Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Kino, Yasushi*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Oka, Toshitaka; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*
JJAP Conference Proceedings (Internet), 9, p.011003_1 - 011003_7, 2023/00
Muon catalyzed fusion ( CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In the
CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In the  CF reaction, muon transfer from deuteron to triton and muonic molecular formation are rate-limiting processes. In this work, we have investigated the role of resonance states of muonic molecule in the
CF reaction, muon transfer from deuteron to triton and muonic molecular formation are rate-limiting processes. In this work, we have investigated the role of resonance states of muonic molecule in the  CF which affects the muonic deuterium atom population. Solving simultaneous rate equations numerically by the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method, we determined the muonic molecular formation rate so that the number of fusion events reproduces a latest experimental result. It is revealed that the resonance states play a role to enhance the fusion rate by accelerating the de-excitation of the muonic atoms.
CF which affects the muonic deuterium atom population. Solving simultaneous rate equations numerically by the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method, we determined the muonic molecular formation rate so that the number of fusion events reproduces a latest experimental result. It is revealed that the resonance states play a role to enhance the fusion rate by accelerating the de-excitation of the muonic atoms.
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 170, p.112712_1 - 112712_4, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:44.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muonic molecule which consists of two hydrogen isotope nuclei (deuteron (d) or tritium (t)) and a muon decays immediately via nuclear fusion and the muon will be released as a recycling muon, and start to find another hydrogen isotope nucleus. The reaction cycle continues until the muon ends up its lifetime of 2.2  s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion (
s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after
CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after  CF reaction.
CF reaction.
Yamashita, Takuma*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 169, p.112580_1 - 112580_5, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:44.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muon ( ) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by
) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by  and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt
and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt . Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt
. Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt , the nuclear fusion, d +t
, the nuclear fusion, d +t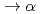 + n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion (
+ n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). Recently, the interest on
CF). Recently, the interest on  CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of
CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of  CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
Okumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I.-H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(5), p.2101704_1 - 2101704_4, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.62(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A superconducting transition-edge sensor (TES) microcalorimeter is an ideal X-ray detector for experiments at accelerator facilities because of good energy resolution and high efficiency. To study the performance of the TES detector with a high-intensity pulsed charged-particle beam, we measured X-ray spectra with a pulsed muon beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in Japan. We found substantial temporal shifts of the X-ray energy correlated with the arrival time of the pulsed muon beam, which was reasonably explained by pulse pileup due to the incidence of energetic particles from the initial pulsed beam.
 X rays
X raysOkumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I. H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:80.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed electronic  X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic
X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic 
 and
and 
 X rays together with the hypersatellite
X rays together with the hypersatellite 
 X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the
X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the  -shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic
-shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic  - and
- and  -shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
-shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
Nagai, Takayuki; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Sasage, Kenichi; Ayame, Yasuo; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Uchiyama, Takafumi*; Okada, Yukiko*; Nezu, Atsushi*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2016-015, 52 Pages, 2016/11
The local structure of waste elements in simulated waste glasses including V was estimated by using synchrotron XAFS measurement in this study. The results are as follows. (1) V has a high possibility which exists in the glass phase in the case of frit, and V can regard both samples as stable 4 coordination structure. (2) Zn, Ce, Nd, Zr, and Mo exist in the glass phase, and the difference is admitted by the percentage of Ce(III) and Ce(IV) by the composition. (3) Ru is separated from the glass phase as RuO crystalline, both of metal and oxide exist in Rh, and Pd is separated out as metal. (4) It was confirmed that the regularity of the local structure of Zr and Mo in the molten glasses retreats as a result of the XAFS measurement at high temperature. (5) The XAFS measurement of molten glasses were performed at 1200
crystalline, both of metal and oxide exist in Rh, and Pd is separated out as metal. (4) It was confirmed that the regularity of the local structure of Zr and Mo in the molten glasses retreats as a result of the XAFS measurement at high temperature. (5) The XAFS measurement of molten glasses were performed at 1200 C, so it would be possible to acquire excellent data by improving the shapes of the sample cell.
C, so it would be possible to acquire excellent data by improving the shapes of the sample cell.
Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Okada, Kenichi*; Yoshihiko, Saito,; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Shibata, Masahiro; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
JNC TN8400 2004-023, 67 Pages, 2005/01
Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) has developed the sorption database for dentonite and rocks in order to assess the retardation capacities of important radioactive elements in natural and engineered barriers in the H12 report. However, there are not enough distribution coefficient data for radioactive elements in saline type groundwater in the database. Thus the batch sorption tests were performed for uranium(U) and thorium(Th) in saline type groundwater. For these elements, there are little registration numbers in the JNC's sorption database, and also these elements are important to evaluate the safety of disposal system. The experiments for each radioactive element were performed on the following conditions; *U:Kd measurements using the solutions (synthesized sea water and distilled water) reacted with sand stone as a function of carbonate concentration, under reducing conditions. *Th:Kd measurements using the solutions (synthesized sea water and distilled water) reacted with sand stone.
