Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsuda, Shohei; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Kobayashi, Toru; Kaneta, Yui; Simonnet, M.; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Honda, Mitsunori; Shimojo, Kojiro; Doi, Reisuke; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 8(20), p.eabn1991_1 - eabn1991_11, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:58.16(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Sugiura, Yuki; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Doi, Reisuke; Francisco, P. C. M.; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Kobayashi, Toru; Matsumura, Daiju; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Tachi, Yukio
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 324(2), p.615 - 622, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.45(Chemistry, Analytical)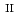 and Si under anoxic and reducing conditions; Structural characteristics of ferrous silicate co-precipitates
and Si under anoxic and reducing conditions; Structural characteristics of ferrous silicate co-precipitatesFrancisco, P. C. M.; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio; Doi, Reisuke; Shiwaku, Hideaki
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 270, p.1 - 20, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:76.71(Geochemistry & Geophysics) (cr) solubility determined by solubility experiments of Se co-existing with Fe
(cr) solubility determined by solubility experiments of Se co-existing with FeDoi, Reisuke; Uchikoshi, Keiji*; Beppu, Hikari*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(10), p.1554 - 1562, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)To determine log K for FeSe
for FeSe (cr) dissolution reaction, solubility experiments of Se co-existing with Fe were performed. Temperature was maintained at 348 K. Se concentration as a function of equilibration periods indicated that Se concentrations were similar at different equilibration periods. Only FeSe
(cr) dissolution reaction, solubility experiments of Se co-existing with Fe were performed. Temperature was maintained at 348 K. Se concentration as a function of equilibration periods indicated that Se concentrations were similar at different equilibration periods. Only FeSe (cr) was detected as the Se solid phase by XRD analysis of the equilibrated precipitates.
(cr) was detected as the Se solid phase by XRD analysis of the equilibrated precipitates. 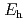 and pH of the equilibrated suspensions ranged from -188.6 to -4.9 mV vs. SHE and 6.00 to 8.76, respectively. Se
and pH of the equilibrated suspensions ranged from -188.6 to -4.9 mV vs. SHE and 6.00 to 8.76, respectively. Se
 and Fe
and Fe are thermodynamically stable in this region. Interpretations using SIT model showed that the relationship between
are thermodynamically stable in this region. Interpretations using SIT model showed that the relationship between 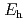 and the measured concentrations could be interpreted well when in the following equation n = 0.50
and the measured concentrations could be interpreted well when in the following equation n = 0.50 0.01 and log K
0.01 and log K  = -17.24
= -17.24 0.31 : 4Fe
0.31 : 4Fe Se(cr) = 4nFe
Se(cr) = 4nFe + Se
+ Se
 + (8n - 2)e
+ (8n - 2)e . The logK
. The logK value calculated from the available thermodynamic data agrees with that determined here.
value calculated from the available thermodynamic data agrees with that determined here.
