Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Sunagawa, Hikaru*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Fujihara, Masayoshi; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.31_1 - 31_6, 2024/12
Mori, Yuichiro*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Takano, Masahiro*; Kakizawa, Sho*; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 634, p.118673_1 - 118673_8, 2024/05
To investigate silicon effects on the hydrogen-induced volume expansion of iron, neutron diffraction and X-ray diffraction experiments were conducted to examine hcp-Fe Si
Si under high pressures and high temperatures. Neutron diffraction experiments were performed on the deuterated hcp-Fe
under high pressures and high temperatures. Neutron diffraction experiments were performed on the deuterated hcp-Fe Si
Si at 13.5 GPa and 900 K, and at 12.1 GPa and 300 K. By combining the P-V-T equation of state of hcp-Fe
at 13.5 GPa and 900 K, and at 12.1 GPa and 300 K. By combining the P-V-T equation of state of hcp-Fe Si
Si , present results indicate that the hydrogen-induced volume expansion of hcp-Fe
, present results indicate that the hydrogen-induced volume expansion of hcp-Fe Si
Si is 10% greater than that of pure hcp iron. Using the obtained values, we estimated the hydrogen content that would reproduce the density deficit in the inner core, which was 50% less than that without the effect of silicon. Possible hydrogen content,
is 10% greater than that of pure hcp iron. Using the obtained values, we estimated the hydrogen content that would reproduce the density deficit in the inner core, which was 50% less than that without the effect of silicon. Possible hydrogen content,  , in the inner core and the outer core was calculated to be 0.07 and 0.12-0.15, respectively, when reproducing the density deficit of the inner core with hcp-Fe
, in the inner core and the outer core was calculated to be 0.07 and 0.12-0.15, respectively, when reproducing the density deficit of the inner core with hcp-Fe Si
Si Hx.
Hx.
Kamikawa, Yutaka; Suzuki, Makoto; Agake, Toshiki; Murakami, Takahiko; Morita, Yusuke; Shiina, Hidenori; Fukushima, Manabu; Hirane, Nobuhiko; Ouchi, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Technology 2023-030, 57 Pages, 2024/03
Owing to the publication of the latest data about aircraft crashes by Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA), it was necessary to re-evaluate the probabilities of aircraft crashes for Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI). By using of the assessment method provided in "Regulatory Guide of the Assessment Standard for Probability of Airplane Crash on a Nuclear Power Reactor Facility", we re-evaluated the probabilities of aircraft crashes against the nuclear facilities in NSRI. As a result of the evaluations, the sum of the probabilities of aircraft crashes against Waste Treatment Facilities (maximum probability among all nuclear facilities in NSRI) is 5.68 10
10 (times/(reactor
(times/(reactor  year)) which is lower than 10
year)) which is lower than 10 (times/(reactor
(times/(reactor  year)) that is the assessment criterion whether aircraft crashes is considered to be "anticipated external human induced events" in design basis or not.
year)) that is the assessment criterion whether aircraft crashes is considered to be "anticipated external human induced events" in design basis or not.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Sugiyama, Yasuyuki*; Okita, Hidefumi; Seiya, Kiyomi*; Nomura, Masahiro; Shimada, Taihei; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; et al.
Proceedings of 68th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High Intensity and High Brightness Hadron Beams (HB2023) (Internet), p.305 - 311, 2024/03
The application of MA cores to the accelerating rf cavities in high intensity proton synchrotrons was pioneered for the J-PARC synchrotrons. The MA cavities can generate high accelerating voltages. The wideband frequency response of the MA cavity enables the frequency sweep without the tuning loop. The dual harmonic operation is indispensable for the longitudinal bunch shaping to alleviate the space charge effects in the RCS. These advantages of the MA cavity are also disadvantages when looking at them from a different perspective. Since the wake voltage consists of several harmonics, the beam loading compensation must be multiharmonic. The operation of tubes in the final stage amplifier is not trivial when accelerating very high intensity beams; the output current is high and the anode voltage is also multiharmonic. We summarize our effort against these issues in the operation of the RCS and MR for more than 10 years.
