Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakanishi, Toshimichi*; Okuno, Mitsuru*; Yamasaki, Keiji*; Hong, W.*; Fujita, Natsuko; Nakamura, Toshio*; Horikawa, Yoshiyuki*; Sato, Eiichi*; Kimura, Haruo*; Tsutsumi, Hiroyuki*
Nagoya Daigaku Nendai Sokutei Kenkyu, 5, p.38 - 43, 2021/03
no abstracts in English
Okuno, Yasuki*; Ishikawa, Norito; Akiyoshi, Masafumi*; Ando, Hirokazu*; Harumoto, Masaki*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 59(7), p.074001_1 - 074001_7, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:18.96(Physics, Applied)Performance degradation prediction for space solar cells under irradiation with low-energy electrons is greatly affected by displacement threshold energy (Ed) when a displacement damage dose (DDD) model is used. According to recent studies, the Ed of P atoms is much lower than the conventional Ed value in InP-type solar cells irradiated with low-energy electrons. This indicates that the value of Ed typically used in DDD model leads to significant error in performance degradation prediction. In this study, degradation of AlInGaP solar cells is observed after irradiation with 60 keV electrons. The results suggest that the Ed of P atoms in AlInGaP solar cells is much smaller than the conventionally used Ed value. By using the DDD model with the Ed value obtained in this study, we demonstrated that the performance degradation predicted by the DDD model agrees well with the experimental results.
Okuno, Yasuki; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*; Okubo, Nariaki; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(4), p.457 - 462, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:61.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)Indium gallium phosphide (InGaP) solar cell with a superior high-radiation resistance is expected to be a powerful candidate for a dosimeter under a high-radiation dose rate environment. In this study, in order to predict the lifetime as the dosimeter using the InGaP solar cell, we clarify the effect of minority-carrier diffusion length ( ) on a radiation-induced current as a dose signal in the InGaP solar cell by irradiation tests and empirical calculations. In the irradiation tests, the short circuit current density (
) on a radiation-induced current as a dose signal in the InGaP solar cell by irradiation tests and empirical calculations. In the irradiation tests, the short circuit current density (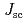 ) as a function of the gamma-ray dose rate is measured to estimate the
) as a function of the gamma-ray dose rate is measured to estimate the  for the InGaP solar cell by irradiation tests. The operational lifetime as a detector using the InGaP solar cell under various dose rates is estimated by using the empirical calculations based on the relation between the L and absorbed dose. The results suggest that the dosimeter using InGaP solar cell is able to be used during more than 10 h in the primary containment vessel of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant and it has a high potential of being a radiation-resistant dosimeter that would contribute to the decommissioning.
for the InGaP solar cell by irradiation tests. The operational lifetime as a detector using the InGaP solar cell under various dose rates is estimated by using the empirical calculations based on the relation between the L and absorbed dose. The results suggest that the dosimeter using InGaP solar cell is able to be used during more than 10 h in the primary containment vessel of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant and it has a high potential of being a radiation-resistant dosimeter that would contribute to the decommissioning.
Okuno, Yasuki; Okubo, Nariaki; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(9-10), p.851 - 858, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:73.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)Decommissioning the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) after the accident caused by a tsunami in 2011 requires characterization of the fuel debris by dose distribution measurement. This paper describes the experimental and theoretical behavior of a radiation detector applied with InGaP solar cells is investigated and allow the localization and characterization of the fuel debris. In the irradiation test, it was observed that the radiation-induced current output of the InGaP solar cells increases linearly with increasing dose rates of  Co
Co  -ray. For measurements at low dose rates, it becomes clear that the minimum detectable dose rate and resolution can be determined by analyzing the noise characterization. The maximum detection limit of radiation dosimetry for the InGaP solar cell was found to be higher than the highest
-ray. For measurements at low dose rates, it becomes clear that the minimum detectable dose rate and resolution can be determined by analyzing the noise characterization. The maximum detection limit of radiation dosimetry for the InGaP solar cell was found to be higher than the highest  -ray dose rate observable at the reactor core for 1F plants. Additionally, as an analysis of the radiation-induced current, it is attempted to express a relational expression between the absorbed dose rate and the creation of radiation-induced current pairs in the solar cells. The experimental and simulation results suggest that solar cells can be powerful tools for radiation dosimetry in high dose rate environments near the debris of the 1F plant.