 , SO
, SO ) precipitates
) precipitatesRai, D.*; Felmy, A. R.*; Moore, D. A.*; Kitamura, Akira; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Doi, Reisuke; Yoshida, Yasushi*
Radiochimica Acta, 102(8), p.711 - 721, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.44(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The solubility of Ba(SeO , SO
, SO ) precipitates was determined as a function of the BaSeO
) precipitates was determined as a function of the BaSeO mole fractions, ranging from 0.0015 to 0.3830, and time with an equilibration period extending to as long as 302 days. Equilibrium/steady state conditions in this system are reached in
mole fractions, ranging from 0.0015 to 0.3830, and time with an equilibration period extending to as long as 302 days. Equilibrium/steady state conditions in this system are reached in  65 days. Pitzer's ion interaction model was used to calculate solid and aqueous phase activity coefficients. Thermodynamic analyses showed that the data do not satisfy Gibbs-Duhem equation, thereby demonstrating that a single-solid solution phase does not control both the selenate and sulfate concentrations. Our extensive data with [Ba], [SeO
65 days. Pitzer's ion interaction model was used to calculate solid and aqueous phase activity coefficients. Thermodynamic analyses showed that the data do not satisfy Gibbs-Duhem equation, thereby demonstrating that a single-solid solution phase does not control both the selenate and sulfate concentrations. Our extensive data with [Ba], [SeO ], and [SO
], and [SO ] can be explained with the formation of an ideal BaSeO
] can be explained with the formation of an ideal BaSeO solid solution phase that controls the selenium concentrations and a slightly disordered/less-crystalline BaSO
solid solution phase that controls the selenium concentrations and a slightly disordered/less-crystalline BaSO (s) that controls the sulfate concentrations. In these experiments the BaSO
(s) that controls the sulfate concentrations. In these experiments the BaSO component of the solid solution phase never reaches thermodynamic equilibrium with the aqueous phase. Thermodynamic interpretations of the data show that both the ideal BaSeO
component of the solid solution phase never reaches thermodynamic equilibrium with the aqueous phase. Thermodynamic interpretations of the data show that both the ideal BaSeO solid solution phase and less-crystalline BaSO
solid solution phase and less-crystalline BaSO (s) phase are in equilibrium with each other in the entire range of BaSeO
(s) phase are in equilibrium with each other in the entire range of BaSeO mole fractions investigated in this study.
mole fractions investigated in this study.
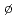 nsted-Guggenheim-Scatchard model
nsted-Guggenheim-Scatchard modelKitamura, Akira; Doi, Reisuke; Yoshida, Yasushi*
JAEA-Data/Code 2014-009, 69 Pages, 2014/06
The latest available thermodynamic data for palladium and tin were critically reviewed and the selected values were included into the JAEA-TDB for performance assessment calculations for geological disposal of radioactive high-level and TRU wastes. We made sure that the selected data are internally consistent with other data included in the compilation. This critical review specifically addressed thermodynamic data for (1) the palladium-hydroxide-chloride system, and (2) the solid oxides and hydroxido complexes of Sn(IV). We also selected thermodynamic data for other tin reactions from critical review of tin by the Nuclear Energy Agency of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA). Furthermore, we refined some thermodynamic data for protactinium to estimate more reliable solubility values. We prepared text files of the updated thermodynamic database (JAEA-TDB) for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC, EQ3/6 and Geochemist's Workbench. Use of the Br nsted-Guggenheim-Scatchard Model (SIT) for ionic strength corrections was applied to the PHREEQC database.
nsted-Guggenheim-Scatchard Model (SIT) for ionic strength corrections was applied to the PHREEQC database.
Doi, Reisuke; Iwata, Hajime; Kitamura, Akira
JAEA-Review 2014-014, 27 Pages, 2014/05
The solubility method is one of the most powerful tools to obtain reliable thermodynamic data for (1) solubility products of discrete solids and double salts, (2) complexation constants for various ligands, (3) development of data in a wide range of pH values, (4) evaluation of data for metals that form very insoluble solids (e.g. tetravalent actinides), (5) determining solubility-controlling solids in different types of wastes and (6) elevated temperatures for redox sensitive systems. This document is focused on describing various aspects of obtaining thermodynamic data using the solubility method. This manuscript deals with various aspects of conducting solubility studies, including selecting the study topic, modeling to define important variables, selecting the range of variables and experimental parameters, anticipating results, general equipment requirements, conducting experiments, and interpreting experimental data.
 (cr) in the aqueous Ba
(cr) in the aqueous Ba -SeO
-SeO
 -Na
-Na -H
-H -OH
-OH -H
-H O system; Extending to high selenate concentrations
O system; Extending to high selenate concentrationsRai, D.*; Felmy, A. R.*; Moore, D. A.*; Kitamura, Akira; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Doi, Reisuke; Yoshida, Yasushi*
Radiochimica Acta, 102(9), p.817 - 830, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.88(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The aqueous solubility of BaSeO (cr) was studied in Na
(cr) was studied in Na SeO
SeO solutions ranging in concentration from 0.0001 to 4.1 mol.kg
solutions ranging in concentration from 0.0001 to 4.1 mol.kg and maintained in a N
and maintained in a N atmosphere at room temperature (296
atmosphere at room temperature (296  2 K). The studies were conducted from both the undersaturation and oversaturation directions, with equilibration periods ranging from 3 to 596 days. The equilibrium in this system was reached rather rapidly (
2 K). The studies were conducted from both the undersaturation and oversaturation directions, with equilibration periods ranging from 3 to 596 days. The equilibrium in this system was reached rather rapidly ( 3 days). The SIT and Pitzer's ion-interaction models were used to interpret these data and the predictions based on both of these models agreed closely with the experimental data.