Morimoto, Kyoichi; Ono, Takahiro; Kakutani, Satomi; Yoshida, Moeka; Suzuki, Soichiro
Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics, 36(1), p.125 - 133, 2024/02
The Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development was established for the purpose of developing and verifying remote control equipment for promoting the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and the external use of this center was started in 2016. The mission of this center is to contribute to the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and for the reconstruction of Fukushima Prefecture. In this review, we describe the equipment related to the full-scale mock-up test, the component test for a remote-control device and the virtual reality system in this center. In addition, the case examples for usage of these equipment are introduced.
Morishita, Yuki; Miyamura, Hiroko; Sato, Yuki; Oura, Masatoshi*
Radiation Measurements, 171, p.107064_1 - 107064_7, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)The detection of alpha and beta contamination locations is important for decontaminating nuclear facilities. In the high radiation dose rate environment at the decommissioning sites, the contamination measurement by the workers is not effective. Thus, we developed a remote automatic contamination measurement system using a new scintillator-based detector. A 50 mm
 100-
100- m-thick YAlO
m-thick YAlO (Ce)(YAP:Ce) scintillator was coupled with a flat panel-type multianode photomultiplier tube. The detector was installed downwards at the bottom of a robot. It has an energy measurement capability, and the energy measurement could discriminate the alpha particles from the beta and
(Ce)(YAP:Ce) scintillator was coupled with a flat panel-type multianode photomultiplier tube. The detector was installed downwards at the bottom of a robot. It has an energy measurement capability, and the energy measurement could discriminate the alpha particles from the beta and  Rn alpha particles. With the energy information, alpha and beta particles could be identified and mapped simultaneously. In addition, a slow-moving robot could be used to obtain statistically sufficient counts in a single run measurement, allowing the evaluation of surface contamination density using only alpha particles. The remote automatic contamination measurement system will be useful in visualizing the contamination distribution in environments that are inaccessible to workers.
Rn alpha particles. With the energy information, alpha and beta particles could be identified and mapped simultaneously. In addition, a slow-moving robot could be used to obtain statistically sufficient counts in a single run measurement, allowing the evaluation of surface contamination density using only alpha particles. The remote automatic contamination measurement system will be useful in visualizing the contamination distribution in environments that are inaccessible to workers.
Nagata, Hiroshi; Omori, Takazumi; Maeda, Eita; Otsuka, Kaoru; Nakano, Hiroko; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2023-033, 40 Pages, 2024/01
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) was decided as a one of decommission facilities in April 2017. In order to submit the decommissioning plan to the Nuclear Regulation Authority, the type of accident assumed in the first stage of the decommissioning plan was selected, and the public exposure dose was evaluated. A fuel handling accident and a fire accident during storage of waste were selected as assumed accidents in the first stage of the decommissioning plan. An evaluation of the public exposure dose from the radioactive materials released into the atmosphere due to these accidents was estimated to be a maximum of 0.019 mSv (due to a fire accident during storage of waste). This estimated value was found to be sufficiently smaller than the judging criteria (5 mSv), and not to pose a significant risk of radiation exposure to the general public.
Okita, Hidefumi; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Nomura, Masahiro; Shimada, Taihei; Saha, P. K.; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Sugiyama, Yasuyuki*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2687(7), p.072005_1 - 072005_7, 2024/01
Longitudinal phase space tomography is an effective measurement tool for acquiring the longitudinal phase space distribution. For the J-PARC synchrotrons, tomography, which can take into account the beam dynamics such as longitudinal space charge effect and nonlinearity, is desired, as the beam power increases. In this study, for the J-PARC synchrotron, the CERN's tomography, which employs the hybrid algorithm that can consider the beam dynamics for reconstruction, is introduced and benchmarked. The benchmark results show that the CERN's tomography has the ability to measure the longitudinal phase space distribution accurately, in the high-power beam operation at the J-PARC synchrotrons.
