Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -rays after neutron capture by
-rays after neutron capture by  La for a T-violation search
La for a T-violation searchOkudaira, Takuya; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Haddock, C. C.*; Ito, Ikuya*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Endo, Shunsuke*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Sato, Takumi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 219, p.09001_1 - 09001_6, 2019/12
Parity violating effects enhanced by up to 10 times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n,
times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n, ) reaction was measured with
) reaction was measured with  La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized
La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized  La target and a 70% polarized
La target and a 70% polarized  He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm
He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm cm are needed. Therefore high quality
cm are needed. Therefore high quality  He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n,
He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n, ) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the
) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the  He spin filter will be presented.
He spin filter will be presented.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Adachi, Taihei*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Nishiyama, Kusuo*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Strasser, P.*; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Kojima, Kenji*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.036017_1 - 036017_4, 2015/09
Kitabatake, Satomi*; Ushiroda, Tota*; Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Furusawa, Yoshiya*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Okahata, Yoshio*; Ito, Atsushi*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 86, 2015/03
Biological effects of high-LET radiation could be understood in terms of the ion track structure. Therefore the evaluation of the contribution of both core and penumbra regions to biological effects is an important issue for the study of high-LET effects. In the present study, we developed a protocol to make a uniform DNA sheet with insoluble nature in aqueous solution, and explored the applicability to the detection of 8-OHdG distributions after heavy-ion irradiation. Water-insoluble DNA sheet was irradiated with proton and neon ion beams at JAEA-Takasaki. After irradiation DNA samples were incubated with an 8-OHdG antibody followed by with a second antibody containing a fluorescence probe. The preliminary results indicated that upon ion irradiation randomly distributed dot-like fluorescence was observed, suggesting that these dots may be from incident ions.
Takegami, Hiroaki; Terada, Atsuhiko; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Ono, Masato; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Ito, Chikara; Hino, Ryutaro; Suzuki, Keiichi*; Onuma, Hiroshi*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2013-032, 25 Pages, 2013/12
We focused on a non-destructive inspection method using cosmic-ray muons as a candidate method for observation of internal the reactor from the outside of a reactor building. In this study, the applicability of this method for the reactor investigation was confirmed by a preliminary examination with High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR). From the results of this examination, it appears that high density structures, such as the core and concrete walls, were able to observe by using muon telescope with coincidence method from the outside of the pressure vessel. Furthermore, we proposed some improvements of this muon inspection system for on-site investigation at the Fukushima Daiichi NPS.
 ions through micro- and nano-capillaries
ions through micro- and nano-capillariesTsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Majima, Takuya*; Tomita, Shigeo*; Sasa, Kimikazu*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Saito, Yuichi; Chiba, Atsuya; Yamada, Keisuke; Hirata, Koichi*; Shibata, Hiromi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 315, p.336 - 340, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.58(Instruments & Instrumentation)Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Uzawa, Akiko*; Matsumoto, Yoshitaka*; Noguchi, Miho; Kase, Yuki*; Takase, Nobuhiro*; Ito, Atsushi*; Koike, Sachiko*; Ando, Koichi*; Okayasu, Ryuichi*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 143(2-4), p.508 - 512, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:71.79(Environmental Sciences)We studied double-strand breaks (DSB) induction and rejoining in clamped and non-clamped transplanted tumours in mice leg after exposure to 80 keV/ m carbon ions and X-rays. The yields of DSB in the tumours were analysed by a static-field gel electrophoresis. The OER of DSB after X-rays was 1.68, and this value was not changed after 1 h rejoining time (1.40). These damages in oxygenated conditions were rejoined 60-70% within 1 h in situ. No difference was found between the exposure to X-rays and carbon ions for the induction and rejoining of DSB. Thus, the values of OER and rejoined fraction after exposure to carbon ions were similar to those after X-rays, and the calculated relative biological effectivenesses of carbon ion were around 1 under both oxygen conditions. The yields of DSB in vivo depend on exposure doses, oxygen conditions and rejoining time, but not on the types of radiation quality.
m carbon ions and X-rays. The yields of DSB in the tumours were analysed by a static-field gel electrophoresis. The OER of DSB after X-rays was 1.68, and this value was not changed after 1 h rejoining time (1.40). These damages in oxygenated conditions were rejoined 60-70% within 1 h in situ. No difference was found between the exposure to X-rays and carbon ions for the induction and rejoining of DSB. Thus, the values of OER and rejoined fraction after exposure to carbon ions were similar to those after X-rays, and the calculated relative biological effectivenesses of carbon ion were around 1 under both oxygen conditions. The yields of DSB in vivo depend on exposure doses, oxygen conditions and rejoining time, but not on the types of radiation quality.
