Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Toyoda, Shin*; Inoue, Kazuhiko*; Yamaguchi, Ichiro*; Hoshi, Masaharu*; Hirota, Seiko*; Oka, Toshitaka; Shimazaki, Tatsuya*; Mizuno, Hideyuki*; Tani, Atsushi*; Yasuda, Hiroshi*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(14), p.1557 - 1564, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)Interlaboratory comparison studies are important for radiation dosimetry in order to demonstrate how the technique is universally available. The set of standard samples are examined in each participating laboratory in the present study. After a set of standard samples together with the samples with unknown doses, which were prepared in the same laboratory as the standard samples, are measured at a participating laboratory, those samples are sent to another participating laboratory for next measurement. There is some small difference observed in the sensitivity (the slope of the dose response line) of the standard samples while the differences in the obtained doses for the samples with unknown doses are rather systematic, implying that the difference is mostly due to the samples but not to measurements.
Nakano, Masanao; Fujii, Tomoko; Nagaoka, Mika; Inoue, Kazumi; Koike, Yuko; Yamada, Ryohei; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Kikuchi, Masaaki*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2019-045, 120 Pages, 2020/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2018. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Ozeki, Hidemasa; Isono, Takaaki; Kawano, Katsumi; Saito, Toru; Kawasaki, Tsutomu; Nishino, Katsumi; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Kido, Shuichi*; Semba, Tomoyuki*; Suzuki, Yozo*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 25(3), p.4200804_1 - 4200804_4, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Morita, Koji*; Zhang, S.*; Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Inoue, Fusao*; Yugo, Hiroaki*; Naito, Masanori*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 241(12), p.4672 - 4681, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:73.77(Nuclear Science & Technology)A five-year research project has been initiated in 2005 to develop a code based on the MPS (Moving Particle Semi-implicit) method for detailed analysis of key phenomena in core disruptive accidents (CDAs) of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). The code is named COMPASS (Computer Code with Moving Particle Semi-implicit for Reactor Safety Analysis). The key phenomena include (1) fuel pin failure and disruption, (2) molten pool boiling, (3) melt freezing and blockage formation, (4) duct wall failure, (5) low-energy disruptive core motion, (6) debris-bed coolability, (7) metal-fuel pin failure. Validation study of COMPASS is progressing for these key phenomena. In this paper, recent COMPASS results of detailed analyses for the several key phenomena are summarized. The present results demonstrate COMPASS will be useful to understand and clarify the key phenomena of CDAs in SFRs in details.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; Uehara, Yasushi*; et al.
Proceedings of 8th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-8) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2010/10
In this paper, FY2009 results of the COMPASS code development are reported. Validation calculations for melt freezing and blockage formation, eutectic reaction of metal fuel, duct wall failure (thermal-hydraulic analysis), fuel pin failure and disruption and duct wall failure (structural analysis) are shown. Phase diagram calculations, classical and first-principles molecular dynamics were used to investigate physical properties of eutectic reactions: metallic fuel/steel and control rod material/steel. Basic studies for the particle method and SIMMER code calculations supported the COMPASS code development. COMPASS is expected to clarify the basis of experimentally-obtained correlations used in SIMMER. Combination of SIMMER and COMPASS will be useful for safety assessment of CDAs as well as optimization of the core design.
Morita, Koji*; Zhang, S.*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Inoue, Fusao*; Yugo, Hiroaki*; et al.
Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-18) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2010/05
A five-year research project has been initiated in 2005 to develop a code based on the MPS (Moving Particle Semi-implicit) method for detailed analysis of specific phenomena in core disruptive accidents (CDAs) of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). The code is named COMPASS (Computer Code with Moving Particle Semi-implicit for Reactor Safety Analysis). The specific phenomena include (1) fuel pin failure and disruption, (2) molten pool boiling, (3) melt freezing and blockage formation, (4) duct wall failure, (5) low-energy disruptive core motion, (6) debris-bed coolability, and (7) metal-fuel pin failure. Validation study of COMPASS is progressing for these key phenomena. In this paper, recent COMPASS results of detailed analyses for the several specific phenomena are summarized.
Terauchi, Makoto; Masai, Jo; Suzuki, Shintaro*
FAPIG, (180), p.30 - 35, 2010/02
Prototype fast breeder reactor in Japan Atomic Energy Agency "MONJU", the aim of strengthening the safety and reliability of maintenance management, maintenance management system from client-server system of updating the Websystem. Fiscal 2008 the Web system started a new maintenance management systems approach. In this paper, we introduce the features and functions of the new maintenance management system.
Sherrill, M. E.*; Abdallah, J.*; Csanak, G.*; Dodd, E. S.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki*; Yamakawa, Koichi; et al.
