Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamaguchi, Masaaki; Suzuki, Yuji*; Kabasawa, Satsuki; Kato, Tomoko
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-001, 21 Pages, 2024/03
Model catchments have developed for use in testing various assessment models that can consider specific surface environmental conditions such as topography, riverine systems, and land use in the biosphere assessment of HLW geological disposal. The model catchments consist of the topography and riverine system of the catchment area created using existing tools, as well as land use and population distribution, river discharge, sediment flux data set by algorithms from topographical data. Datasets of three types of model watersheds (Types 1 to 3, watershed area: 730 to 770 km ) with different topographical characteristics have released as raster data that can be handled by geographic information systems (GIS). Since the model catchments were created virtually reflecting as much as possible the main characteristics of Japan's surface environment, they can be used as a test bed for conducting hydraulic/mass transport analysis to set the GBI and compartment model.
) with different topographical characteristics have released as raster data that can be handled by geographic information systems (GIS). Since the model catchments were created virtually reflecting as much as possible the main characteristics of Japan's surface environment, they can be used as a test bed for conducting hydraulic/mass transport analysis to set the GBI and compartment model.
Takahashi, Tomoyuki*; Fukaya, Yukiko*; Iimoto, Takeshi*; Uni, Yasuo*; Kato, Tomoko; Sun, S.*; Takeda, Seiji; Nakai, Kunihiro*; Nakabayashi, Ryo*; Uchida, Shigeo*; et al.
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 56(4), p.288 - 305, 2021/12
We report the results of activities related to the Task Group of Parameters Used in Biospheric Dose Assessment Models for Radioactive Waste Disposal at the Japan Health Physics Society.
Kato, Tomoko
KURNS-EKR-11, p.19 - 28, 2021/03
In order to extract the knowledge that will be helpful in setting the biospheric dose assessment parameters and their database for safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal in Japan, a methodology of setting the biospheric dose assessment parameters was surveyed in the safety assessment of the radioactive waste disposal in Sweden. In this study, the handling in the biospheric dose assessment in SR-PSU was specifically focused. SR-PSU was the project about the safety assessment for final repository of short-lived radioactive waste in Sweden, SFR.
Yamaguchi, Masaaki; Kato, Tomoko; Suzuki, Yuji*; Makino, Hitoshi
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 27(2), p.72 - 82, 2020/12
An efficient analytical tool to calculate temporal change of topography and repository depth due to uplift and erosion was developed for use in performance assessment of high level radioactive waste geological disposal. The tool was developed as ArcGIS model, incorporating simplified landform development simulation, to enable trial calculation of various conditions such as initial topography, uplift rate and its distributions, and repository location. This tool enables to support decision on which processes, features, and their changes should be taken into account for performance assessment, by calculating topography change and repository depth change under various conditions.
Kato, Tomoko; Fukaya, Yukiko*; Sugiyama, Takeshi*; Nakai, Kunihiro*; Oda, Chie; Oi, Takao
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-002, 162 Pages, 2019/03
The radioactive waste generated from Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power station (FDNPS) accident have features such as wide range of radioactivity level (from low to high) and huge amount etc. It would be necessary for the waste from the FDNPS accident to develop suitable disposal concept and to be disposed safely and reasonably. When considering such appropriate disposal concepts in site-generic phase, it is necessary to appropriately develop models and parameters depending on the disposal concepts, such as disposal depth and specification of engineered barrier. In addition, it is desirable to evaluate the safety of repository with common models and parameters independent on the disposal concepts. In the safety assessment of disposal, it is useful to show the difference in performance of repository with "dose" as an indicator of safety assessment. Biosphere model and parameter set and flux-to-dose conversion factors calculated using them are originally dependent on the disposal concepts. However, the biosphere models and the parameter set in safety assessment of near-surface disposal, sub-surface disposal and geological disposal are prepared in each case, and are different according to the age and purpose of the discussion. In this study, an example of biosphere model and parameter-set of groundwater sceinario commonly applicable to various disposal concepts were shown, to calculate flux-to-dose conversion factors, as common indicators independent to disposal concept. And, a set of flux-to-dose conversion factors was also calculated by using the commonly available biosphere model and parameter set. By applying the flux-to-dose conversion factors, it is possible to compare the performance of disposal concepts to the waste generated from FDNPS accident, focusing on the parts depending on the disposal concepts.