3 days). The SIT and Pitzer's ion-interaction models were used to interpret these data and the predictions based on both of these models agreed closely with the experimental data.
Doi, Reisuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(3), p.359 - 368, 2014/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.44(Nuclear Science & Technology)Cyclic voltammetry was performed to determine the molar entropy of the Se(VI/IV) couple. In order to obtain the ion interaction coefficient between HSeO
 and Na
and Na ,
, 
 (HSeO
(HSeO
 , Na
, Na ), the following reaction involving uncharged species as reductant was used: HSeO
), the following reaction involving uncharged species as reductant was used: HSeO
 + 3H
+ 3H + 2e
+ 2e = H
= H SeO
SeO + H
+ H O. Half wave potentials were measured in acidic sodium nitrate solutions as a function of the molality of Na
O. Half wave potentials were measured in acidic sodium nitrate solutions as a function of the molality of Na . A number of temperatures were used: 15, 25, 35 and 50
. A number of temperatures were used: 15, 25, 35 and 50 C. SIT was used to calculate the HSeO
C. SIT was used to calculate the HSeO
 /H
/H SeO
SeO standard potential,
standard potential, 
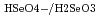 (
( , 0), and
, 0), and 
 (HSeO
(HSeO
 , Na
, Na ) at each temperature. The following molar entropy was derived from the temperature dependence of
) at each temperature. The following molar entropy was derived from the temperature dependence of 
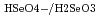 (
( , 0):
, 0): 
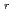 S
S
 /2
/2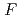 = -0.3
= -0.3 0.3 mV K
0.3 mV K . At 25
. At 25 C
C 
 (HSeO
(HSeO
 , Na
, Na ) was 0.29
) was 0.29 0.04 kg mole
0.04 kg mole .
.
Doi, Reisuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(1), p.56 - 63, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:64.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)To obtain the reliable standard potential of Se(VI/IV), a study by cyclic voltametry was performed in Se pure system where the elements other than Se have no effects on the system. High pH solutions were used to make all the tetravalent Se species SeO
 in the bulk solution. Instead of the measured pH of high-ionic-strength solutions, pH was correctly estimated. The half-wave potentials were determined varying molality of Na
in the bulk solution. Instead of the measured pH of high-ionic-strength solutions, pH was correctly estimated. The half-wave potentials were determined varying molality of Na . Experimental data have been interpreted by using SIT to give the following data, E
. Experimental data have been interpreted by using SIT to give the following data, E (SeO
(SeO
 /SeO
/SeO
 ) = 0.8227
) = 0.8227 0.0032 V vs. SHE,
0.0032 V vs. SHE, 
 = 0.59
= 0.59 0.12 kg/mol. This E
0.12 kg/mol. This E (SeO
(SeO
 /SeO
/SeO
 ) agreed with the corrected value for OECD/NEA's and could make a contribution to more reliable prediction of speciation especially in the oxidizing ground water than OECD/NEA's.
) agreed with the corrected value for OECD/NEA's and could make a contribution to more reliable prediction of speciation especially in the oxidizing ground water than OECD/NEA's.
Doi, Reisuke
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 19(2), p.65 - 66, 2012/12
This is errata to "Experimental study by cyclic voltametry of standard potential of Se(IV)/Se(VI) redox system", where the equation for the formal potential of the target reaction was wrong.
