Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fujiyama, Hiroki*; Takahashi, Hiroki; Okabe, Kota; Ito, Yuichi*; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Suzuki, Takahiro*; Otsu, Satoru*; Yamakawa, Ryuto*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.529 - 531, 2023/01
Stepper motors are used for mechanical drive in collimators and wire scanner monitors of J-PARC accelerators. Many of these drive unit hardware have been used since the beginning of J-PARC construction, and it is necessary to take measures against aging deterioration. Therefore, we started updating the motor and control system from around 2017. However, when the stepper motor was updated to the current product in the RCS H0 collimator, a malfunction occurred. This is because the drive unit control system cannot correctly recognize the state of the LS (limit switch) due to the noise generated by the motor driver, which hinders the operation. When the noise generated from the old and new stepper motors was measured in a simple test environment for confirmation, it was found that the current product was clearly larger. As a countermeasure, when the wiring of the stepper motor, which was bundled in a single multi-core cable, was separated into separate cables for the power system and LS signal system, the noise level was reduced to about 1/10 and normal operation was restored. I was able to. In this case, we report on noise countermeasures for the RCS H0 collimator drive unit.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
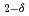 CoGa
CoGa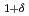 films
filmsKubota, Takahide*; Takano, Daichi*; Kota, Yohei*; Mohanty, S.*; Ito, Keita*; Matsuki, Mitsuhiro*; Hayashida, Masahiro*; Sun, M.*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Saito, Yuji; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(4), p.044405_1 - 044405_12, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:59.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Shamoto, Shinichi*; Akatsu, Mitsuhiro*; Matsuura, Masato*; Kawamura, Seiko; Harii, Kazuya*; Ono, Masao*; Chang, L.-J.*; Ito, Takashi; Nemoto, Yuichi*; Ieda, Junichi
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(1), p.013245_1 - 013245_7, 2022/03
Ultrasound injection effect on a magnetic Bragg peak of yttrium iron garnet has been studied by quasielastic neutron scattering. The magnetic Bragg peak is vastly enhanced with decreasing temperature. The energy width increases proportionally to the square root of the sample temperature increase induced by the ultrasound injection. Because the magnetic Bragg peak is enhanced by the lattice vibration, the enhancement is expected to relate to the spin-lattice coupling closely. An observed sharp drop above 100 K in the longitudinal mode suggests the degradation of the spin-lattice coupling. It is consistent with the decline of spin Seebeck effect with increasing temperature above 100 K, proving the degradation mechanism by the spin-lattice coupling.
Takahashi, Hiroki; Suzuki, Takahiro*; Ishiyama, Tatsuya*; Ito, Yuichi*
Proceedings of 18th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.914 - 917, 2021/10
In the event of an abnormal situation, a machine protection system (MPS) that immediately inhibits the beam is indispensable to minimize the damage and the radioactivation by beam loss. The existing MPS was developed during the construction period, and there are many MPS modules that have been used from the beginning of J-PARC operation, Therefore, as a measure against aging, we started designing, manufacturing and updating the new MPS module in 2018. In this paper, the specifications and the results of performance test about the newly designed and manufactured the MPS signal aggregation module and the E/O converter module will be described.
Suzuki, Shintaro*; Takubo, Ko*; Kuga, Kentaro*; Higemoto, Wataru; Ito, Takashi; Tomita, Takahiro*; Shimura, Yasumichi*; Matsumoto, Yosuke*; Bareille, C.*; Wadachi, Hiroki*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 3(2), p.023140_1 - 023140_12, 2021/05
We report our experimental discovery of the transition temperature reaching 20 K in a Yb-based compound at ambient pressure. The Mn substitution at the Al site in an intermediate valence state of  -YbAlB
-YbAlB not only induces antiferromagnetic transition at a record high temperature of 20 K but also transforms the heavy-fermion liquid state in
not only induces antiferromagnetic transition at a record high temperature of 20 K but also transforms the heavy-fermion liquid state in  -YbAlB
-YbAlB into a highly resistive metallic state proximate to a Kondo insulator.
into a highly resistive metallic state proximate to a Kondo insulator.