Harjo, S.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Ito, Takayoshi; Arima, Hiroshi; Abe, Jun; Moriai, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Nakatani, Takeshi; Iwahashi, Takaaki; et al.
Materials Science Forum, 652, p.99 - 104, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:99.32(Materials Science, Characterization & Testing)The construction of The Engineering Materials Diffractometer, TAKUMI of J-PARC has been finished on March 2009, and the commissioning has been started from September 2008 being parallel with the final stage of the construction. In the commissioning, after checking the validity and the stability of the detectors and the data acquisition system, we checked powder diffraction data of a 2 mm diameter of annealed piano wire with combination of beam collimation (high resolution mode), and confirmed that resolution 
 /
/ of less than 0.2% can be achieved. We also reports preliminary results from researches using TAKUMI.
of less than 0.2% can be achieved. We also reports preliminary results from researches using TAKUMI.
Sakasai, Kaoru; To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Harjo, S.; Moriai, Atsushi; Ito, Takayoshi; Abe, Jun; Aizawa, Kazuya; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Katagiri, Masaki*; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS-19) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2010/07
Neutron detectors for Engineering Materials Diffractometer, named TAKUMI, at J-PARC have been developed under international cooperation between Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (RAL) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), and installed successfully at the end of March 2009. The detector size was 805 1370
1370 217 mm which was about 1.5 times larger than those installed in ENGIN-X, ISIS facility, RAL. Neutrons are detected based on a nuclear reaction of
217 mm which was about 1.5 times larger than those installed in ENGIN-X, ISIS facility, RAL. Neutrons are detected based on a nuclear reaction of  Li(n,
Li(n,  )
) H using ZnS/
H using ZnS/ LiF scintillator. The data acquisition electronics and decoding module were also manufactured. The overall performances of the detectors have been tested using various sources. The results showed that the detectors had good performances such as a position resolution of 3 mm, a neutron detection efficiency of more than 50% at 1
LiF scintillator. The data acquisition electronics and decoding module were also manufactured. The overall performances of the detectors have been tested using various sources. The results showed that the detectors had good performances such as a position resolution of 3 mm, a neutron detection efficiency of more than 50% at 1  -neutrons, and a
-neutrons, and a  -ray sensitivity of less than 10
-ray sensitivity of less than 10 at 1.3 MeV-
at 1.3 MeV- -ray by
-ray by  Co source, which met the requirements of TAKUMI, and they will be presented at the meeting.
Co source, which met the requirements of TAKUMI, and they will be presented at the meeting.
Kita, Kenichiro; Narisawa, Masaki*; Nakahira, Atsushi*; Mabuchi, Hiroshi*; Ito, Masayoshi*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Advances in Polymer Derived Ceramics and Composites; Ceramic Transactions, Vol.213, p.45 - 50, 2010/06
Abe, Jun; Arakawa, Masashi*; Hattori, Takanori; Arima, Hiroshi; Kagi, Hiroyuki; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Sano, Asami; Uwatoko, Yoshiya*; Matsubayashi, Kazuyuki*; Harjo, S.; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 81(4), p.043910_1 - 043910_5, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:30.89(Instruments & Instrumentation)A compact cubic-anvil high-pressure device was developed for in situ neutron powder diffraction studies. In this device, a cubic shaped pressure medium is compressed by six anvils, and neutron beam pass through gaps between the anvils. The first high-pressure experiment using this device was conducted at J-PARC and clearly showed the neutron diffraction patterns of Pb. Combining the cubic-anvil high-pressure device with a pulsed neutron source will prove to be a useful tool for neutron diffraction experiments.
Abe, Jun; Hattori, Takanori; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi; Arakawa, Masashi*; Sano, Asami; Kagi, Hiroyuki; Harjo, S.; Ito, Takayoshi; Moriai, Atsushi; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 215, p.012023_1 - 012023_6, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:81.49(Instruments & Instrumentation)A high-intensity proton accelerator facility named J-PARC has been constructed, and the first neutron beam at J-PARC/MLF was extracted in May of 2008, and user-operation commenced in December of the year. The fist feasibility test of high-pressure neutron experiments were performed with the engineering materials diffractometer "TAKUMI". As results, diffraction profiles of sample embedded in high-pressure devices were obtained. Therefore, it was confirmed that in situ high-pressure neutron diffraction was feasible with the engineering materials diffractometer "TAKUMI".