Kitamura, Akira; Fujiwara, Kenso; Doi, Reisuke; Yoshida, Yasushi*
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-006, 65 Pages, 2012/07
We additionally selected thermodynamic data for solid and gaseous phases of nickel, selenium, zirconium, technetium, thorium, uranium, neptunium, plutonium and americium to our thermodynamic database JAEA-TDB for geological disposal of radioactive waste of high-level and TRU wastes. We thermodynamically obtained equilibrium constant from addition and subtraction of Gibbs free energy of formation, which were selected in the thermochemical database project by the Nuclear Energy Agency in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Furthermore, we collected and updated thermodynamic data on iodine, changed master species of technetium(IV), and added thermodynamic data on selenium due to improving reliability of the thermodynamic database. We prepared text files of the updated thermodynamic database (JAEA-TDB) for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC, EQ3/6 and Geochemist's Workbench. These text files are contained in the attached CD-ROM and will be available on our Website.
Kitamura, Akira; Doi, Reisuke; Yoshida, Yasushi*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010), Vol.2, p.365 - 373, 2011/00
We evaluated and estimated solubility of the 25 elements in the simulated pore waters established in the second progress report (H12) for safety assessment of geological disposal of HLW in Japan using the updated thermodynamic database (JAEA-TDB) and compared with the solubility values using the previous thermodynamic database (JNC-TDB). Furthermore, we tried to establish a technique to determine the solubility limiting solid for all target elements. It was found that most of the evaluated and estimated solubility values were not changed drastically, but the solubility values and dominant aqueous species for some elements were changed using the JAEA-TDB, e.g., due to introducing the formation constant of polynuclear hydrolysis species of zirconium and replacing the formation constant of mixed carbonatohydoxo complexes of thorium. Detail of the comparison and discussion about the evaluated and estimated solubility values between the JAEA- and the JNC- TDBs will be presented.
Kitamura, Akira; Fujiwara, Kenso; Doi, Reisuke; Yoshida, Yasushi*; Mihara, Morihiro; Terashima, Motoki; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Data/Code 2009-024, 84 Pages, 2010/03
A thermodynamic database was established to develop a thermodynamic database for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level and TRU wastes. Twenty-four elements (actinides, fission products and their daughters) which are of importance for the performance assessment of geological disposal have been selected. The fundamental plan was in principle based on the guidelines established by the Nuclear Energy Agency in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA). Additional unique guidelines were established due to a requirement from the performance assessment to select tentative thermodynamic values obtained from chemical analogues and/or models for elements with insufficient thermodynamic values. Selected thermodynamic data were compiled for geochemical calculation programs.
Doi, Reisuke; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*; Yui, Mikazu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 47(3), p.278 - 285, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)Se solubility and its solubility-limiting solid phase were investigated in a simulated geological repository environment. Experiments in bentonite equilibrated waters and the simple condition experiment without bentonite were performed. With bentonite approximately 10 mol/dm
mol/dm Se concentration was obtained. The experiment without bentonite was conducted to confirm the solubility-limiting solid phase. This experiment was carried out at a higher temperature (80
Se concentration was obtained. The experiment without bentonite was conducted to confirm the solubility-limiting solid phase. This experiment was carried out at a higher temperature (80 C) to accelerate the solid transformation of Se. The Se concentration decreased with increasing time. Several Se solid phases were identified. Though Se(cr) was dominant at first, this solid phase gradually transformed with time and Fe-Se solids began to form. It is suggested that FeSe
C) to accelerate the solid transformation of Se. The Se concentration decreased with increasing time. Several Se solid phases were identified. Though Se(cr) was dominant at first, this solid phase gradually transformed with time and Fe-Se solids began to form. It is suggested that FeSe , which is the most thermodynamically stable phase, is likely to be the Se solubility-limiting solid phase under a geological repository environment in the long-term.
, which is the most thermodynamically stable phase, is likely to be the Se solubility-limiting solid phase under a geological repository environment in the long-term.
