Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wang, Y. L.; Sato, Isamu*; Toyama, Shinichi; Himeno, Yoshiaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 30(12), p.1261 - 1274, 1993/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:44.87(Nuclear Science & Technology)None
Toyama, Shinichi; Wang, Y. L.; Emoto, Takashi; Nomura, Masahiro; Takahashi, Nobutomo; Oshita, Hironori; Hirano, Koichiro; Himeno, Yoshiaki
Proceedings of 1993 Particle Accelerator Conference (PAC 1993), p.546 - 548, 1993/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.04(Instruments & Instrumentation)None
; Saeki, Akira; ; Himeno, Yoshiaki
Mathematical Methods and Supercomputing in Nulear Applications, 0 Pages, 1993/00
None
Toyama, Shinichi; Emoto, Takashi; Himeno, Yoshiaki; Hirano, Koichiro; Konashi, Kenji; Oshita, Hironori; Sasao, Nobuyuki; Takahashi, Nobutomo; Wang, Y. L.; 12 of others*
Proceedings of 3rd European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC '92), p.533 - 535, 1992/04
None
Miyahara, Shinya; ; Himeno, Yoshiaki
Nuclear Technology, 97(2), p.212 - 226, 1992/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:61.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)None
Miyahara, Shinya; ; Watanabe, Tomoo; Haga, Kazuo; Himeno, Yoshiaki
Nuclear Technology, 97(2), p.177 - 185, 1992/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:57.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)None
Himeno, Yoshiaki; Morikawa, Satoshi; Kawada, Koji; Yorita, E.*; Fujiwara, T.*; Kaneshige, T.*; Irie, S.*
PNC TN9410 91-092, 11 Pages, 1991/01
To develop a ceramic liner, a selection test of materials, an improvement test of selected material, and a feasibility test of the liner have been conducted.in the selection test, fifty commercially available high temperature cement and ceramics were subjected to thermal shock test (tst), sodium exposure test(set), and sodium flame exposure test (sfet). From test results, alumina/silicon-carbide (Al O
O -sic)mixture base castable refractory was selected in consideration of material cost, and material availability for a simpler liner construction in the buildings. The selected material was subjected to the improvement test. from the test, proper weight fractions of additives such as alumina cement and silica were determined. Drying conditions were also determined. Finally, a sodium burning pan made of concrete whose inner surfaces were covered with the improved Al
-sic)mixture base castable refractory was selected in consideration of material cost, and material availability for a simpler liner construction in the buildings. The selected material was subjected to the improvement test. from the test, proper weight fractions of additives such as alumina cement and silica were determined. Drying conditions were also determined. Finally, a sodium burning pan made of concrete whose inner surfaces were covered with the improved Al O
O -sic base castable refractory was fabricated and was used for a sodium burning test.
-sic base castable refractory was fabricated and was used for a sodium burning test.
Haga, Kazuo; ; Watanabe, Tomoo; ; Himeno, Yoshiaki
PNC TN9410 91-091, 13 Pages, 1991/01
A series of tests has been conducted to obtain gas-liquid equilibrium partition coefficient Kd of volatile fission products such as cesium,iodine,and tellurium in sodium. In the test a sodium pool mixed with an FP simulant was heated by an electric furnace and the solvent of trapped vapors by filters was quantitatively analyzed. The results are,(1)Cs shows the highest Kd (20-100), (2)Kd of iodine scatters as wide as 0.02-0.5at 450 and 0.3-0.8 at 650
and 0.3-0.8 at 650 ,(3)the Kd values of Cs and I agree well with the theoretical ones reported by Castleman et al., and (4)if a sodium-telluride which is hard to vaporize than pure Te is assumed, measured Kd of Te agrees with that theoretical.
,(3)the Kd values of Cs and I agree well with the theoretical ones reported by Castleman et al., and (4)if a sodium-telluride which is hard to vaporize than pure Te is assumed, measured Kd of Te agrees with that theoretical.
Ohno, Shuji; Kawata, Koji; Morikawa, Satoshi; Himeno, Yoshiaki
PNC TN9410 91-029, 11 Pages, 1991/01
Code development and experimental researches have been carried out for more realistic evaluation of the sodium fire accidents in the FBRs. A three-dimensional sodium fire analysis code,SOLFAS, is under development, SOLFAS consists of many calculational models for the detailedsodium fire analysis. Among the models,those of turbulent heat-mass transfer in an atmospheric gas,sodium pool combustion, and thermal conduction in heat structures havebeen developed to date. The gas solver including the turbulence model was verified with the sample calculations. Combustion rates of a low temperature sodium pool in a low oxygen concentration atmosphere and those of a sodium columnar fire in an air atmosphere were obtained from the experiments conducted in the SAPFIRE facility at PNC. Derived empirical formulae of the sodium combustion rate will contribute to the code development in the near future.