Kita, Kenichiro; Narisawa, Masaki*; Nakahira, Atsushi*; Mabuchi, Hiroshi*; Ito, Masayoshi*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Journal of Materials Science, 45(1), p.139 - 145, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:37.13(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The polymer blends of polycarbosilane (PCS) and polymethylohydrosiloxane with high molecular weight (PMHS-h) were prepared by freeze-drying process. Melt viscosity, themogravimetric analysis, and gas evolution from the polymer blends were analyzed. The polymer blend of HSah15 (15 mass% PMHS-h to PCS) was melt-spun to fiber form, curing by thermal oxidation and pyrolyzed at various temperatures up to 1773 K. The fibers were investigated by tensile tests, FE-SEM observation, and XRD (X-ray diffraction) analysis. After pyrolysis at 1273 K, there were amounts of pores in the cross sections of the fiber derived from HSah15, and after pyrolysis at 1773 K, no remarkable  -SiC crystal were formed on the outside surface of the fiber derived from HSah15.
-SiC crystal were formed on the outside surface of the fiber derived from HSah15.
Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Matsumoto, Yoshitaka*; Kase, Yuki*; Noguchi, Miho; Ando, Koichi*; Ito, Atsushi*; Okayasu, Ryuichi*; Furusawa, Yoshiya*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 78(12), p.1175 - 1178, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:62.2(Chemistry, Physical)The contribution of OH radical-mediated indirect action by particle beams under hypoxic irradiation condition was investigated by using a radical scavenger. V79 cells were irradiated with 150 MeV/nucleon helium ions at an LET of 2.2 keV/mm in the presence or absence of DMSO, and their colony survivals were determined. The contribution of indirect action to cell killing under hypoxic condition was estimated to be 52 %. We conclude that OH radical mediated indirect action still has a half in total contribution on cell killing under hypoxic condition.
Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Ito, Atsushi*; Tomita, Masanori*; Tsukada, Teruyo*; Yatagai, Fumio*; Noguchi, Miho; Matsumoto, Yoshitaka*; Kase, Yuki*; Ando, Koichi*; Okayasu, Ryuichi*; et al.
Radiation Research, 171(2), p.212 - 218, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:119 Percentile:95.63(Biology)The biological effects of radiation originate principally in damages to DNA. DNA damages by X-rays as well as heavy ions are induced by a combination of direct and indirect actions. The contribution of indirect action in cell killing can be estimated from the maximum degree of protection by dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), which suppresses indirect action without affecting direct action. Exponentially growing Chinese hamster V79 cells were exposed to high-LET radiations of 20 to 2106 keV/ m in the presence or absence of DMSO and their survival was determined using a colony formation assay. The contribution of indirect action to cell killing decreased with increasing LET. However, the contribution did not reach zero even at very high LETs and was estimated to be 32% at an LET of 2106 keV/
m in the presence or absence of DMSO and their survival was determined using a colony formation assay. The contribution of indirect action to cell killing decreased with increasing LET. However, the contribution did not reach zero even at very high LETs and was estimated to be 32% at an LET of 2106 keV/ m. Therefore, even though the radiochemically estimated G value of OH radicals was nearly zero at an LET of 1000 keV/
m. Therefore, even though the radiochemically estimated G value of OH radicals was nearly zero at an LET of 1000 keV/ m, indirect action by OH radicals contributed to a substantial fraction of the biological effects of high-LET radiations. The RBE determined at a survival level of 10% increased with LET, reaching a maximum value of 2.88 at 200 keV/
m, indirect action by OH radicals contributed to a substantial fraction of the biological effects of high-LET radiations. The RBE determined at a survival level of 10% increased with LET, reaching a maximum value of 2.88 at 200 keV/ m, and decreased thereafter. When the RBE was estimated separately for direct action (RBE(D)) and indirect action (RBE(I)); both exhibited an LET dependence similar to that of the RBE, peaking at 200 keV/
m, and decreased thereafter. When the RBE was estimated separately for direct action (RBE(D)) and indirect action (RBE(I)); both exhibited an LET dependence similar to that of the RBE, peaking at 200 keV/ m. However, the peak value was much higher for RBE(D) (5.99) than RBE(I) (1.89). Thus direct action contributes more to the high RBE of high-LET radiations than indirect action does.
m. However, the peak value was much higher for RBE(D) (5.99) than RBE(I) (1.89). Thus direct action contributes more to the high RBE of high-LET radiations than indirect action does.