-ray dose rate observable at the reactor core for 1F plants. Additionally, as an analysis of the radiation-induced current, it is attempted to express a relational expression between the absorbed dose rate and the creation of radiation-induced current pairs in the solar cells. The experimental and simulation results suggest that solar cells can be powerful tools for radiation dosimetry in high dose rate environments near the debris of the 1F plant.
Okuno, Mitsuru*; Nagaoka, Shinji*; Kokubu, Yoko; Nakamura, Toshio*; Kobayashi, Tetsuo*
Fukuoka Daigaku Rigaku Shuho, 48(1), p.1 - 5, 2018/03
Kuju volcanic group, located in central Kyushu, Japan, consists of over twenty volcanoes (lava domes as well as small stratovolcanoes). The Kurodake is largest lava dome with a volume of 1.6 km , and generated Kurodake pyroclastic-flow (Kj-Kd) and ash-fall (Kj-KdA) deposits. To refine age of the Kurodake eruption, we conducted radiocarbon dating of a charcoal fragment in the Kj-Kd with an AMS system at Tono Geoscience Center, JAEA. The obtained
, and generated Kurodake pyroclastic-flow (Kj-Kd) and ash-fall (Kj-KdA) deposits. To refine age of the Kurodake eruption, we conducted radiocarbon dating of a charcoal fragment in the Kj-Kd with an AMS system at Tono Geoscience Center, JAEA. The obtained  C date, 1505
C date, 1505 40 BP, can correspond to 1310-1423 cal BP (probability= 74.6%), 1430-1442 cal BP (2.4%) and 1456-1521 cal BP (23.0%) in 2
40 BP, can correspond to 1310-1423 cal BP (probability= 74.6%), 1430-1442 cal BP (2.4%) and 1456-1521 cal BP (23.0%) in 2 confidence level. The medium probability date, 1391 cal BP, is consistent with the stratigraphy and gives the reliable age for the Kj-Kd.
confidence level. The medium probability date, 1391 cal BP, is consistent with the stratigraphy and gives the reliable age for the Kj-Kd.
Okuno, Mitsuru*; Nagaoka, Shinji*; Kokubu, Yoko; Nakamura, Toshio*; Kobayashi, Tetsuo*
Radiocarbon, 59(2), p.483 - 488, 2017/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.88(Geochemistry & Geophysics)We present here results of AMS  C dating to refine the history of the middle and western parts of the Kuju Volcanic Group, located in middle Kyushu, Japan, which consists of more than 20 lava domes and cones.
C dating to refine the history of the middle and western parts of the Kuju Volcanic Group, located in middle Kyushu, Japan, which consists of more than 20 lava domes and cones.  C dating has conducted by AMS (JAEA-AMS-TONO) under the Common-Use Facility Program of JAEA. The Handa PF deposits, which are products of the largest eruption of the group, were dated to
C dating has conducted by AMS (JAEA-AMS-TONO) under the Common-Use Facility Program of JAEA. The Handa PF deposits, which are products of the largest eruption of the group, were dated to  53.5 ka BP. The Shirani and Muro PF deposits, which are block-and-ash flows, were dated to 44 to
53.5 ka BP. The Shirani and Muro PF deposits, which are block-and-ash flows, were dated to 44 to  50 cal ka BP and 35
50 cal ka BP and 35 39 cal ka BP, respectively. These ages can be correlated with the TL ages for the lava domes. Therefore, both TL and
39 cal ka BP, respectively. These ages can be correlated with the TL ages for the lava domes. Therefore, both TL and  C methods can be useful tools in establishing the eruptive sequence of lava domes and pyroclastic flows. This study also demonstrates that these eruptive activities occurred after the Handa pfl, the biggest eruption during the last 150 kyrs without a significant time interval.
C methods can be useful tools in establishing the eruptive sequence of lava domes and pyroclastic flows. This study also demonstrates that these eruptive activities occurred after the Handa pfl, the biggest eruption during the last 150 kyrs without a significant time interval.