Miyahara, Shinya; Haga, Kazuo; Himeno, Yoshiaki
PNC TN9410 91-027, 16 Pages, 1991/01
A series of tests was conducted to studythe mechanical release of non-volatile fission products during sodium-concrete reaction,in which hydrodynamic break-up by the hydrogen bubble bursting is predominant at the sodium pool surface. In thetests,non-radioactive materials,namely strontium oxide,europium oxide,and ruthenium particles whose sizes ranged from some microns to several tens of microns,were used as simulated non-volatile fission products. The following results were obtained from the present study: (1) The sodium aerosol release rate during the sodium-concrete reaction was larger than that of natural evaporation. The difference,however,became smaller with the increase in the sodium temperature; nearly 10 times at 400 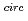 C and 3 times at 700
C and 3 times at 700 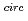 C. (2) Retention factors of these non-volatile materials in sodium pool increased inthe range of 0.5 to the fourth power of10 with the increase in the sodium temperature from 400
C. (2) Retention factors of these non-volatile materials in sodium pool increased inthe range of 0.5 to the fourth power of10 with the increase in the sodium temperature from 400 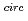 C to 700
C to 700 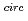 C
C
*; *; Himeno, Yoshiaki; Haga, Kazuo*; Miyake, Osamu; *; *
PNC TN9410 90-119, 58 Pages, 1990/03
With a view to giving reasonable requirements for design of containment features in a large LMFBR, this study discusses the following issues: selection of representative events considered in the safety design/evaluation, consideration of the effect of sodium on FP retention in the "Hypothetical Accident" (site evaluation accident), and evaluation of safety margin against beyond-design-basis events. This report contains some technical documents which are provided to the study group meeting.
Seino, Hiroshi; Miyake, Osamu; Morikawa, Satoshi; Himeno, Yoshiaki
PNC TN9410 91-025, 12 Pages, 1990/01
Evaluation of the aerosol behavior is esential in the safety analyses of the LMFBRs. This is because, in the case of a sodium leak accident, radioactive materialscould be released to the containment atmosphere, and they would behave together with the sodium aerosols during the accidents. From 1988 to 1989, PNC participatedin the Second International Sodium Aerosol Code Benchmark Study performed underthe auspices of the Commission of EC inan attempt to validate the aerosol behavior module of the CONTAIN code. The other organizations participating in the study are CEA-France, KfK-W. Germany and UKAEA-U.K. This paper describes an outline ofthe comparison between the test resultsand the calculational results made by PNC, whereas the international comparison is presented separately(Ref.1). Results revealed that the suspended aerosol mass concentration and the aerodynamic mass median diameter obtained from both the pre - and post - test calculations agreed fairly well with the test results.
Hamada, Hirotsugu; *; Himeno, Yoshiaki; *
PNC TN9410 89-146, 85 Pages, 1989/08
Steam wastage tests of the duplex-wall heat transfer tubes for the steam generators were conducted by placing its emphasis on the investigation of the possible occurrence of a subsequent failure on an outer-wall of the tube in case of its inner-wall leak. Based on the limitation from the test rig, the test tubes, each of which has an artificial crack on its outer-wall instead of on its inner-wall, were manufactured and were subjected to the test. In the test, a super-heated and pressurized steam as conceptual plant design or a nitrogen gas was fed to the tube and was impinged against the inner-wall through its crack for 24 hours which are conservative enough to evaluate test results. The test with a nitrogen gas was to obtain reference data. Before and after the test, equivalent hydraulic diameter of the crack was determined by measuring a pressure drop due to a flowing helium assuming that the crack can be regarded as an orifice. Then, changes in the equivalent diameter of the crack were determined. After the test, the tubes were subjected to the post-test metallurgical examination. Results thus obtained are as follows: (1)In all tubes, equivalent diameter of the cracks decreased after the test. Some cracks were even plugged by stream corrosion products. No enlargements of the crack, therefore, was found. (2)Post-test metallurgical examination showed no evidence of a steam wastage. Only steam corrosion products were found in the gap between the inner and outer walls. In conclusion, within the extent of the present test, failure possibility of the duplex-wall tube following a generation of an initial crack on an inner-wall is negligible.
