Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sugino, Hiroyuki; Suyama, Kenya; Okuno, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2007), p.144 - 150, 2007/05
Accurate calculation the isotopic composition of spent nuclear fuels (SNF) is important to evaluate the criticality safety of fuel cycle facilities. In the burnup calculation, the burnup value is traditionally used to obtain the exposure value of PIE samples. Because calculation codes and data libraries have been revised progressively, re-evaluation of the burnup values using the latest nuclear data library and calculation method is important to confirm quality of burnup analysis. Based on this idea, the burnup value of Obrigheim PIE data was re-examined to understand the level of the influence. This study shows that the maximum difference of 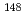 Nd calculation from experimental results is reduced from 1.0 % to 0.7 % by re-evaluation of the burnup value using latest nuclear data, and the deviation of neutron multiplication factor is approximately 0.5 %.
Nd calculation from experimental results is reduced from 1.0 % to 0.7 % by re-evaluation of the burnup value using latest nuclear data, and the deviation of neutron multiplication factor is approximately 0.5 %.
Awano, Toshihiko*; Sakai, Akira*; Sugino, Hiroyuki*
JNC TJ1400 2002-012, 94 Pages, 2001/06
None
; Sugino, Hiroyuki; Yui, Mikazu
JOINT WORKSHOP ON HLW MANAGEMENT BETWEEN KOREA ANDJAPAN, 0 Pages, 2000/00
None
Sugino, Hiroyuki; Fujita, Tomoo; Taniguchi, Wataru; Iwasa, Kengo; Hasegawa, Hiroshi
JNC TN8400 99-096, 23 Pages, 1999/12
The Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) has prepared a second progress report (entitled H12) on research and development for geological disposal of high-level waste (HLW) in Japan. H12 report consist of a Project Overview Report and three Supporting Reports which cover the three major fields described in the AEC Guidelines: (1)evaluation of the geological environment, (2)repository design and engineering technology, (3)performance assessment. This report is prepared to explain background information of buffer design which is descried in Supporting Report 2 (Repository Design and Engineering Technology). In buffer design of H12 report, the design requirements of the buffer are assumed and the relationship between buffer thickness and density was shown corresponding design requirement as an area map. This report describes the background information such as the numerical formulations, assumptions, engineering judgement and so on.
Taniguchi, Wataru; Suzuki, Hideaki*; Sugino, Hiroyuki*; Matsumoto, Kazuhiro*; Chijimatsu, Masakazu*; Shibata, Masahiro
JNC TN8400 99-052, 73 Pages, 1999/12
For the buffer of geological disposal of High-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan, it is expected to maintain its low water permeability, self-sealing properties, radionuclides adsorption retardation properties, thermal conductivity, etc. It is considered that compacted bentonite or a compacted sand-mixtured bentonite that satisfy many of the expected properties mentioned above are superior. JNC (Japan Nuclear Fuel Development Corporation) has studied the measurement method for the properties of buffer and measured to use the measurement results for the design and performance assessment analysis. Also, we have conducted the design of engineered barrier and underground facility based on assuming geological condition. For the design of engineered barrier and underground facility, high thermal conductivity of buffer is design requirement to avoid mineralogical alternation. Also, the design is not conducted using the density of buffer less than the bulk density (powder-mass density). Therefore, the bulk density (powder-mass density) is one of the design requirements. In this report, the thermal properties and the bulk density (powder-mass density) of the buffer material is measured. Then thermal analysis in the near field is conducted using the measurement results, and we studied the relationships between the dry density, sand-mixtured ratio, water content and thickness of the buffer to satisfy the design requirement from the view point of thermal condition, based on the temperature constraint of the buffer.
Takachi, Kazuhiko; Sugino, Hiroyuki
JNC TN8400 99-043, 52 Pages, 1999/11
In the near field, as tunnels and pits are excavated, a redistribution of stresses in the surrounding rock will occur. For a long period of time after the emplacement of waste packages various events will take place, such as the swelling of the buffer, sinking of the overpack under its own weight, deformation arising from expansion of overpack corrosion products and the creep deformation of the rock mass. The evaluation of what effects these changes in the stress-state will have on the buffer and rock mass is a major issue from the viewpoint of safety assessment. Therefore, rock creep analysis, overpack corrosion expansion analysis and overpack sinking analysis have been made in order to examine the longterm mechanical stability of the near field and the interaction of various events that may affect the stability of the near field over a long period of time. As the results, rock creep behavior, the variations of the stress-state and the range of the influence zone differ from the rock strength, strength of buffer in the tunnel and side pressure coefficient etc. about the hard rock system and soft rock system established as basic cases. And the magnitude of the stress variations for buffer by the overpack sinking and rock creep deformation is negligible compared with it by the overpack corrosion expansion. Furthermore, though very limited zone of buffer around the overpack is close to the critical state by the overpack corrosion expansion, the engineered barrier system attains a comparatively stable state for a long period of time.