Okuno, Mitsuru*; Nagaoka, Shinji*; Kokubu, Yoko
Gekkan Chikyu, 37(4), p.119 - 121, 2015/04
Onidake scoria fall deposit at Goto-Fukue Island, Japan is a product of the latest eruption of the Onidake volcano group. Radiocarbon date and C/N ratio of humic soil below the deposit are 19,840 120 BP and 9.14, respectively. It shows that the soil proceeded with decomposition in part and the date might be younger than the true one. However the date is older than the result (18,090
120 BP and 9.14, respectively. It shows that the soil proceeded with decomposition in part and the date might be younger than the true one. However the date is older than the result (18,090 100 BP) in the soil of the same layer reported by Nagaoka and Furuyama (2004) and is consistent with stratigraphical correlation with widespread tephra such as AT and K-Ah. The calibrated date is approximately 24 cal kBP.
100 BP) in the soil of the same layer reported by Nagaoka and Furuyama (2004) and is consistent with stratigraphical correlation with widespread tephra such as AT and K-Ah. The calibrated date is approximately 24 cal kBP.
Mirabueno, M. H. T.*; Torii, Masayuki*; Laguerta, E. P.*; Delos Reyes, P. J.*; Fujiki, Toshiyuki*; Bariso, E. B.*; Okuno, Mitsuru*; Nakamura, Toshio*; Danhara, Toru*; Kokubu, Yoko; et al.
Chigaku Zasshi, 123(5), p.751 - 760, 2014/10
Core drilling at site IRBH-2 within Irosin caldera, southern Luzon, reached 50 m. Systematic logging and documentation were done to describe the sediments. AMS  C dates were obtained for plant fragments from the peaty layers. Lahars and fluvial deposits were the predominant deposits in the core sequence. The upper 12 m was comprised mostly by andesitic fluvial and minor lahars. Eight fallouts were intercalated with reworked sediments from depth interval of 20 to 50 m. The refractive index measurement of analyzed samples indicated that post-caldera eruptions generated andesite, dacite and minor rhyolite. The similarity in petrographic characteristics between the rhyolite fallout and the Irosin ignimbrite indicates that small-scale eruptions involving magma from the caldera event occurred during post-caldera stage.Young radiocarbon dates obtained from the peaty layers shows that volcaniclastic deposits in the upper levels were likely derived from the eruptions of Bulusan volcano.
C dates were obtained for plant fragments from the peaty layers. Lahars and fluvial deposits were the predominant deposits in the core sequence. The upper 12 m was comprised mostly by andesitic fluvial and minor lahars. Eight fallouts were intercalated with reworked sediments from depth interval of 20 to 50 m. The refractive index measurement of analyzed samples indicated that post-caldera eruptions generated andesite, dacite and minor rhyolite. The similarity in petrographic characteristics between the rhyolite fallout and the Irosin ignimbrite indicates that small-scale eruptions involving magma from the caldera event occurred during post-caldera stage.Young radiocarbon dates obtained from the peaty layers shows that volcaniclastic deposits in the upper levels were likely derived from the eruptions of Bulusan volcano.
Okuno, Mitsuru*; Nakamura, Toshio*; Geshi, Nobuo*; Kimura, Katsuhiko*; Kokubu, Yoko; Kobayashi, Tetsuo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 294, p.602 - 605, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.87(Instruments & Instrumentation)We found numerous wood trunks from pumiceous deposits along Nagata, Isso and Miyanoura rivers on the northern side of Yakushima Island, 60 km south of Kyushu Island, and conducted radiocarbon dating using accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS). The obtained  C dates were around 6500 BP, and geological characteristics of the pumiceous deposits indicate that these specimens were buried during the Kikai-Akahoya (K-Ah) eruption from the Kikai caldera. However, they are not charred, suggesting that the origin of these deposits is not of pyroclastic flow but that of tsunami. Fourteen taxa were identified through anatomical characteristics. This is the first discovery on species of the forest of the Yakushima Island before the devastating eruption.