Nagao, Fumiya; Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ito, Satomi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Dohi, Terumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Funaki, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Research 2020-007, 249 Pages, 2020/10
The accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. occurred due to the Great East Japan Earthquake, Sanriku offshore earthquake, of 9.0 magnitude and the accompanying tsunami. As a result, large amount of radioactive materials was released into the environment. Under these circumstances, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting "Long-term Assessment of Transport of Radioactive Contaminants in the Environment of Fukushima" concerning radioactive materials released in environment, especially migration behavior of radioactive cesium since November 2012. This report is a summary of the research results that have been obtained in environmental dynamics research conducted by JAEA in Fukushima Prefecture.
Fujihara, Masayoshi*; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Mole, R.*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Toyama, Takami*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Yu, D.*; Sota, Shigetoshi*; Kuwai, Tomohiko*; Koda, Akihiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.3429_1 - 3429_7, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:90.63(Multidisciplinary Sciences) He
He
 excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron-
excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron- He absorption reaction
He absorption reactionSonnenschein, V.*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kokuryu, Shoma*; Kubo, Wataru*; Suzuki, So*; Tomita, Hideki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Matsushita, Taku*; Wada, Nobuo*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(3), p.033318_1 - 033318_12, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Instruments & Instrumentation)Oba, Yojiro; Ito, Daisuke*; Saito, Yasushi*; Onodera, Yohei*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Oikawa, Kenichi
Materials Research Proceedings, Vol.15, p.160 - 164, 2020/02
Lead Bismuth eutectic (LBE) is a promising candidate of the coolant for accelerator driven system (ADS) and fast breeder reactor. Neutron transmission imaging is a powerful technique to investigate the LBE in flow channel. However, previous studies have focused on the analysis of the neutron transmission spectra due to Bragg diffraction (Bragg edge transmission) from the solid phase of the LBE. If the neutron transmission spectra due to the diffraction from a liquid phase can be observed, it is useful to study the behavior of the molten LBE in the flow channel. Therefore, the energy-resolved neutron transmission imaging measurements of the molten LBE was carried out. The observed neutron transmission spectra can be explained by those calculated from the scattering profiles of the molten LBE. This indicates that the structure of the molten LBE can be characterized and mapped using the neutron transmission imaging.
Nagao, Fumiya; Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ito, Satomi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Dohi, Terumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Funaki, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-002, 235 Pages, 2019/08
The accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (hereinafter referred to 1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. occurred due to the Great East Japan Earthquake, Sanriku offshore earthquake, of 9.0 magnitude and the accompanying tsunami. As a result, large amount of radioactive materials was released into the environment. Under these circumstances, JAEA has been conducting Long-term Environmental Dynamics Research concerning radioactive materials released in environment, especially migration behavior of radioactive cesium since November 2012. This report is a summary of the research results that have been obtained in environmental dynamics research conducted by JAEA in Fukushima Prefecture.
 He
He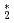 clusters via neutron-
clusters via neutron- He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulence
He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulenceMatsushita, Taku*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Guo, W.*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hirota, Katsuya*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Ito, Daisuke*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 196(1-2), p.275 - 282, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.76(Physics, Applied)Strasser, P.*; Abe, Mitsushi*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 198, p.00003_1 - 00003_8, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:99.06(Quantum Science & Technology)Tsai, P.-E.; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Abe, Shinichiro; Ito, Masatoshi*; Watabe, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2017) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2018/11
The energy spectra of primary knock-on atoms (PKAs) are essential for radiation damage assessment in design of accelerator facilities. However up to date the experimental data are still limited, due to the poor mass resolution and the high measurement threshold energies in the conventional setup of nuclear physics experiments using solid state detectors, which are typically above a few MeV/nucleon. In this study, a novel detection system consisting of two time detectors and one dE-E energy detector is proposed and being constructed to measure the PKA spectra. The system and detector design was based on Monte Carlo simulations by using the PHITS code. The PHITS simulations show that the system is able to distinguish the PKA isotopes above  0.2-0.3 MeV/nucleon for A=20
0.2-0.3 MeV/nucleon for A=20 30 amu; the PKA mass identification thresholds decrease to
30 amu; the PKA mass identification thresholds decrease to  0.1 MeV/nucleon for PKAs lighter than 20 amu. The detection system will be tested in the summer of 2017, and the test results will be presented at the conference.
0.1 MeV/nucleon for PKAs lighter than 20 amu. The detection system will be tested in the summer of 2017, and the test results will be presented at the conference.