*; *; Himeno, Yoshiaki; Kuroha, Mitsuo
PNC TN9410 89-123, 54 Pages, 1989/08
In the present study, a tube protection sleeve was designed and manufactured as one of the positive measure against tube failure propagation. Its effectiveness was confirmed by water leak test in sodium. The tube protection sleeve manufactured was made of (1)a turn buckle, (2)a spacer and (3)a belt that are made from SUS304 steel. It was attached to a heat transfer tube by a belt of 30mm in width. Its attachment is able to be done easily in short time and is not necessary to weld. In the test, steam was fed to a tube attached by a tube protection sleeve in sodium. An artifitial hole is drilled in the initial leak tube. Sodium temperature was 505 C at the test. Results of the test revealed that the tube protection sleeve has enough function to postpone the failure propagation. Major results are as follows: (1)Sodium - water reaction occurred near both ends of the tube protection sleeve. Nevertheless, neighboring tube was not wasted until the failure of the sleeve. (2)At the water leak rate 10g/s, the secondary failure was delayed to six times in comparison to a tube having no sleeve. Therefore, it is possible to detect water leak(normal detection time is over 120sec) well in advance to the secondary failure. Effectiveness of the tube protection sleeve against the failure propagation was demonstrated by test. But, for its application to the SG component, several problem, such as durability and attachment property are still remained.
C at the test. Results of the test revealed that the tube protection sleeve has enough function to postpone the failure propagation. Major results are as follows: (1)Sodium - water reaction occurred near both ends of the tube protection sleeve. Nevertheless, neighboring tube was not wasted until the failure of the sleeve. (2)At the water leak rate 10g/s, the secondary failure was delayed to six times in comparison to a tube having no sleeve. Therefore, it is possible to detect water leak(normal detection time is over 120sec) well in advance to the secondary failure. Effectiveness of the tube protection sleeve against the failure propagation was demonstrated by test. But, for its application to the SG component, several problem, such as durability and attachment property are still remained.
Hamada, Hirotsugu; *; Himeno, Yoshiaki
PNC TN9520 89-016, 158 Pages, 1989/07
"SWACS" is an integrated computer code consisting of four calculition modules to analyze the consequence of large scale sodium-water reaction: the initial pressure spike and its propagation in the secondary system, the quasi-steady-state pressure, and the water leak rate from failed tube that governs whole accident sequence. The original SWACS code was developed for prototype fast breeder reactor to evaluate the accidents in their steam generators having cover gas spaces. Following to the development, modification of the code is conducting to apply it to steam generators having no-cover gas spaces as well as to improve an accuracy of the ealculated results. So far, modifications of the initial pressure spike and its propagation calculation modules have been completed. Therefore, the present user's manual was prepared. This report presents the overview of the modified version of the code. Its contents are the calculation flow, the input/output format, the calculation models, the date files, the results of sample calculations, and the operation of plotter program.
Hamada, Hirotsugu; *; Himeno, Yoshiaki
PNC TN9410 89-087, 89 Pages, 1989/05
For the safety design of the SGs (steam generators) for the prototype fast breeder reactor, the computer code "SWACS" was developed to analyze the pressure/fluid-flow phenomena during the large scale sodium water reaction accidents. The SGs have cover gas space at their top. Follow to the development. the modification was added to the code to improve an accuracy of the calculated pressure wave propagation and to make the code applicable to the SGs having non cover gas space that is one of the design option of SGs for a demonstration fast breeder reactor. With the SGs having non cover gas space, the initial pressure spike and propagated pressure would become relatively high. Thus, it is required to calculate those pressure wave more accurately than before. The report presents the modification and validation of the code in regard to the calculations of the initial pressure spike and the propagated pressure. The modification of the code includes implementation of the detailed rupture disk response models for a single and a double membranes type rupture disks and that of the boundary tracking model (BTM). The former enables the code to calculate the disk-fluid interaction using the finite element. The latter enables the code to simulate the physical phenomena more accurately for a longer time during a sodium-water reaction. After the modification, the code was validated by test results from LLTR (Large Leak Test Rig at ETEC) and PEPT (Pressure Effluence System Performance Test Rig at PNC). Reasonable agreement between the calculated and tests results are obtained. The results of the present study showed that the modified SWACS accurately calculates the pressure wave propagation for the SGs having non cover gas space. Thus, one can conclude that the code is applicable to any types of large SGs.
*; *; Himeno, Yoshiaki; Hamada, Hirotsugu
PNC TN9410 89-079, 65 Pages, 1989/04
The paper presents review of studies for sodium-water reaction phenomena, water leak propagation process, evaluation of SG safety, and development of SG tube material for an LMFBR. The paper also presents Alloy 800 wastage characteristics studied with the SWAT-2 small leak sodium-water reaction test loop (OEC, PNC, Japan) and their comparion with those of 9Cr-ferritic steel. In regard to the latter wastage characteristics, this is the first time to show the data of Alloy 800 and 9Cr-ferritic steel wastage obtained from SWAT-2. The results revealed that Alloy 800 has the highest resistance against sodium-water reaction wastage.