Wakasugi, Keiichiro; Yamaguchi, Masaaki; Koo, Shigeru*; Nagao, Fumiya; Kato, Tomoko; Suzuki, Yuji*; Ebashi, Takeshi; Umeki, Hiroyuki*; Niibori, Yuichi*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 16(1), p.15 - 33, 2017/03
This study provides a method of safety assessment for the geological disposal of HLW to evaluate the effects of uplift and erosion which are widespread phenomena identified on regional and global scales, and are more or less difficult to avoid in Japan. This method enables to deal with different uplift rate and erosion rate, and to evaluate repository depth, the time required for a repository to reach the weathered zone and surface of the ground, and the number of waste packages eroded as a function of time by using a landform evolution model. Based on trial analysis, the result shows that the maximum dose in the Base Case (uplift rate: 0.3 mm/y) is less than the targeted criterion suggested by the international organization even if the repository reaches the ground surface. Furthermore, the diversifying effect on timing the waste packages to reach to weathered zone due to heterogeneity on altitude of bottom of weathered zone reduces one order magnitude of result of the existed dose assessment. The new method is applicable to evaluate safety of geological disposal based on realistic phenomena of uplift and erosion and to quantify a safety margin and robustness of the disposal system.
Kurikami, Hiroshi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Kato, Tomoko; Kitamura, Akihiro; Kanno, Mitsuhiro*; Kurosawa, Naohiro*
JAEA-Research 2016-020, 50 Pages, 2017/01
In this report, we developed a compartment model of radionuclide migration in environment based on exposure pathways in a river basin scale and performed a preliminary calculation. The results showed good agreement with some measurement, although the comparison of bed sediment, transportation to outer sea and to agricultural products with the measurement was not enough. We continue to validate the model.
Nagao, Fumiya; Kato, Tomoko; Suzuki, Yuji*; Itazu, Toru*
JAEA-Research 2016-003, 80 Pages, 2016/05
In the performance assessment study in the geological disposal of the high-level radioactive waste in Japan, the assessment technique that can treat local characteristics is examined, and establishing the method for the biosphere modeling using specific local information is aimed. In this report, the basic matrices were compiled which contain transport and exposure processes in the surface environment from a generic point of view. And the method was shown to construct the steady-state biosphere model in the actual surface environments by the combination of the basic matrices. To confirm applicability of the method, the biosphere modeling for the hypothetical site was tried. In addition, the important issues to describe the surface environmental condition and human lifestyle were identified to extract future problems and viewpoints by referring to the earlier study of the biosphere assessment at the actual repository site in Sweden.
Kato, Tomoko
Hosha Kagaku No Jiten, p.204 - 205, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Kitamura, Akihiro; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Yamaguchi, Masaaki; Oda, Yoshihiro; Saito, Tatsuo; Kato, Tomoko; Niizato, Tadafumi; Iijima, Kazuki; Sato, Haruo; Yui, Mikazu; et al.
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 179(1), p.104 - 118, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:56.13(Nuclear Science & Technology)The prediction of the distribution and fate of radioactive materials eventually deposited at surface in the Fukushima area is one of the main objectives and expected to be achieved in an efficient manner. In order to make such prediction, a number of mathematical models of radioactive contaminants, with particular attention on cesium, on the land and in rivers, lakes, and estuaries in the Fukushima area are developed. Simulation results are examined with the field investigations simultaneously implemented. The basic studies of the adsorption/absorption mechanism of cesium and soils have been performed to shed light on estimating distribution coefficient between dissolved contaminant and particulate contaminant.
 Be
Be O
O for high-functional tritium breeders
for high-functional tritium breedersHoshino, Tsuyoshi; Oikawa, Fumiaki; Natori, Yuri*; Kato, Kenichi*; Sakka, Tomoko*; Nakamura, Mutsumi*; Tatenuma, Katsuyoshi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(9-10), p.2268 - 2271, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)Lithium titanate with additional Li (Li TiO
TiO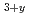 ) and lithium orthosilicate (Li
) and lithium orthosilicate (Li SiO
SiO ) is one of the most promising candidates for use in a tritium breeder because of its good chemical and mechanical stabilities. Currently, mixtures of tritium breeder pebble and neutron multiplier (Be or Be
) is one of the most promising candidates for use in a tritium breeder because of its good chemical and mechanical stabilities. Currently, mixtures of tritium breeder pebble and neutron multiplier (Be or Be Ti) pebble are being considered for use in increasing the tritium breeding ratio in a breeding blanket. However, lithium and beryllium are gradually reacted under practical operating conditions, and therefore a high-functional tritium breeder such as lithium beryllium oxide (Li
Ti) pebble are being considered for use in increasing the tritium breeding ratio in a breeding blanket. However, lithium and beryllium are gradually reacted under practical operating conditions, and therefore a high-functional tritium breeder such as lithium beryllium oxide (Li Be
Be O
O ) needs to be developed to compensate for this reactive characteristic under high temperature use. In this study, methods of synthesizing Li
) needs to be developed to compensate for this reactive characteristic under high temperature use. In this study, methods of synthesizing Li Be
Be O
O have been extensively investigated by means of solid-phase reaction. The solid-phase reaction of LiOH(H
have been extensively investigated by means of solid-phase reaction. The solid-phase reaction of LiOH(H O) and BeO is a suitable synthesis method for lithium beryllium oxide (Li
O) and BeO is a suitable synthesis method for lithium beryllium oxide (Li Be
Be O
O ). It is expected that single-phase Li
). It is expected that single-phase Li Be
Be O
O will be stable under the mixture conditions of a tritium breeder and neutron multiplier in the blanket region at high temperatures.
will be stable under the mixture conditions of a tritium breeder and neutron multiplier in the blanket region at high temperatures.
