Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Furusawa, Naoya*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154799_1 - 154799_20, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The thermal conductivities of near-stoichiometric (U,Pu,Am)O doped with Nd
doped with Nd O
O /Sm
/Sm O
O , which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT)
, which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT) . The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C
. The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C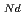 and C
and C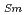 , respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70
, respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70  10
10 + 0.93C
+ 0.93C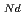 + 1.20C
+ 1.20C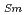 , B(m/W)=2.39
, B(m/W)=2.39  10
10 .
.
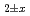 mixed oxides
mixed oxidesVauchy, R.; Matsumoto, Taku; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154786_1 - 154786_13, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hirooka, Shun; Horii, Yuta; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Uno, Hiroki*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Vauchy, R.; Hayashizaki, Kohei; Nakamichi, Shinya; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1313 - 1323, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:95.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Additive MOX pellets are fabricated by a conventional dry powder metallurgy method. Nd O
O and Sm
and Sm O
O are chosen as the additive materials to simulate the corresponding soluble fission products dispersed in MOX. Shrinkage curves of the MOX pellets are obtained by dilatometry, which reveal that the sintering temperature is shifted toward a value higher than that of the respective regular MOX. The additives, however, promote grain growth and densification, which can be explained by the effect of oxidized uranium cations covering to a pentavalent state. Ceramography reveals large agglomerates after sintering, and Electron Probe Micro-Analysis confirms that inhomogeneous elemental distribution, whereas XRD reveals a single face-centered cubic phase. Finally, by grinding and re-sintering the specimens, the cation distribution homogeneity is significantly improved, which can simulate spent nuclear fuels with soluble fission products.
are chosen as the additive materials to simulate the corresponding soluble fission products dispersed in MOX. Shrinkage curves of the MOX pellets are obtained by dilatometry, which reveal that the sintering temperature is shifted toward a value higher than that of the respective regular MOX. The additives, however, promote grain growth and densification, which can be explained by the effect of oxidized uranium cations covering to a pentavalent state. Ceramography reveals large agglomerates after sintering, and Electron Probe Micro-Analysis confirms that inhomogeneous elemental distribution, whereas XRD reveals a single face-centered cubic phase. Finally, by grinding and re-sintering the specimens, the cation distribution homogeneity is significantly improved, which can simulate spent nuclear fuels with soluble fission products.
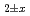 and (U,Pu,Am,Np)O
and (U,Pu,Am,Np)O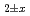
Hirooka, Shun; Matsumoto, Taku; Kato, Masato; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Uno, Hiroki*; Yamada, Tadahisa*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 542, p.152424_1 - 152424_9, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:60.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The measurement of oxygen potential was conducted at 1,673, 1,773, and 1,873 K for (U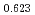 Pu
Pu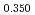 Am
Am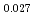 )O
)O and at 1,873 and 1,923 K for (U
and at 1,873 and 1,923 K for (U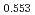 Pu
Pu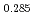 Am
Am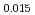 Np
Np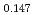 )O
)O by using a thermo-gravimeter and an oxygen sensor. Am inclusion in terms of substituting the U significantly increased the oxygen potential. Similarly, the inclusion of Np as a substitute for U increased the oxygen potential; however, the effect was not as large as that with the Pu or Am addition at the same rate. The results were analyzed via defect chemistry and certain defect formations were suggested in the reducing region and the near-stoichiometric region by plotting the relationship between PO
by using a thermo-gravimeter and an oxygen sensor. Am inclusion in terms of substituting the U significantly increased the oxygen potential. Similarly, the inclusion of Np as a substitute for U increased the oxygen potential; however, the effect was not as large as that with the Pu or Am addition at the same rate. The results were analyzed via defect chemistry and certain defect formations were suggested in the reducing region and the near-stoichiometric region by plotting the relationship between PO and the deviation from the stoichiometry. The equilibrium constants of the defect reactions were arranged to reproduce the experiment such that Am/Np contents were included in the entropy with coefficients fitting the experimental data.
and the deviation from the stoichiometry. The equilibrium constants of the defect reactions were arranged to reproduce the experiment such that Am/Np contents were included in the entropy with coefficients fitting the experimental data.