 X-ray diffraction of graphite-diamond transformation using various catalysts under high pressures and high temperatures
X-ray diffraction of graphite-diamond transformation using various catalysts under high pressures and high temperaturesUtsumi, Wataru; Okada, Taku; Taniguchi, Takashi*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Kikegawa, Takumi*; Hamaya, Nozomu; Shimomura, Osamu
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 16(14), p.S1017 - S1026, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:55.96(Physics, Condensed Matter)The graphite-diamond transformation was investigated using in-situ time-resolved X-ray diffraction experiments with a MgO dissolved aqueous fluid as the diamond forming catalyst under conditions of 6.6-8.8 GPa and 1400-1835 C. Experiments were conducted using a 180-ton DIA-type cubic-anvil apparatus installed on the beamline BL14B1 at SPring-8, a third-generation synchrotron radiation facility in Japan. By analyzing the kinetic data using the JMAK rate equation, it was clarified that altering the pressure-temperature conditions drastically changes the nucleation and growth process of diamond.
C. Experiments were conducted using a 180-ton DIA-type cubic-anvil apparatus installed on the beamline BL14B1 at SPring-8, a third-generation synchrotron radiation facility in Japan. By analyzing the kinetic data using the JMAK rate equation, it was clarified that altering the pressure-temperature conditions drastically changes the nucleation and growth process of diamond.
Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Okada, Kenichi*; Muroi, Masayuki*; Shibata, Masahiro; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
JNC TN8400 2003-039, 44 Pages, 2004/02
We carried out the batch sorption experiments for Sn, Pb and Th in saline type groundwater to obtain the distribution coefficient (Kd) data that were lack in the JNC sorption database. As the results, the following data were obtained. Sn: in artificial sea water, Kd=1 m3/kg on sand stone, Pb: in artificial sea water, Kd=2 m3/kg on sand stone and Kd=4-10 m3/kg on tuff, Th: in artificial sea water, Kd=1-8 m3/kg on sand stone, in artificial sea water with high carbonate concentration, Kd=0 m3/kg on sand stone.
Terasaki, Hidenori*; Kato, Takumi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Kiminori*; Suzuki, Akio*; Okada, Taku
Geophysical Research Letters, 29(8), p.68_1 - 68_3, 2002/05
The in situ viscosity measurements of the pure molten Fe under high pressures were made by falling sphere X-ray radiography method. Viscosity coefficients at about 2000 K were 15-24 mPa s at 2.7-5.0 GPa, and 4-9 mPa s at 5.0-7.0 GPa. Drastic decrease was found at around 5 GPa, at which stable solid phase below the melting temperatures change from delta (bcc) to gamma (fcc) phases. The observation indicates the possibility that the structural change in the molten Fe occurs in a narrow pressure interval (1 GPa) at the similar condition with the phase transformation in the solid.
Terasaki, Hidenori*; Kato, Takumi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Suzuki, Akio*; Okada, Taku; Maeda, Makoto*; Sato, Jin*; Kubo, Tomoaki*; Kasai, Shizu*
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 190(1-2), p.93 - 101, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:68.52(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The Fe-FeS melt is thought to be the major candidate of the outer core material. Its viscosity is one of the most important physical properties to study the dynamics of the convection in the outer core. We performed the in situ viscosity measurement of the Fe-FeS melt under high pressure using X-ray radiography falling sphere method with a novel sample assembly. Viscosity was measures in the temperature, pressure, and compositional conditions of 1233-1923 K, 1.5-6.9 GPa, and Fe-Fe 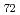 S
S 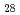 (wt %), respectively. The viscosity coefficients obtained by 17 measurements change systematically in the range of 0.008-0.036 Pa s. An activation energy of the viscous flow, 30 kJ/mol, and the activation volume, 1.5 cm
(wt %), respectively. The viscosity coefficients obtained by 17 measurements change systematically in the range of 0.008-0.036 Pa s. An activation energy of the viscous flow, 30 kJ/mol, and the activation volume, 1.5 cm  /mol, are determined as the temperature and pressure dependence, and the viscosity of the Fe
/mol, are determined as the temperature and pressure dependence, and the viscosity of the Fe 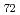 S
S 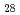 melt is found to be smaller than that of the Fe melt by 15 %. These tendencies can be well correlated with the structural variation of the Fe-FeS melt.
melt is found to be smaller than that of the Fe melt by 15 %. These tendencies can be well correlated with the structural variation of the Fe-FeS melt.