C dates were around 6500 BP, and geological characteristics of the pumiceous deposits indicate that these specimens were buried during the Kikai-Akahoya (K-Ah) eruption from the Kikai caldera. However, they are not charred, suggesting that the origin of these deposits is not of pyroclastic flow but that of tsunami. Fourteen taxa were identified through anatomical characteristics. This is the first discovery on species of the forest of the Yakushima Island before the devastating eruption.
Sugimoto, Makoto; *; Isono, Takaaki; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Nakajima, Hideo; Kato, Takashi; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Matsui, Kunihiro; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Ando, Toshinari; et al.
Proc. of 15th Int. Conf. on Magnet Technology (MT-15), p.409 - 412, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Sugimoto, Makoto; *; Isono, Takaaki; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Nakajima, Hideo; Kato, Takashi; Nishi, Masataka; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Ando, Toshinari; Tsuji, Hiroshi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 32(4), p.2328 - 2331, 1996/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:50.82(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
 Al insert
Al insertKoizumi, Norikiyo; *; Ando, Toshinari; Sugimoto, Makoto; *; *; *; Tsuji, Hiroshi; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Tsukamoto, Hideo*; et al.
Proc. of 16th Int. Cryogenic Engineering Conf. /Int. Cryogenic Materials Conf., 0, p.791 - 794, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Ara, Hiroshige*; Fukumitsu, Kenji*; Iizuka, Yunosuke*; Ishii, Takashi*; Izumiya, Yasushi*; Imazu, Masanori*; Utsugida, Yoshizo*; Hasegawa, Makoto*; Maeda, Masaya*; Yabe, Yukio*; et al.
PNC TJ199 84-04VOL1, 20 Pages, 1984/03
None
Okuno, Mitsuru*; Nagaoka, Shinji*; Kokubu, Yoko; Nakamura, Toshio*; Kobayashi, Tetsuo*
no journal, ,
Kuju volcano, located between Aso and Yufu-Tsurumi volcanoes in middle Kyushu, Japan, consists of more than 20 eruptive centers. We present here results of AMS radiocarbon dating to refine the history of the middle and western parts of Kuju volcano taking in the ages of Thermoluminescence (TL) dating. Radiocarbon ages for pyroclastic flows of Handa, Shirani and Muro on the southern sector of the volcano were ca. 30 - 50 kBP. These dates can be correlated with the TL ages for the lava domes. These results shows the lava domes formed relatively constant and the pyroclastic flows ran down toward the base of the volcano after the pyroclastic flow of Handa. Eruptions released at different periods are difficult to distinguish each other because their petrographical features are similar. Therefore, both TL and radiocarbon dating methods can be useful tools in establishing the eruptive sequence of lava domes and pyroclastic flows.
Okuno, Mitsuru*; Wada, Keiji*; Torii, Masayuki*; Danhara, Toru*; Nakamura, Toshio*; Kokubu, Yoko; Gualtieri, L.*; Brenn, S.*
no journal, ,
Adak Island, a member of the Andreanof Islands in the Aleutian Islands, Alaska is covered with Holocene sequences of soil-tephra complexes. Tephra layers are useful for establishing a chronographic framework on the island. Black (1976) described the three conspicuous tephra deposits (Main, Intermediate and Sandwich in ascending order). In order to re-evaluate the chronological framework, we conducted AMS radiocarbon dating and petrographic analysis on cored peat deposits collected from near Haven Lake. Charcoal fragments collected from around Three Arm Bay, southwestern area, are also dated. This poster presents petrography and radiocarbon dates. Based on our results, eruption ages of the Main, Intermediate, Sandwich, YBO and Forty Yeartephra were dated to approximately 9.5, 7.2, 4.7, 3.6 and 0.4 cal ka BP, respectively.