Suzuki, Kiichi; Kato, Masato; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Uno, Hiroki*; Carvajal-Nunez, U.*; Nelson, A. T.*; McClellan, K. J.*
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 102(4), p.1994 - 2008, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:90.42(Materials Science, Ceramics)The fundamental properties of CeO were assessed using a range of experimental techniques. The oxygen potential of CeO
were assessed using a range of experimental techniques. The oxygen potential of CeO was measured by the thermogravimetric technique, and a numerical fit for the oxygen potential of CeO
was measured by the thermogravimetric technique, and a numerical fit for the oxygen potential of CeO is derived based on defect chemistry. Mechanical properties of CeO
is derived based on defect chemistry. Mechanical properties of CeO were obtained using sound velocity measurement, resonant ultrasound spectroscopy and nanoindentation. The obtained mechanical properties of CeO
were obtained using sound velocity measurement, resonant ultrasound spectroscopy and nanoindentation. The obtained mechanical properties of CeO are then used to evaluate the Debye temperature and Gruneisen constant. The heat capacity and thermal conductivity of CeO
are then used to evaluate the Debye temperature and Gruneisen constant. The heat capacity and thermal conductivity of CeO were also calculated using the Debye temperature and the Gruneisen constant. Finally, the thermal conductivity was calculated based upon laser flash analysis measurements. This result demonstrates that the thermal conductivity has strong dependence upon material purity.
were also calculated using the Debye temperature and the Gruneisen constant. Finally, the thermal conductivity was calculated based upon laser flash analysis measurements. This result demonstrates that the thermal conductivity has strong dependence upon material purity.
Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato; Suzuki, Kiichi; Uno, Hiroki*
Proceedings of 2010 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '10) (CD-ROM), p.1859 - 1865, 2010/06
The sintering behavior of the de-waxed pellets containing about 3000 ppm of carbon was analyzed during the sintering process using thermal gravimetry and dilatometer measurements as a parameter of the ratio of hydrogen partial pressure-to-moisture partial pressure (H /H
/H O) in the sintering atmosphere. The attained O/M ratio and the shrinkage rate increased with decreasing H
O) in the sintering atmosphere. The attained O/M ratio and the shrinkage rate increased with decreasing H /H
/H O ratio in the sintering atmosphere. As a result, it is considered that a carbothermic reduction caused the significant decrease of the O/M ratio in the case of the sintering in the atmosphere of high H
O ratio in the sintering atmosphere. As a result, it is considered that a carbothermic reduction caused the significant decrease of the O/M ratio in the case of the sintering in the atmosphere of high H /H
/H O ratio. In contrast, decrement of O/M ratio could be inhibited by keeping the oxygen potential of the atmosphere high in the case of the sintering in the atmosphere of lower H
O ratio. In contrast, decrement of O/M ratio could be inhibited by keeping the oxygen potential of the atmosphere high in the case of the sintering in the atmosphere of lower H /H
/H O ratio.
O ratio.
 Pu
Pu )O
)O (1.92
(1.92 x
x 2.00) based fuels containing actinides and/or lanthanides
2.00) based fuels containing actinides and/or lanthanidesKomeno, Akira; Kato, Masato; Uno, Hiroki*; Takeuchi, Kentaro; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kashimura, Motoaki
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 9, p.012016_1 - 012016_7, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:93.82(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)It is expected that the important data for design of fast reactor fuel can be provided by evaluating the relationship between fuel composition and phase separation with reported and new measurement data. According to evaluation with reported data and new measured data, a relationship between fuel composition and phase separation temperature of MOX fuel was indicated. Higher minor actinides-containing MOX had a lower phase separation temperature at O/M ratio region from 1.92 to 1.96.