Sugino, Hiroyuki; *
JNC TN8400 99-040, 75 Pages, 1999/11
The buffer material that will be buried as a component of the engineered barriers system swells when saturation by groundwater. As a result of this swelling, buffer material may penetrate into the peripheral rock zone surrounding the buffer through open fractures. If sustained for extremely in long-period of time, The buffer material extrusion could lead to reduction of buffer density, which may in turn degrade the assumed performance assessment properties (e.g., permeability, diffusion coefficient) JNC has been conducted the study of bentonite extrusion into fractures of rock mass as a part of high level waste research. In 1997, JNC has reported the test results concerning buffer material extrusion and buffer material erosion. These tests have been done using test facilities in Geological Isolation Basic Research Facility. After 1997, JNC also conducted analytical study of buffer material extrusion. This report describes the analysis results of this study which are reflected to the H12 report. In this analysis, The diffusion coefficient was derived as a function of the swelling pressure and the viscosity resistance of the buffer materials. Thus, the reduction in density of buffer materials after emplacement in saturated rock was assessed. The assessment was made assuming parallel-plate radial fractures initially filled by water only. Because fractures in natural rock masses inevitably have mineral inclusions inside of them and fractures orientation leads to fractures intersecting other fractures, this analysis gives significantly conservative conditions with respect to long-term extrusion of buffer and possible decrease in buffer density.
; Taniguchi, Wataru; Koo, Shigeru*; Hasegawa, Hiroshi; Sugino, Hiroyuki; Kubota, Shigeru*; Dewa, Katsuyuki*
JNC TN8400 99-037, 281 Pages, 1999/11
It is planned to construct the tunnels and emplace waste packages at several hundred meters to 1,000 meters under the ground for the repository of high-level radioactive waste based on a policy to assure the safe life environment. It is required to be mechanically stable for the tunnels to assure the work safety throughout the construction, operation and closure phase. In this report, the mechanical stability of tunnels, that is a factor of design requisites, was evaluated by the analyses to present an outline of the technical reliability of geological disposal. To put it concretely, the tunnel sections were determined to have the required areas and shapes, and the analyses on the mechanical stability at tunnel excavations and earthquake, at tunnel intersections were conducted by the theoretical analysis and finite element method. The results obtained by these investigations are shown below: (1)It will be able to construct the tunnels with present techniques. The mechanical stability of tunnels will be assured if proper supports are given, and adequate tunnel spacing and disposal-pit pitches are set. (2)The mechanical stability will be assured at the tunnels intersections if proper reinforcement measures are taken. The reinforcement will be required for the intersection areas over the distance of 1D (D: diameter of tunnels) on the obtuse angle side, and 4D on the acute angle side, when intersection angle is set at 30 degrees. (3)The investigations were conducted on the assumption that the experienced big earthquake occurred. The results show that the effect of earthquake on the mechanical stability of tunnels is small, and tunnels are stable at the earthquake when the mechanical stability at tunnel excavations is assured.
Taniguchi, Wataru; Takachi, Kazuhiko; Sugino, Hiroyuki; Mori, Koji*
JNC TN8400 99-054, 140 Pages, 1999/09
For the buffer material of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan, it is considered to use a compacted bentonite or a compacted sand-mixture bentonite that is one kind of clay. The buffer material is expected to maintain long-term mechanical stability, to hold the waste in designated place, and to avoid the effects on the radionuclides migration. It is considered that the cyclic load due to seismic activities affects long-term mechanical stability in Japan, where many earthquakes have been occurring. In this report, aseismic mechanical stability of engineered barrier of HLW is studied by dynamic analysis based on equation of vibration, mainly in the view point of mechanical stability of the buffer. The analytical computer code that has been developed by JNC in cooperative project with National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention Science and Technology Agency is used in this study. Seismic wave at the disposal depth in the assumed geological environment is established by multiple reflection theory analysis, and then seismic wave at the disposal depth is used for the aseismic mechanical stability analysis. For the aseismic mechanical stability, total stress analyses (single-phase system) with the target field of near field are conducted to evaluate the shear failure of the buffer, the displacement of overpack, and vibrational behavior of the engineered barrier, and then effective stress analyses (two-phase system) with the target field of the engineered barrier are conducted to evaluate excursion in the pore water pressure within the buffer (i. e. liquefaction), concerning the non-linear dynamic properties of the buffer material. From the results, the following conclusions are obtained. (1)From the results of the total stress analyses, it is confirmed that the buffer must not reach a shear failure condition from the stresses caused by an earthquake and the overpack must not move significantly due to the ...
Sugino, Hiroyuki; Matsumoto, Kazuhiro*
Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Radioactive Waste Management and Environmental Remediation (ICEM '99), 0 Pages, 1999/00
None