Kawahara, Takahiro; Suda, Shoya; Fujikura, Toshiki; Masai, Seita; Omori, Kanako; Mori, Masakazu; Kurosawa, Tsuyoshi; Ishihara, Keisuke; Hoshi, Akiko; Yokobori, Tomohiko
JAEA-Technology 2023-020, 36 Pages, 2023/12
We have been storing drums containing radioactive waste (radioactive waste packages) at waste storage facilities. We have been managing radioactive waste packages along traditional safety regulations. However, over 40 years has passed from a part of them were brought in pit-type waste storage facility L. Most of them are carbon steel 200 L drums, and surface of them are corroded. For better safety management, we started to take drums out from the pit and inspect them in FY 2019. After each inspection, we repair them or remove the contents of the drum and refill new drums if necessary. In this report, we will introduce the planning, the review of the plan, and the trial operation of this project.
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Nakayoshi, Akira; Arai, Yoichi; Sato, Takumi; Ohgi, Hiroshi; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Yamaguchi, Yukako; Morishita, Kazuki; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-005, 418 Pages, 2023/12
For safe and steady decommissioning of Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), information concerning composition and physical/chemical properties of fuel debris generated in the reactors should be estimated and provided to other projects conducting the decommissioning work including the retrieval of fuel debris and the subsequent storage. For this purpose, in FY2021, samples of contaminants (the wiped smear samples and the deposits) obtained through the internal investigation of the 1F Unit 2 were analyzed to clarify the components and to characterize the micro-particles containing uranium originated from fuel (U-bearing particles) in detail. This report summarized the results of analyses performed in FY2021, including the microscopic analysis by SEM and TEM, radiation analysis, and elemental analysis by ICP-MS, as a database for evaluating the main features of each sample and the probable formation mechanism of the U-bearing particles.
 O/H
O/H O vapor generator for contrast-variation neutron scattering
O vapor generator for contrast-variation neutron scatteringArima-Osonoi, Hiroshi*; Takata, Shinichi; Kasai, Satoshi*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Miyata, Noboru*; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Iwase, Hiroki*; Hiroi, Kosuke; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(6), p.1802 - 1812, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Otsuki, Daiki*; Ishida, Tatsuhiro*; Tsutsumi, Naoya*; Kobayashi, Masaki*; Inagaki, Kodai*; Yoshida, Teppei*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Fujimori, Shinichi; Yasui, Akira*; Kitagawa, Saiki*; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(12), p.124601_1 - 124601_6, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Tobita, Minoru*; Goto, Katsunori*; Omori, Takeshi*; Osone, Osamu*; Haraga, Tomoko; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Tsuchida, Daiki; Mitsukai, Akina; Ishimori, Kenichiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-011, 32 Pages, 2023/11
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to the study of radioactivity concentration evaluation methods for radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities, we collected and analyzed concrete samples generated from JRR-3, JRR-4 and JAERI Reprocessing Test Facility. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 23 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Ag,
Ag,  Cs,
Cs,  Ba,
Ba,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2021-2022.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2021-2022.
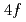 states in the electronic structure of the intermediate-valence superconductor CeIr
states in the electronic structure of the intermediate-valence superconductor CeIr
Fujimori, Shinichi; Kawasaki, Ikuto; Takeda, Yukiharu; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Sasabe, Norimasa*; Sato, Yoshiki*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Nakamura, Ai*; Maruya, A.*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Electronic Structure (Internet), 5(4), p.045009_1 - 045009_7, 2023/11
Morii, Shiori; Yomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
KEK Proceedings 2023-2, p.132 - 137, 2023/11
New analytical method of a combination of laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) and isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) for quantification of Zr isotopes in a solid sample was investigated. Solid Zr-isotope reference was added to a simulated radioactive waste sample as a spike, then Zr isotope ratio was measured by LA-ICP-MS. As a result, we successfully quantify Zr isotopes in the simulated radioactive waste sample by new IDMS. There is a possibility that this new method can be applied for quantification of Zr-93 in difficult to dissolve radioactive wastes.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Okita, Hidefumi; Hotchi, Hideaki*; Saha, P. K.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Seiya, Kiyomi*; Sugiyama, Yasuyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.64 - 68, 2023/11
The J-PARC 3GeV synchrotron (RCS) provides high intensity proton beams to the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) and the Main Ring (MR). The harmonic number (h) of the RCS is 2 and the RCS normally accelerates two bunches. For some experiments at the MLF, a single bunch is preferred. In this case, one of the rf bucket is filled with protons and the other is empty. Therefore the beam intensity is halved. If the RCS can accelerate with h=1, the intensity per bunch can be doubled, enabling to provide single bunch beams to the MLF with the maximum intensity. This possibly increases the MR beam power by injecting high intensity single bunches eight times. In this presentation, we report mainly on the consideration of h=1 acceleration in the RCS by longitudinal simulations.
