*
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-32-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 8 Pages, 2011/11
To support inspections under an Integrated Safeguards regime into Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP), the IAEA suggested making use of Remote Monitoring (RM) capabilities to the inspection equipment (surveillance camera and NDA systems) installed in the spent fuel storage area at TRP. Since the spent fuel storage area in TRP did not have pre-prepared cabling infrastructure for data transmission, the option of wireless LAN was chosen over the telephone line due to its lower installation costs. Feasibility studies and tests were performed by TRP on communication and particularly on long-term continuous communication using wireless LAN equipment (AP: Access Point) and an external antenna for introducing wireless LAN technology to RM. As a result it was recognized that wireless LAN has enough ability to communicate for long periods of time and consequently the IAEA installed AP and an external antenna to each inspection equipment and the wireless LAN technology was applied for RM.
Asano, Takashi; Fujiwara, Shigeo; Takahashi, Saburo; Nagatani, Taketeru; Fukuhara, Junichi; Kodani, Yoshiki; Kimura, Takashi; Miura, Yasushi
Proceedings of INMM 50th Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2009/00
JAEA commenced to consider the integrated safeguards (IS) approach for JNC-1 site as the new concept of safeguards for further reduction of influence of facility operation by the safeguards activity. On the other hand, the board of governors of IAEA led the broader conclusion to Japan on June 2004 and safeguards implementation in Japan was transferred to the IS scheme in September 2004. IAEA aimed to improve efficiency of safeguards implementation for the plutonium handling facility by optimization of use of advanced safeguards systems and new safeguards regime without reduction of effectiveness of safeguards. The IS approach for JNC-1 site was developed and implemented on August 2008 after many discussions among IAEA, Japan Safeguards Office (JSGO) and JAEA. This paper shows contributions by JAEA to development of this approach from the operator's view point and influence to the operator by implementation of IS approach.
Bakhtiari, M.; Tamai, Hiroshi; Kawano, Yasunori; Kramer, G. J.*; Isayama, Akihiko; Nakano, Tomohide; Kamiya, Kensaku; Yoshino, Ryuji; Miura, Yukitoshi; Kusama, Yoshinori; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(5), p.318 - 325, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:78.65(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In the previous works we had shown that injecting a mixture of large amounts of hydrogen and small amounts of argon can terminate a tokamak discharge quickly with avoiding runaway electron generation. In this work we have done the same experiments but with different gases in addition to argon. In fact we compared the effect of the puffing of argon, krypton, and xenon gases with and without simultaneous hydrogen gas puffing on disruption mitigation. We observed that injecting all impurities in the form of an admixture in hydrogen lead to faster plasma shutdowns with less runaway electron generation. We also found that injecting krypton gas (with or without hydrogen) seems to be a good candidate for plasma shutdown purposes since it induces low heat flux to divertor plates and avoids runaway electron generation more effectively.
Bakhtiari, M.; Kawano, Yasunori; Tamai, Hiroshi; Miura, Yushi; Yoshino, Ryuji; Nishida, Yasushi*
Nuclear Fusion, 42(10), p.1197 - 1204, 2002/10
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:80.12(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Asano, Yoshihiro; Matsumura, Toru; Chiba, R.*; Hashimoto, Tomoyuki*; Miura, Akio*; Shimizu, Hajime*; Tajima, Yasuhisa*; Yoshida, H.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 451(2), p.658 - 696, 2000/11
no abstracts in English
Harding; ; ; ;
ASME/JSME PVP Conference, 0 Pages, 1999/00
None
; Ouchi, Yuichiro; ; ; Harding
ASME/JSME PVP Conference, 0 Pages, 1999/00
None
; Ouchi, Yuichiro; ; ; Harding*
ASME/JSME PVP Conference, 0 Pages, 1999/00
None
Miura, Yasushi; Fukuhara, Junichi
no journal, ,