 ; A
; A  Ge-nuclear-quadrupole-resonance study under pressure
Ge-nuclear-quadrupole-resonance study under pressureHarada, Atsushi*; Kawasaki, Shinji*; Mukuda, Hidekazu*; Kitaoka, Yoshio*; Haga, Yoshinori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Onuki, Yoshichika; Ito, Kohei*; Haller, E. E.*; Harima, Hisatomo*
Physical Review B, 75(14), p.140502_1 - 140502_4, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:72.15(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This paper reports that a different type of superconducting order parameter has been realized in the ferromagnetic states in UGe via
via  Ge-nuclear-quadrupole-resonance experiments performed under pressure. Measurements of the nuclear spin-lattice relaxation rate (1/
Ge-nuclear-quadrupole-resonance experiments performed under pressure. Measurements of the nuclear spin-lattice relaxation rate (1/
 ) have revealed an unconventional nature of superconductivity such that the up-spin band is gapped with line nodes, but the down-spin band remains gapless at the Fermi level. This result is consistent with that of a ferromagnetic spin-pairing model in which Cooper pairs are formed among ferromagnetically polarized electrons. The present experiment has shed light on the possible origin of ferromagnetic superconductivity, which is mediated by ferromagnetic spin-density fluctuations relevant to the first-order transition inside the ferromagnetic states.
) have revealed an unconventional nature of superconductivity such that the up-spin band is gapped with line nodes, but the down-spin band remains gapless at the Fermi level. This result is consistent with that of a ferromagnetic spin-pairing model in which Cooper pairs are formed among ferromagnetically polarized electrons. The present experiment has shed light on the possible origin of ferromagnetic superconductivity, which is mediated by ferromagnetic spin-density fluctuations relevant to the first-order transition inside the ferromagnetic states.
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Nakamura, Shu*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Shirai, Toshiyuki*; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 14(4), p.043104_1 - 043104_6, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:88.33(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Fast protons are observed by a newly-developed  time-of-flight spectrometer, which provides
time-of-flight spectrometer, which provides 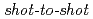 proton-energy distributions immediately after the irradiation of a laser pulse having an intensity of
proton-energy distributions immediately after the irradiation of a laser pulse having an intensity of 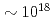 W/cm
W/cm onto a 5-
onto a 5- m-thick copper foil. The maximum proton energy is found to increase when the intensity of a fs-prepulse arriving 9 ns before the main pulse increases from 10
m-thick copper foil. The maximum proton energy is found to increase when the intensity of a fs-prepulse arriving 9 ns before the main pulse increases from 10 to 10
to 10 W/cm
W/cm . Interferometric measurement indicates that the preformed-plasma expansion at the front surface is smaller than 15
. Interferometric measurement indicates that the preformed-plasma expansion at the front surface is smaller than 15  m, which corresponds to the spatial resolution of the diagnostics. This sharp gradient of the plasma makes a beneficial effect on increasing the absorption efficiency of the main-pulse energy, resulting in the increase in the proton energy. This is supported by the result that the X-ray intensity from the laser plasma clearly increases with the prepulse intensity.
m, which corresponds to the spatial resolution of the diagnostics. This sharp gradient of the plasma makes a beneficial effect on increasing the absorption efficiency of the main-pulse energy, resulting in the increase in the proton energy. This is supported by the result that the X-ray intensity from the laser plasma clearly increases with the prepulse intensity.