Okuno, Mitsuru*; Nagaoka, Shinji*; Kokubu, Yoko; Nakamura, Toshio*; Kobayashi, Tetsuo*
no journal, ,
Kuju Volcanic Group, located in middle Kyushu, Japan, consists of lava domes and small stratovolcanoes. We present here results of AMS  C dating of pyroclastic flow deposits (Pfl) on southern slope of the Kuju Volcanic Group. The
C dating of pyroclastic flow deposits (Pfl) on southern slope of the Kuju Volcanic Group. The  C dating has conducted by AMS (JAEA-AMS-TONO) under the Common-Use Facility Program of JAEA. The Handa Pfl was the biggest eruption during the last 200 kyrs and the AMS
C dating has conducted by AMS (JAEA-AMS-TONO) under the Common-Use Facility Program of JAEA. The Handa Pfl was the biggest eruption during the last 200 kyrs and the AMS  C age was about 54 kBP. Shirani Pfl and Muro Pfl are block-and ash flow type and the
C age was about 54 kBP. Shirani Pfl and Muro Pfl are block-and ash flow type and the  C ages were 48 kBP and 41 kBP, 32 - 34 kBP, respectively. These ages can be correlated with Thermoluminescence ages for lava domes of Kutsukake-yama and Hossho-zan. This study demonstrates that the lava dome and block-and ash flow deposits formed at the summit area after the eruption of Handa Pfl.
C ages were 48 kBP and 41 kBP, 32 - 34 kBP, respectively. These ages can be correlated with Thermoluminescence ages for lava domes of Kutsukake-yama and Hossho-zan. This study demonstrates that the lava dome and block-and ash flow deposits formed at the summit area after the eruption of Handa Pfl.
Okuno, Yasuki; Kitamura, Akane; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Okubo, Nariaki; Akiyoshi, Masafumi*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Shibata, Yuichi*; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*
no journal, ,
In the vicinity of the reactor core of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, it is a very high radiation environment due to the accident. In order to investigate the conditions at the inside of the reactor pressure vessele and the building, the current radiation measuring device has limitations in performance and function. Therefore, a simple and highly radiation-tolerant monitor, which can be used under high radiation dose environment, is required. Solar cells are known to be able to measure doses easily. However, the problem is that signals of dose are degraded by radiation damage. In this study, a measurement method of electric current induced by radiaiton and a signal compensation technique applied by a displacement damage prediction model will be reported by using an InGaP solar cell with a high radiation resistance.
Okuno, Yasuki; Kitamura, Akane; Ishikawa, Norito; Akiyoshi, Masafumi*; Ando, Hirokazu*; Harumoto, Masaki*; Shibata, Yuichi*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*
no journal, ,
The displacement damage dose (DDD) for space solar cell is greatly affected by the displacement threshold energy (Ed) during degradation by irradiation with low-energy electrons. In the proposed study, the unpredictable degradation of AlInGaP solar cells in the present DDD model is observed. The findings suggest that the predicted degradation during exposure to low-energy electrons may differ from the actual value. However, it is clarified that if the Ed value is rederived, the nonionizing energy loss can indicate the induced-defect rates in the AlInGaP under irradiation with electrons with a wide range of energy.
Okuno, Yasuki; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*
no journal, ,
In the theory of irradiation damage, a primary knock-on-atoms is considered to be generated, if the transferred energy (ET) given to the atom from the radiation by the interaction is larger than displacement threshold energy (Ed). A value of Ed has been conventionally determined by elements, without considering material dependency. In previous research, it was suggested that the Ed of each P in InGaP solar cell was 4 eV instead of 9 eV that has been used in the method of radiation degradation prediction of space solar cell. Additionally, the Ed of P in InP has been calculated to be 7.7 eV in the report by A. Sibille et al.. In the theory of radiation damage, the factor that determines Ed is considered to be a binding energy (EB) and a jumping energy (EJ). The EB value of P in InP and InGaP is calculated as cohesive energy by the first principles calculation based on density functional theory. In the results, it was suggested that EB has no correlation with the Ed value, and has little effect on the one.
Okuno, Yasuki; Okamoto, Tamotsu*; Goto, Yasuhito*; Akiyoshi, Masafumi*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*
no journal, ,
A solar cell type detector has features such as a thin film structure and no power supply drive by an internal electric field, and it is considered to be useful in a 1 F decommissioning environment. In this presentation, radiation behavior of InGaP and CdTe solar cells with high radiation resistance are reported.