Doi, Reisuke; Kitamura, Akira; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Review 2009-051, 18 Pages, 2010/02
Within the scope of the JAEA thermodynamic database project for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level and TRU radioactive wastes, the selection of the thermodynamic data on the inorganic compounds and complexes of selenium have been carried out. Selection of thermodynamic data of selenium has been based on a thermodynamic database of selenium published by the Nuclear Energy Agency in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA). The remarks of a thermodynamic database by OECD/NEA found by the authors were noted in this report and then thermodynamic data have been reviewed after surveying latest literatures. Some thermodynamic values of iron selenides not selected by OECD/NEA due to low reliability, which are important for the performance assessment of geological disposal of radioactive wastes, were selected as a tentative value with specifying reliability and needs of the value to be determined.
Doi, Reisuke; Yui, Mikazu
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 16(1), p.35 - 42, 2009/12
The standard potential of Se(IV)/Se(VI) couple has been obtained by cyclic voltametry in the relatively pure system. The formal potentials of the selenium redox reaction have been determined in NaClO medium of various ionic strength (I (mol/kg) = 0.500, 1.00, 1.50, 2.00) at room temperature. These data have been interpreted by using the Specific Ion Interaction Theory to give the following standard potential. In addition, the reactive chemical species have been identified by the dependence of peak potential of oxidation wave on Se concentration. As a result, the following standard potential was determined: HSeO
medium of various ionic strength (I (mol/kg) = 0.500, 1.00, 1.50, 2.00) at room temperature. These data have been interpreted by using the Specific Ion Interaction Theory to give the following standard potential. In addition, the reactive chemical species have been identified by the dependence of peak potential of oxidation wave on Se concentration. As a result, the following standard potential was determined: HSeO
 + H
+ H O = SeO
O = SeO
 + 3H
+ 3H + 2e
+ 2e E
E = 0.821
= 0.821 0.002 V vs. SHE.
0.002 V vs. SHE.
Tachi, Yukio; Seida, Yoshimi; Doi, Reisuke; Xia, X.*; Yui, Mikazu
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1124, p.573 - 579, 2009/00
Doi, Reisuke; Xia, X.*; Shibata, Masahiro; Kitamura, Akira; Yoshikawa, Hideki
JAEA-Research 2007-007, 21 Pages, 2007/03
Assessment for radionuclides sorption onto a rock in deep underground is important for the safety assessment of HLW geological disposal. Distribution coefficient, K is an available parameter to assess the sorption in the current safety assessment. We applied a model that the sorption of Cs is dominated by the ion exchange reaction on illite to experimental results of Cs sorption onto Horonobe sedimentary rocks. The equilibrium concentration of Cs was calculated under the conditions same as those adopted in the experiment to estimate the K
is an available parameter to assess the sorption in the current safety assessment. We applied a model that the sorption of Cs is dominated by the ion exchange reaction on illite to experimental results of Cs sorption onto Horonobe sedimentary rocks. The equilibrium concentration of Cs was calculated under the conditions same as those adopted in the experiment to estimate the K value. Comparing the calculated results with the experimental data, the model could explain well the dependence of K
value. Comparing the calculated results with the experimental data, the model could explain well the dependence of K values on Cs equilibrium concentration. By using the model, it is possible to assess Cs sorption onto a sedimentary rock. However, some differences were also obtained between the experimental data and the calculated one.
values on Cs equilibrium concentration. By using the model, it is possible to assess Cs sorption onto a sedimentary rock. However, some differences were also obtained between the experimental data and the calculated one.
Doi, Reisuke; Shibata, Masahiro
JAEA-Research 2006-038, 30 Pages, 2006/07
To calculate the solubility of radioactive elements which is the important parameter for assessing performances in geological environments, the thermodynamic database must be reliable and based on the latest information. In this research, we compared the solubilities of the representative radioactive elements in the porewater compositions of the compacted bentonite which were set up in the second progress report (H12). The solubility was calculated with the thermodynamic databases of JAEA, OECD/NEA, Nagra/PSI. And we investigated the causes of the differences among three thermodynamic databases.