High-Power Laser Ablation VII (Proceedings of SPIE Vol.7005), p.70051R_1 - 70051R_11, 2008/06
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Akino, Noboru; Ebisawa, Noboru; Hanada, Masaya; Inoue, Takashi; Honda, Atsushi; Kamada, Masaki; Kawai, Mikito; Kazawa, Minoru; Kikuchi, Katsumi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(5-14), p.791 - 797, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:80.6(Nuclear Science & Technology)Modification of JT-60U to a superconducting device (so called JT-60SA) has been planned to contribute to ITER and DEMO. The NBI system is required to inject 34 MW for 100 s. The upgraded NBI system consists of twelve positive ion based NBI (P-NBI) units and one negative ion based NBI (N-NBI) unit. The injection power of the P-NBI units are 2 MW each at 85 keV, and the N-NBI unit will be 10 MW at 500 keV, respectively. On JT-60U, the long pulse operation of 30 s at 2 MW (85 keV) and 20 s at 3.2 MW (320 keV) have been achieved on P-NBI and N-NBI units, respectively. Since the temperature increase of the cooling water in both ion sources is saturated within 20 s, further pulse extension up to 100 s is expected to mainly modify the power supply systems in addition to modification of the N-NBI ion source for high acceleration voltage. The detailed technical design of the NBI system for JT-60SA is presented.
Nagata, Shinji*; Higashi, Seijiro*; Tsuchiya, Bun*; To, Kentaro*; Shikama, Tatsuo*; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Ozaki, Koichi*; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Inoue, Aichi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 257(1-2), p.420 - 423, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:71.98(Instruments & Instrumentation)Structural modification and primary precipitates in the Zr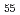 Al
Al Ni
Ni Cu
Cu alloy films (50-100
alloy films (50-100  m thickness) caused by radiation with 300-500 keV H, Ag, Cu and Au ions has been studied. The results of XRD indicated that a metastable primary phase was formed in the alloy by the heat treatment after ion irradiation, but no difference was observed just after the ion irradiation at room temperature. Furthermore, higher incident Au ion fluence effectively suppressed thermal precipitation of the Zr
m thickness) caused by radiation with 300-500 keV H, Ag, Cu and Au ions has been studied. The results of XRD indicated that a metastable primary phase was formed in the alloy by the heat treatment after ion irradiation, but no difference was observed just after the ion irradiation at room temperature. Furthermore, higher incident Au ion fluence effectively suppressed thermal precipitation of the Zr Ni type crystalline phase in the alloy. The deposited energy dependence of the precipitation behavior indicated an increase of the nucleation sites by the implanted metal atoms, simultaneously with a decrease of the growth rate by higher energy deposition density.
Ni type crystalline phase in the alloy. The deposited energy dependence of the precipitation behavior indicated an increase of the nucleation sites by the implanted metal atoms, simultaneously with a decrease of the growth rate by higher energy deposition density.
Fukuda, Yuji; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Hayashi, Yukio; Homma, Takayuki; Inoue, Norihiro*; Kando, Masaki; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
Physics Letters A, 363(2-3), p.130 - 135, 2007/02
Collimated relativistic electrons up to 58 MeV with an electron charge of 2.1 nC were generated by the interaction of intense laser pulses with the Ar cluster target at the laser intensity of 3.5 10
10 W/cm
W/cm . The resulting spectrum does not fit a Maxwellian distribution, but is well described by a two-temperature Maxwellian, which indicates two mechanisms of the electron acceleration. Two dimensional particle-in-cell simulations demonstrate an important role of clusters. The higher energy electrons are injected when they are expelled from the clusters by the laser pulse field. They then gain their energy during the direct acceleration by the laser pulse, whose phase velocity in the underdense plasma is larger than speed of light in vacuum. The lower energy electrons, which are injected during the plasma wave breaking, are accelerated by the wakefield.
. The resulting spectrum does not fit a Maxwellian distribution, but is well described by a two-temperature Maxwellian, which indicates two mechanisms of the electron acceleration. Two dimensional particle-in-cell simulations demonstrate an important role of clusters. The higher energy electrons are injected when they are expelled from the clusters by the laser pulse field. They then gain their energy during the direct acceleration by the laser pulse, whose phase velocity in the underdense plasma is larger than speed of light in vacuum. The lower energy electrons, which are injected during the plasma wave breaking, are accelerated by the wakefield.
Sugita, Akihiro; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yamada, Hidetaka; Inoue, Norihiro*; Aoyama, Makoto; Yamakawa, Koichi
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 46(1), p.226 - 228, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:30.05(Physics, Applied)Generation of broadband mid-infrared (MIR) laser pulses by difference frequency mixing (DFM) is reported. Two-color femtosecond pulses from a Ti: Sapphire laser system is mixed in an AgGaS crystal utilizing a noncollinear phase matching scheme. The relative bandwidth of the generated MIR pulse has been measured to be 23 % to the central frequency, the broadest in DFM-based MIR sources reported so far. It is found that the type-I crystal can give broader phase matching range of spectrum than the type-II crystal within this scheme.
crystal utilizing a noncollinear phase matching scheme. The relative bandwidth of the generated MIR pulse has been measured to be 23 % to the central frequency, the broadest in DFM-based MIR sources reported so far. It is found that the type-I crystal can give broader phase matching range of spectrum than the type-II crystal within this scheme.
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Akiba, Masato; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Inoue, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S428 - S432, 2006/12
To contribute DEMO and ITER, the design to modify the present JT-60U into superconducting coil machine, named National Centralized Tokamak (NCT), is being progressed under nationwide collaborations in Japan. Mission, design and strategy of this NCT program is summarized.