Itazu, Toru; Kato, Tomoko; Maekawa, Keisuke
Nihon Chikasui Gakkai 2011-Nen Shunki Koenkai Koen Yoshi, p.34 - 39, 2011/05
Biosphere assessment, which is a part of safety assessment for geological disposal of radioactive waste, addresses the migration of radionuclide from underground to near the ground surface. Advection-dispersion calculation for this purpose must take into the consideration the following factors: long-distance migration of solute, a requirement to calculate the inflow of solute into the rivers or sea bed supposed to be the final position, demand to control numerical dispersion in heterogeneous field. In this study, we adopt the Random-Walk Method having functions required to biosphere assessment and developed a program available to groundwater analysis by using MODFLOW. The program is verified by comparison with the analytical solution and studied about application method to biosphere assessment.
Ebina, Takanori*; Inagaki, Manabu*; Kato, Tomoko
JAEA-Data/Code 2010-029, 41 Pages, 2011/03
The safety assessment model at "Second Progress Report on Research and Development for TRU Waste Disposal in Japan" (TRU-2 report) was designed using the numerical code TIGER, that allows the physical and chemical properties within the system to vary with time. At the analysis using TIGER, the migration (i.e engineered barrier system, host rock and fault) have to be analysed independently at each region, consequently the huge number of complicated parameter setting have been required. On the other hand, by using numerical code GoldSim, all regions are analyzed synchronously and parameters can be defined at same model. In future, safety analyses of TRU waste package disposal will be carried out according as study of an optimization of nuclear fuel cycle. Therefor, safety assessment model for TRU waste disposal using GoldSim was designed, and calculation results were verified by comparing with the result of TRU-2 report.
Kato, Tomoko; Itazu, Toru; Suzuki, Yuji*
JAEA-Review 2010-075, 42 Pages, 2011/02
As the biosphere assessment of geological disposal covers an extremely long time period, it is difficult to predict the future human environment and lifestyles. IAEA-TECDOC addresses that a stylized approach is proposed for selecting critical groups and biospheres in future situations where human behaviour or biosphere conditions cannot be known with any certainty, although it is possible to construct biosphere models based on the characteristics and evolution of the surface environment at the actual site in shorter time period. BIOMASS methodology is especially effective for treating uncertainty of biosphere in these situations. To address the approaches of biosphere modelling, time period after closure of repository was divided; period 0 to 100 years, 100 years to 10,000 years and beyond them. Critical issues of biosphere modelling were specified through summarising the past progresses in domestic and foreign institutes. Based on the critical issues specified, 5-year research plan on biosphere assessment were identified.
Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kato, Kenichi; Kameo, Yutaka; Takahashi, Kuniaki
Bunseki Kagaku, 60(1), p.87 - 90, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Analytical)In order to dissolve radioactive ash (fly ash and bottom ash) and cement-solidified product of radioactive liquid wastes, a dissolution method using microwave heating devices was developed. In present method, most metal elements in samples were extracted with HCl and HNO to sample solution and a precipitate with silica as the main ingredient was decomposed with HF and HNO
to sample solution and a precipitate with silica as the main ingredient was decomposed with HF and HNO . As a result, fluoride residue was sufficiently reduced and more than 99% of radionuclides were recovered to sample solution. The ash and cement-solidified product samples were successfully dissolved in a shorter time as compared with a conventional method by external heating.
. As a result, fluoride residue was sufficiently reduced and more than 99% of radionuclides were recovered to sample solution. The ash and cement-solidified product samples were successfully dissolved in a shorter time as compared with a conventional method by external heating.
Kato, Tomoko
JAEA-Review 2009-052, 23 Pages, 2010/02
It is difficult to assume future evaluations of surface environments and human activities accurately and to describe them in a biosphere assessment scenario of geological disposal. Accurate assumption on their evolution is not necessary, because a biosphere assessment aims to illustrate the radiological impact to human as an index of performance for repository. Consequently, it is important to develop the methodology to describe the biosphere system with long-term evolution of geosphere according to a regulatory guideline or an assessment purpose, that is, the methodology to stylize evaluations of surface environments and human activities. In this report, we reviewed regulatory guidelines and scenarios of performance assessment applied to natural processes and human intrusion in foreign countries, and discussed the view-points when evolution of biosphere and future human activity are stylized in performance assessment of geological disposal.