Tachi, Yukio; Ito, Tsuyoshi*; Akagi, Yosuke*; Sato, Hisao*; Martin, A. J.*
Water Resources Research, 54(11), p.9287 - 9305, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.57(Environmental Sciences)Effects of fine-scale surface alterations on radionuclide migration in fractured crystalline rocks were investigated by a comprehensive approach coupling a series of laboratory tests, microscopic observations and modelling, using a single fractured granodiorite sample from the Grimsel Test Site, Switzerland. Laboratory tests including through-diffusion, batch sorption and flow-through tests using five tracers indicated that tracer retention was consistently in the sequence of HDO, Se, Cs, Ni, Eu, and as well as showing the existence of a diffusion-resistance layer near the fracture surface, cation excess and anion exclusion effects for diffusion. Microscale heterogeneities in structural properties around the fracture were clarified quantitatively by coupling X-ray CT and EPMA. A three layer model including weathered vermiculite, foliated mica and undisturbed matrix layers, and their properties such as porosity, sorption and diffusion parameters, could provide a reasonable interpretation for breakthrough curves and concentration distributions near fracture surface of all tracers, measured in flow-through tests.
Ito, Hiroto*; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Tanaka, Yoichi*; Nishihara, Satomichi*; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-012, 42 Pages, 2018/10
Chemical composition of fission products transported in nuclear facilities in severe accidents is controlled by slower chemical reaction rates, therefore, it could be different from that evaluated on the chemical equilibrium assumption. Hence, it is necessary to evaluate the chemical composition with reaction kinetics. On the other hand, databases applicable to the analysis of nuclear facilities have not been constructed because knowledge of reaction rates of complex chemical reactions in severe accidents is currently limited. Accordingly, we have developed the CHEMKEq code based on a partial mixed model with chemical equilibrium and reaction kinetics to decrease uncertainties of the chemical composition caused by the reaction rate. The CHEMKEq code, under mass conservation law, firstly evaluates chemical species obeying the chemical equilibrium model, and then, relatively slow reactions are solved by the reaction kinetics model. Moreover, the CHEMKEq code has a multiplicity of use in evaluations of chemical composition because general chemical equilibrium and reaction kinetics models are also available and databases required to calculation are external file formats. This report is the user's guide of the CHEMKEq code, showing models, solution methods, structure of the code and calculation examples. And information to run the CHEMKEq code is summarized in appendixes.
Shamoto, Shinichi; Ito, Takashi; Onishi, Hiroaki; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Matsuura, Masato*; Akatsu, Mitsuhiro*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Nakao, Akiko*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; et al.
Physical Review B, 97(5), p.054429_1 - 054429_9, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:65.6(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nuclear and magnetic structure and full magnon dispersions of yttrium iron garnet Y Fe
Fe O
O have been studied by neutron scattering. The lowest-energy dispersion below 14 meV exhibits a quadratic dispersion as expected from ferromagnetic magnons. The imaginary part of
have been studied by neutron scattering. The lowest-energy dispersion below 14 meV exhibits a quadratic dispersion as expected from ferromagnetic magnons. The imaginary part of  -integrated dynamical spin susceptibility
-integrated dynamical spin susceptibility  "(
"( ) exhibits a square-root energy-dependence in the low energies. The magnon density of state is estimated from the
) exhibits a square-root energy-dependence in the low energies. The magnon density of state is estimated from the  "(
"( ) obtained on an absolute scale. The value is consistent with a single chirality mode for the magnon branch expected theoretically.
) obtained on an absolute scale. The value is consistent with a single chirality mode for the magnon branch expected theoretically.
Ino, Kohei*; Hernsdorf, A. W.*; Konno, Yuta*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Yanagawa, Katsunori*; Kato, Shingo*; Sunamura, Michinari*; Hirota, Akinari*; Togo, Yoko*; Ito, Kazumasa*; et al.
ISME Journal, 12(1), p.31 - 47, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:91.33(Ecology)In this study, we found the dominance ofanaerobic methane-oxidizing archaea in groundwater enriched in sulfate and methane from a 300-m deep underground borehole in granitic rock.
Ueno, Yasuhiro*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 238(1), p.14_1 - 14_6, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:86.59(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Sakasai, Kaoru; Sato, Setsuo*; Seya, Tomohiro*; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Yamagishi, Hideshi*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(2), p.10_1 - 10_35, 2017/09
Neutron devices such as neutron detectors, optical devices including supermirror devices and  He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.