Sherrill, M. E.*; Abdallah, J. Jr.*; Csanak, G.*; Dodd, E. S.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki*; Yamakawa, Koichi; et al.
Physical Review E, 73(6), p.066404_1 - 066404_6, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:75.57(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A model that solves simultaneously both the electron and atomic kinetics was used to generate synthetic He X-ray spectra to characterize a high intensity ultrashort laser driven Ar cluster target experiment. In particular, level populations were obtained from a detailed collisional-radiative model where collisional rates were computed from a time varying electron distribution function obtained from the solution of the zero dimensional Boltzmann equation. In addition, aparticle-in-cell simulation was used to model the laser interaction with the cluster target and provided the initial electron energy distribution function (EEDF) for the Boltzmann solver. This study suggests that the high density plasma contribution to the time-integrated He
X-ray spectra to characterize a high intensity ultrashort laser driven Ar cluster target experiment. In particular, level populations were obtained from a detailed collisional-radiative model where collisional rates were computed from a time varying electron distribution function obtained from the solution of the zero dimensional Boltzmann equation. In addition, aparticle-in-cell simulation was used to model the laser interaction with the cluster target and provided the initial electron energy distribution function (EEDF) for the Boltzmann solver. This study suggests that the high density plasma contribution to the time-integrated He spectrum was in a highly non-equilibrium state in both the EEDF and the ion level populations and provides a prediction of 5.7 ps for the average cluster integrity time for this high density state.
spectrum was in a highly non-equilibrium state in both the EEDF and the ion level populations and provides a prediction of 5.7 ps for the average cluster integrity time for this high density state.
Sherrill, M. E.*; Abdallah, J. Jr.*; Csanak, G.*; Kilcrease, D. P.*; Dodd, E. S.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki; et al.
Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer, 99(1-3), p.584 - 594, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:18.36(Optics)In this work, we present a model that solves self-consistently the electron and atomic kinetics to characterize highly non-equilibrium plasmas, in particular for those systems where both the electron distribution function is far from Maxwellian and the evolution of the ion level populations are dominated by time dependent atomic kinetics. In this model, level populations are obtained from a detailed collisional-radiative model where collision rates are computed from a time varying electron distribution function obtained from the solution of the zero-dimensional Boltzmann equation. The Boltzmann collision term includes the effects of electron-electron collisions, electron collisional ionization, excitation and de-excitation. An application for He spectra from a short pulse laser irradiated argon cluster target will be shown to illustrate the results of our model.
spectra from a short pulse laser irradiated argon cluster target will be shown to illustrate the results of our model.
Inoue, Kazuhiko*; Shibamoto, Hiroshi*; Takahashi, Kenji; Ikutama, Shinya*; Morishita, Masaki; Aoto, Kazumi; Kasahara, Naoto; Asayama, Tai; Kitamura, Seiji
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 48(5), p.333 - 338, 2006/05
no abstracts in English
Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Fujita, Takaaki; Takase, Yuichi*; Sakurai, Shinji; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kurita, Genichi; Morioka, Atsuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(3), p.S29 - S38, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:41.68(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The National Centralized Tokamak (NCT) facility program is a domestic research program for advanced tokamak research to succeed JT-60U incorporating Japanese university accomplishments. The mission of NCT is to establish high beta steady-state operation for DEMO and to contribute to ITER. The machine flexibility and mobility is pursued in aspect ratio and shape controllability, feedback control of resistive wall modes, wide current and pressure profile control capability for the demonstration of the high-b steady state.
Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1599 - 1605, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Enoeda, Mikio; Sato, Masayasu; Isono, Takaaki; Sakurai, Shinji; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Sato, Satoshi; Suzuki, Satoshi; Ando, Masami; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1151 - 1158, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:124 Percentile:99.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English

 ) and Cs(7
) and Cs(7
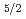 ) by femtosecond laser pulses
) by femtosecond laser pulsesYamada, Hidetaka; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Teranishi, Yoshiaki*; Sugita, Akihiro; Shirai, Toshizo*; Aoyama, Makoto; Akahane, Yutaka; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki*; Yamakawa, Koichi; et al.
Physical Review A, 72(6), p.063404_1 - 063404_5, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:31.16(Optics)A demonstration of coherent quantum control for ultrafast precise selection of closely-lying states is reported. A phase-locked pair of femtosecond laser pulses is generated through a pulse shaper to excite the ground-state cesium atom to the Cs(7
 ) and Cs(7
) and Cs(7
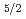 ) states by two-photon absorption. The excited state population is measured by detecting fluorescence from each spin-orbit state. By controlling the phase-difference of the pulse pair, an ultrafast precise selection is accomplished. The contrast ratio of the maximal to minimal selection ratio exceeds 10
) states by two-photon absorption. The excited state population is measured by detecting fluorescence from each spin-orbit state. By controlling the phase-difference of the pulse pair, an ultrafast precise selection is accomplished. The contrast ratio of the maximal to minimal selection ratio exceeds 10 with the delay less than 400 fs.
with the delay less than 400 fs.