Smith, G.*; Kato, Tomoko
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 42(1), p.1 - 8, 2010/02
Geological disposal is designed to provide safe containment of radioactive waste for very long times, with the containment provided by a combination of engineered and geological barriers. In the extreme long term, after many thousands of years or longer, residual amounts of long-lived radionulides such as Cl-36, but also radionuclides in the natural decay chains, may be released into the environment normally accessed and used by humans, termed here, the biosphere. It is necessary to ensure that any such releases meet radiation protection objectives through the development of a safety case, which will include assessment of radiation doses to humans. The design of such dose calculations over such long timeframes is not straightforward, because of the range of potentially relevant assumptions which could be made, concerning environmental change and changes in human behavior. The issue has therefore been subject to international cooperation for many years. This paper summarizes the evolution and results of that collaboration leading up to the present day, taking account of developments in international recommendations on radiation protection objectives and the more recent greater focus on preparation of site specific safety cases.
Itazu, Toru; Inagaki, Manabu; Kato, Tomoko; Suzuki, Yuji*; Oyamada, Kiyoshi*; Ebashi, Takeshi; Kawamura, Makoto; Ebina, Takanori*; Miyahara, Kaname
JAEA-Review 2009-015, 59 Pages, 2009/07
The project of high-level radioactive waste disposal is in the stage of site selection in Japan, and the site-specific performance assessment using the methodology of site-generic study has been developed after the publication of the second progress report (H12). In the same way, biosphere assessment using the behavior of radionuclides, which depends on the site-specific condition, has been started. In this paper, the following issues have been addressed. (1) Survey of the foreign literature relating to the surface and near- surface hydrology for biosphere assessments. (2) Survey of the domestic literature of flow and transport in subsurface systems valuable for biosphere assessments. (3) Trial of transport analysis in surface and near-surface environment of the model site. (4) The setting and boundary conditions of model used for the surface and near-surface hydrological analysis. About the fist issue, from literature of Sweden, we studied the calculation of the dose with account to radionuclides migration in the Quaternary. Concerning the second item, collecting and compiling the useful information for the surface and near-surface hydrological analysis from literature related to groundwater flow and pollution survey in Japan, we learned about the environmental tracer method and so on. Concerning the third point, transport analysis in surface and near-surface environment using site-specific data for sensitivity analysis after this has been carried out to check out the influence of some parameters on transport phenomena, and the relative high sensitivity of the difference of the source positions were shown. Concerning the fourth item, we examined the setting and the boundary conditions of model whose outputs include groundwater flow and transport rate into river, lake, sea. These outputs are used as inputs of biosphere assessment model.
Kato, Tomoko; Suzuki, Yuji*; Oi, Takao
Hoken Butsuri, 44(1), p.72 - 79, 2009/03
It is difficult to acquire all of biosphere parameters at the repository site because we have to deal with several hundreds of the parameters in one calculation case of the biosphere assessment. Before site-specific activities, it is important to develop the data acquisition methodology of biosphere parameters applicable to any proposed repository site. In this study, we developed the methodology for identification of the priority of the parameters for the effective data acquisition of biosphere parameters at the site. First of all, flow diagram was constructed to evaluate the availability of the existing generic biosphere dataset. We found that it was effective for the data acquisition at the site to focus on the element-specific parameters with the existing dataset. Secondly, we identified the priority of the data acquisition for element-specific parameters at the site, with considering the variation of radiation dose by combining the significant element-specific parameters. As a result, we identified the availability of the existing generic biosphere dataset and the priority on data acquisition of the element-specific parameters of key radionuclides in the safety assessment of geological disposal that should be acquired at the site. This priority list would be useful for effective data acquisition at the site.
Kato, Tomoko; Suzuki, Yuji*
JAEA-Research 2008-021, 148 Pages, 2008/03
A great effort is necessary when all of the biosphere parameters need to be collected at the actual surface environment of any proposed repository, because a great number of biosphere parameters, such as element-specific parameters, parameters specific to the surface environment or human behavior, are used in the biosphere assessment. Therefore, it is helpful to identify the biosphere parameters that should be collected at the actual environment in advance. For this purpose, the following approaches were developed in this study: (1) Extraction of the significant biosphere parameters through sensitivity analysis including estimation of the influences of variation of element-specific parameters on flux-to-dose conversion factors. (2) Checking the data sources of the significant biosphere parameters on the present dataset. (3) Making the priority list in future data acquisition. So far, steps (1) and (2) have been done, therefore this report summarizes the results obtained from these steps.