Ueta, Shinzo*; *; *; Muroi, Masayuki*; *; Izumi, Jun*; *
JNC TJ8400 2001-025, 130 Pages, 2001/03
As concern the study on the property of Iodine-129 waste-forms, the solubilities of iodine-sodalite and tourmaline and leachabilities of hidroxy-apatite and fluoro-apatite were measured last year. The results in this year are summarized as follows. (1)Solubility and Leachability of lodine-sodalite were measured under the condition of Leachabilities and solubilities of the synthesized iodine-sodalite were measured by means of a long-term leach test in the solution with chloride ions and high pH (12.5). The measured solubilities were within a range of 10 - 10
- 10 M. It showed a tendency to increase with increasing temperature. The lieachabilities showed a tendency to decrease as time passed, and were within a range of 10
M. It showed a tendency to increase with increasing temperature. The lieachabilities showed a tendency to decrease as time passed, and were within a range of 10 - 10
- 10 g/cm
g/cm /d(10
/d(10 - 10
- 10 m/y). After the leach test, the solid phases were analyzed and the alternation was not observed. It was confirmed by the experiments that the sodalite waste form had a certain capability to contain iodine even though the chloride ion existence. (2)Leaching property of high density apatite sample The following results were obtained by the manufacture examination of high density apatite sample and leaching experiments; (a)As a manufacture technology for apatite molding body, Plasma-hotpress technology was applied. To the porosity which aims 5%, the porosity of hydroxyapatite and fluoroapatite was under 2%. (b)Ca and P leaching concentration from hydroxyapatite reached 10
m/y). After the leach test, the solid phases were analyzed and the alternation was not observed. It was confirmed by the experiments that the sodalite waste form had a certain capability to contain iodine even though the chloride ion existence. (2)Leaching property of high density apatite sample The following results were obtained by the manufacture examination of high density apatite sample and leaching experiments; (a)As a manufacture technology for apatite molding body, Plasma-hotpress technology was applied. To the porosity which aims 5%, the porosity of hydroxyapatite and fluoroapatite was under 2%. (b)Ca and P leaching concentration from hydroxyapatite reached 10 M order, which was same order solubility estimated by PHREEQE code. From this test results, it was indicated that apatite material has a possibility for a waste of low-Leachability and high density performance.
M order, which was same order solubility estimated by PHREEQE code. From this test results, it was indicated that apatite material has a possibility for a waste of low-Leachability and high density performance.
 X-ray observation of cubic BC
X-ray observation of cubic BC N formation under high pressures and temperatures
N formation under high pressures and temperaturesUtsumi, Wataru; Okada, Taku; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Shimomura, Osamu
Proceeding of the 8th NIRIM International Symposium on Advanced Materials (ISAM 2001), p.39 - 40, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Yanagisawa, Ichiro*; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*; Izumi, Jun*; Saigusa, Moriyuki*; *; *; *; Ueta, Shinzo*
JNC TJ8400 2000-038, 202 Pages, 2000/02
(1)Sodalite and tourmaline are natural-occurring minerals, which can contain halide in their aluminosilicate lattices. Therefore, these materials have possibilities of immobilization of I-129. In this study, solubility measurements for these materials were carried out. It was confirmed from dissolution behaviors obtained for some kinds of sodalite and calculated results of solubilities based on thermodynamic data that dissolution of sodalite to aqueous solution could be limited by its solubility. Solubility of sodalite had tendencies of "synthesized one  natural one" and "chloride
natural one" and "chloride  iodide". Immobilized iodine in sodalite crystalline lattice was not replaced by chlolide ion in the solution. It was indicated that tourmaline has a possibility as a waste material containing I-129 from comparison of dissolution behavior of element with sodalite. (2)Leaching property of a multi-layered waste-form, that is composed of (1)iodine bearing material (zeolite), (2)coating layer (silica and apatite) and 3)low solubility matirx (apatite), was studied under reducing condition. The following results were obtained by the leaching experiments: (1)The coating layer of hidroxyapatite can reduce the iodine leaching rate by 4 order compared with that of bare iodine bearing material. (2)Ca and P concentration after one-month dipping reached the solubility estimated by the theoretical calculation using PHREEQE code. As a conclusion, it was indicated that this waste-form concept has potential to show low leaching rate.
iodide". Immobilized iodine in sodalite crystalline lattice was not replaced by chlolide ion in the solution. It was indicated that tourmaline has a possibility as a waste material containing I-129 from comparison of dissolution behavior of element with sodalite. (2)Leaching property of a multi-layered waste-form, that is composed of (1)iodine bearing material (zeolite), (2)coating layer (silica and apatite) and 3)low solubility matirx (apatite), was studied under reducing condition. The following results were obtained by the leaching experiments: (1)The coating layer of hidroxyapatite can reduce the iodine leaching rate by 4 order compared with that of bare iodine bearing material. (2)Ca and P concentration after one-month dipping reached the solubility estimated by the theoretical calculation using PHREEQE code. As a conclusion, it was indicated that this waste-form concept has potential to show low leaching rate.