Kato, Masato; Komeno, Akira; Uno, Hiroki*; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Nakae, Nobuo; Konashi, Kenji*; Kashimura, Motoaki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 393(1), p.134 - 140, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:92.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In plutonium compounds, the lattice parameter increases due to self-radiation damage by  -decay of plutonium isotopes. The lattice parameter change and its thermal recovery in plutonium and uranium mixed dioxide (MOX) were studied. The lattice parameter for samples of MOX powders and pellets that had been left in the air for up to 32 years was measured. The lattice parameter increased and was saturated at about 0.29%. The change in lattice parameter was formulated as a function of self-radiation dose. Three stages in the thermal recovery of the damage were observed in temperature ranges of below 673K, 673-1073K and above 1073K. The activation energies in each recovery stage were estimated to be 0.12 eV, 0.73 eV and 1.2 eV, respectively, and the corresponding mechanism for each stage was considered to be the recovery of the anion Frenkel defect, the cation Frenkel defect and a defect connected with helium, respectively.
-decay of plutonium isotopes. The lattice parameter change and its thermal recovery in plutonium and uranium mixed dioxide (MOX) were studied. The lattice parameter for samples of MOX powders and pellets that had been left in the air for up to 32 years was measured. The lattice parameter increased and was saturated at about 0.29%. The change in lattice parameter was formulated as a function of self-radiation dose. Three stages in the thermal recovery of the damage were observed in temperature ranges of below 673K, 673-1073K and above 1073K. The activation energies in each recovery stage were estimated to be 0.12 eV, 0.73 eV and 1.2 eV, respectively, and the corresponding mechanism for each stage was considered to be the recovery of the anion Frenkel defect, the cation Frenkel defect and a defect connected with helium, respectively.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Komeno, Akira; Nakamichi, Shinya; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Sugata, Hiromasa*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-049, 32 Pages, 2006/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed a fast breeder reactor(FBR), and plutonium and uranium mixed oxide (MOX) having low density and 20-30%Pu content has used as a fuel of the FBR, Monju. In plutonium, Americium has been accumulated during long-term storage, and Am content will be increasing up to 2-3% in the MOX. It is essential to evaluate the influence of Am content on physical properties of MOX on the development of FBR in the future. In this study melting points and thermal conductivities which are important data on the fuel design were measured systematically in wide range of composition, and the effects of Am accumulated were evaluated. The solidus temperatures of MOX were measured as a function of Pu content, oxygen to metal ratio(O/M) and Am content using thermal arrest technique. The sample was sealed in a tungsten capsule in vacuum for measuring solidus temperature. In the measurements of MOX with Pu content of more than 30%, a rhenium inner capsule was used to prevent the reaction between MOX and tungsten. In the results, it was confirmed that the melting points of MOX decrease with as an increase of Pu content and increase slightly with a decrease of O/M ratio. The effect of Am content on the fuel design was negligible small in the range of Am content up to 3%. Thermal conductivities of MOX were evaluated from thermal diffusivity measured by laser flash method and heat capacity calculated by Nuemann- Kopp's law. The thermal conductivity of MOX decreased slightly in the temperature of less than 1173K with increasing Am content. The effect of Am accumulated in long-term storage fuel was evaluated from melting points and thermal conductivities measured in this study. It is concluded that the increase of Am in the fuel barely affect the fuel design in the range of less than 3%Am content.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kihara, Yoshiyuki; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Uno, Hiroki*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
JNC TN8400 2004-022, 44 Pages, 2005/03
Japan Nuclear Development Institute has developed homogeneous mixed oxide fuel containing minor actinide as a fuel of an advanced fast reactor. Study on the sintering behavior of the fuel was carried out and the heat treatment technique for preparing homogeneous low O/M fuel had been developed. In this report, oxygen potential was measured and phase relation was evaluated, which are needed essentially for developing the new type fuel.Oxygen potential of (Npsub0.02Amsub0.02Pusub0.3Usub0.66)Osub2-X was measured by gas equilibrium method as a function of temperature and O/M ratio. The MOX with MA has slightly higher oxygen potential as compared with that of MOX without MA. And the model of oxygen potential was derived from the measurement results based on lattice defect theory.In samples with low O/M ratio, two fcc phases were observed at room temperature. The temperature of the phase separation was measured and it is observed that the addition of MA have the effect to be decreased the phase separation temperature. In the MOX containing MA and Nd simulated a low decontaminated fuel, the Pu-Am-Nd oxides were precipitated by decreasing O/M ratio in less than 1.96.
Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Aono, Shigenori; Uno, Hiroki*
JNC TN8400 2004-017, 64 Pages, 2004/11
The use of high plutonium concentration MOX fuel is considered because of an increase of high-order plutonium from high burnup fuel, the shortage of the enriched uranium etc. The melting temperature and the thermal conductivity etc are necessary for the using of MOX fuel from the viewpoint of the safety evaluation and the fuel design. But reports about the melting temperature of MOX are few, so it is necessary to obtain more melting temperature data. This report describes the melting temperature measurement of MOX fuel whose compositions are from 0 to 100 atom% PuO2 (O/M is 2.00) and that whose O/M are from 1.922 to 1.983 (Pu concentration is 28 atom%). The result of the former experiment agree approximately with that of previous reports. About the later experiment, the variance of melting temperature by O/M is so complicated that this behavior did not show a simple increasing tendency or decreasing tendency. In these experiments, it is found that MOX samples with high O/M reacts with tungsten which is a material of sample container. In order to prevent this reaction, the sample container was made from alloy of tungsten and rhenium. And the applicability of this container was evaluated.
Kato, Masato; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Endo, Hideo
JNC TN8400 2003-013, 48 Pages, 2003/05
JNC have been manufacturing MOX fuels from Plutonium and Uranium mixed oxide powder (1:1 MOX) that were prepared by microwave direct denitration method. It is well known that MOX raw material oxidize in storage and manufacturing process due to heat generation by self-radiation. The oxidation process and rate of MOX powder were examined for three kinds of powders having different surface area. The examination of isothermal and non-isothermal oxidation was carried out by TG-DTA. The oxidized samples were analyzed by X-ray diffraction measurement. The oxidation of MOX powders proceeded in two steps and the oxidation process changed depending on the surface area of the powder as follows. Process 1 (Surface Area : 2.24m /g) First Step : MO
/g) First Step : MO
 MO
MO
 MO
MO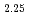 Second Step : MO
Second Step : MO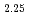
 MO
MO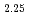 +M
+M O
O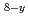 Process 2 (Surface Area : 5.59, 3.86m
Process 2 (Surface Area : 5.59, 3.86m /g) First Step : MO
/g) First Step : MO
 MO
MO +MO
+MO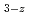
 MO
MO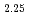 +MO
+MO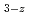 Second Step : MO
Second Step : MO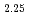 +MO
+MO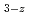
 MO
MO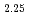 +M
+M O
O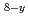 +MO
+MO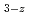 The kinetic analysis of the oxidation was evaluated by Avrami-Erofeev equation. The equation of O/M change on the MOX powder was obtained as function of temperature, keeping time and the surface area of the powder.
The kinetic analysis of the oxidation was evaluated by Avrami-Erofeev equation. The equation of O/M change on the MOX powder was obtained as function of temperature, keeping time and the surface area of the powder.

Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Nishiyama, Motokuni; Endo, Hideo; Kono, Shusaku; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Sugata, Hiromasa*
JNC TN8400 2003-011, 32 Pages, 2003/01
MOX fuel containing Neptunium is being developed as candidate fuel for an advanced nuclear fuel recycle. In this report, influence of Np on the sintering behavior, phase separation behavior of MOX fuel pellets and the homogeneity of MOX fuel pellets were evaluated. It was observed that the high Np containing pellets had a low sintered density and the microstructure changes of the pellets during the sintering were slow compared with MOX without Np. The pellets were also analyzed via Ceramography, X-ray diffraction measurement and an electron probe microanalysis. The phase separation behavior of MOX with Np was similar to that of MOX. The homogeneity of the pellet produced with this experiment was acceptable to the fuel specification.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki; Uno, Hiroki*; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Shibata, Katsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
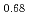 Pu
Pu Am
Am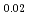 )O
)O (x=1.90
(x=1.90 2.00)
2.00)Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Komeno, Akira; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
To examine the influences of O/M ratio on the thermal conductivity of MOX fuel, the thermal diffusivities of the MOX fuel with 30% Pu content were measured, and thermal conductivities were evaluated.
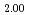
Komeno, Akira; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakamichi, Shinya; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Shibata, Katsuya*; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Komeno, Akira; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English