 -ray analysis and construction of its beam line
-ray analysis and construction of its beam lineOshima, Masumi; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Ebihara, Mitsuru*; Oura, Yasuji*; Ito, Yasuo*; Sawahata, Hiroyuki*; Matsuo, Motoyuki*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 271(2), p.317 - 321, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:61(Chemistry, Analytical)By combining neutron activation analysis with multiple  -ray detection, we have proved better sensitivity and resolution for the trace element analysis than the ordinary single
-ray detection, we have proved better sensitivity and resolution for the trace element analysis than the ordinary single  -ray detection method. We now try to apply the multiple
-ray detection method. We now try to apply the multiple  -ray detection method to the prompt
-ray detection method to the prompt  -ray analysis (PGA). We have established a new cold neutron beam line for PGA in Japan Research Reactor, JRR-3M, at Tokai establishment of Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute(JAERI). It consists of a beam shutter, a beam attenuator, a
-ray analysis (PGA). We have established a new cold neutron beam line for PGA in Japan Research Reactor, JRR-3M, at Tokai establishment of Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute(JAERI). It consists of a beam shutter, a beam attenuator, a  -ray detector array, a sample changer, and a beam stopper. We construct a high-efficiency
-ray detector array, a sample changer, and a beam stopper. We construct a high-efficiency  -ray detector array specially designed for this purpose. Its performance has been evaluated with the Monte Carlo simulation code, GEANT 4.5.0.
-ray detector array specially designed for this purpose. Its performance has been evaluated with the Monte Carlo simulation code, GEANT 4.5.0.
Yura, Kei; Shionyu, Masafumi*; Hagino, Kei*; Hijikata, Atsushi*; Hirashima, Yoshinori*; Nakahara, Taku*; Eguchi, Tatsuya*; Shinoda, Kazuki*; Yamaguchi, Akihiro*; Takahashi, Kenichi*; et al.
Gene, 380(2), p.63 - 71, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:72.21(Genetics & Heredity)Alternative splicing is a molecular mechanism that produces multiple proteins from a single gene, and is thought to produce variety in proteins translated from a limited number of genes. Here we analyzed how alternative splicing produced variety in protein structure and function, by using human full-length cDNAs, on the assumption that all of the alternatively spliced mRNAs were translated to proteins. We found that the length of alternatively spliced amino acid sequences, in most cases, fell into a size shorter than that of average protein domain. We evaluated comprehensively the presumptive three-dimensional structures of the alternatively spliced products to assess the impact of alternative splicing on gene function. We found that more than half of the products encoded proteins which were involved in signal transduction, transcription and translation, and more than half of alternatively spliced regions comprised interaction sites between proteins and their binding partners, including substrates, DNA/RNA, and other proteins. Intriguingly, 67% of the alternatively spliced isoforms showed significant alterations to regions of the protein structural core, which likely resulted in large conformational change. Based on those findings, we speculate that there are a large number of cases that alternative splicing modulates protein networks through significant alteration in protein conformation.
 ;
; 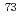 Ge-NQR study under pressure
Ge-NQR study under pressureHarada, Atsushi*; Kawasaki, Shinji*; Mukuda, Hidekazu*; Kitaoka, Yoshio*; Haga, Yoshinori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Onuki, Yoshichika; Ito, Kohei*; Haller, E. E.*; Harima, Hisatomo*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 378-380, p.963 - 964, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.63(Physics, Condensed Matter)The superconducting characteristics on the itinerant ferromagnetic superconductor UGe have been investigated via the
have been investigated via the 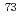 Ge-NQR measurements under pressure (
Ge-NQR measurements under pressure ( ) near the critical pressure
) near the critical pressure 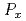 where the first-order transition takes place from the low-temperature (
where the first-order transition takes place from the low-temperature ( ) and low-
) and low- ferromagnetic phase (FM2) to high-
ferromagnetic phase (FM2) to high- and high-
and high- one (FM1). The measurements of nuclear spin-lattice relaxation rate
one (FM1). The measurements of nuclear spin-lattice relaxation rate  have revealed a power-law like behavior as
have revealed a power-law like behavior as 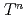 without the coherence peak, whereas at low temperatures, it deviates from the
without the coherence peak, whereas at low temperatures, it deviates from the 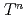 dependence to a
dependence to a  -linear like behavior. These results that depend on the pressure are well understood in terms of non-unitary spin-triplet pairing state where the ferromagnetic up-spin band is gapped, but the down-spin band remains gapless at the Fermi level. We will argue an intimate relationship of the onset of SC with FM1 and FM2.
-linear like behavior. These results that depend on the pressure are well understood in terms of non-unitary spin-triplet pairing state where the ferromagnetic up-spin band is gapped, but the down-spin band remains gapless at the Fermi level. We will argue an intimate relationship of the onset of SC with FM1 and FM2.