Yanagisawa, Ichiro*; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*; Izumi, Jun*; Saigusa, Moriyuki*; Kitao, Hideo*; Tsuzuki, Yasuo*; Neyama, Atsushi*; Kato, Hiroyasu*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Okada, Kenichi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-037, 61 Pages, 2000/02
no abstracts in English
Nomura, Yasushi; *; *; *; *; Nishio, Gunji; *; *; *; Sugiyama, Toshihide*; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 33(4), p.318 - 328, 1991/04
no abstracts in English
 C pellet and cladding material in a sodium environment (II)
C pellet and cladding material in a sodium environment (II)*; *; Yato, Tadao*; *; *
PNC TJ9211 89-001, 75 Pages, 1989/03
Out-of-pile tests were performed to study the compatibility between B C pellet and cladding material in the sodium bonding B
C pellet and cladding material in the sodium bonding B C absorber pin. No harmful change is observed in B
C absorber pin. No harmful change is observed in B C pellet except with a little change in the suface colour after heating at 650
C pellet except with a little change in the suface colour after heating at 650 C for 5,000 hours. The reaction between cladding material and B
C for 5,000 hours. The reaction between cladding material and B C pellet is negligible at the temperature below 550
C pellet is negligible at the temperature below 550 C. The Cr, C, B-rich and Ni-deficient reaction layer is formed at 650
C. The Cr, C, B-rich and Ni-deficient reaction layer is formed at 650 C. The thickness of this reaction layer increases with heating time and reaches about 40
C. The thickness of this reaction layer increases with heating time and reaches about 40 m after 5,000 hours. The microstructure of cladding changes by annealing and a precipitation of (Cr, Mo)
m after 5,000 hours. The microstructure of cladding changes by annealing and a precipitation of (Cr, Mo) C
C is observed in the inner part of cladding. In three candidate cladding materials, the reaction behaviors of advanced SUS316 steel and high strength ferite/martensite steel are almost same as that of cladding material. Formation of surface reaction layer and microstructure change are observed little in advanced austenite steel. Ni cannot be expected as the barrier materiale because of the penetration of B and C, Cr, Nb and Ti can be expected as the barrier materiale.
is observed in the inner part of cladding. In three candidate cladding materials, the reaction behaviors of advanced SUS316 steel and high strength ferite/martensite steel are almost same as that of cladding material. Formation of surface reaction layer and microstructure change are observed little in advanced austenite steel. Ni cannot be expected as the barrier materiale because of the penetration of B and C, Cr, Nb and Ti can be expected as the barrier materiale.
Yamashita, Takuma*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
A muon ( ) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion (
) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion ( CF) between deuteron (d) and triton (t). In this work, we have solved simultaneous reaction rate equations by the 4th-order Runge-Kutta method for the jointed
CF) between deuteron (d) and triton (t). In this work, we have solved simultaneous reaction rate equations by the 4th-order Runge-Kutta method for the jointed  CF cycles in the two layers (H
CF cycles in the two layers (H /D
/D and D
and D /T
/T ). The T
). The T concentration to maximize the intensities of fusion neutrons and muons emitted to the vacuum will be discussed.
concentration to maximize the intensities of fusion neutrons and muons emitted to the vacuum will be discussed.
 CF experiment at J-PARC MLF
CF experiment at J-PARC MLFNatori, Hiroaki*; Doiuchi, Shogo*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kino, Yasushi*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Miyashita, Konan*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Nagatani, Yukinori*; Nishimura, Shoichiro*; Oka, Toshitaka; et al.
no journal, ,
A muonic molecule which consists of muon and two hydrogen isotope nuclei (deuteron (d) or tritium (t)) decays immediately via nuclear fusion (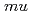 CF) and the muon will be released as a recycling muon. We attempted to use these muons to develop the scanning muon microscope. In this work, we will report the detection of neutron which emits during the
CF) and the muon will be released as a recycling muon. We attempted to use these muons to develop the scanning muon microscope. In this work, we will report the detection of neutron which emits during the  CF reaction.
CF reaction.
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muon catalized fusion ( CF) is expected to be a high-quality muon beam source for undestructive measurement and a monoenergetic neutron source. In this work, we attemped to observe a released muon after intermolecular nuclear reaction using muonic X-ray.
CF) is expected to be a high-quality muon beam source for undestructive measurement and a monoenergetic neutron source. In this work, we attemped to observe a released muon after intermolecular nuclear reaction using muonic X-ray.