Morii, Shiori; Yomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 72(10.11), p.441 - 448, 2023/10
Rapid analytical method for the determination of Zr-93 in radioactive wastes has been developed. Laser ablation (LA)-ICP-MS was applied to the analysis of Zr isotopes in simulated high-level radioactive waste (HLW). Sample preparation time was dramatically reduced by using a DGA resin as the adsorbent for Zr. Direct quantification of Zr isotopes in this resin sample was carried out by LA-ICP-MS. Laser settings were optimized to obtain a reliable isotope ratio of the sample by LA-ICP-MS. Quantification of Zr isotopes in the simulated HLW solution by isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) was examined. The amount of Zr-90 in the sample obtained by IDMS corresponded to a value calculated from the given concentration of Zr in the sample within uncertainty. Thus, this method can be applied for the quantification of Zr-93 in radioactive wastes.
 MnGa metamagnetic shape memory alloy with small energy loss
MnGa metamagnetic shape memory alloy with small energy lossIto, Tatsuya; Xu, X.*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Kainuma, Ryosuke*
Busseiken Dayori, 63(3), p.8 - 10, 2023/10
no abstracts in English
Akiyama, Yoichi; Shibanuma, So; Yanagisawa, Kenichi*; Yamada, Taichi; Suzuki, Kenta; Yoshida, Moeka; Ono, Takahiro; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Watanabe, Kaho; Morimoto, Kyoichi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2023-015, 60 Pages, 2023/09
Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development (NARREC) was established in Japan Atomic Energy Agency to promote a decommissioning work of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (Fukushima Daiichi NPS). NARREC consists of a Full-scale Mock-up Test Building and Research Management Building. Various test facilities are installed in these buildings for the decommissioning work of Fukushima Daiichi NPS. These test facilities are intended to be used for various users, such as companies engaged in the decommissioning work, research and development institutions, educational institutions and so on. The number of NARREC facility uses was 84 in FY2021. We participated booth exhibitions and presentations on the decommissioning related events. Moreover, we also contributed to the development of human resources by supporting the 6th Creative Robot Contest for Decommissioning. As a new project, "Narahakko Children's Classroom" was implemented for elementary school students in Naraha Town. This report summarizes the activities of NARREC in FY2021, such as the utilization of facilities and equipment of NARREC, the development of remote-control technologies for supporting the decommissioning work, arrangement of the remote-control machines for emergency response, and training for operators by using the machines.
Kumada, Takayuki; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Miura, Daisuke; Sekine, Yurina; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Hiroi, Kosuke; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Oku, Takayuki; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 14(34), p.7638 - 7643, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)The structure of nano-ice crystals in rapidly frozen glucose solution was elucidated by using spin-contrast-variation small-angle neutron scattering, which distinguishes the nano-ice crystal signal from the frozen amorphous solution signal by the polarization-dependent neutron scattering. The analysis revealed that the nano-ice crystals form a planar structure with a diameter exceeding tens of nanometers and a thickness of 1 nm, which is close to the critical nucleation size. This result suggests that the glucose molecules are preferentially bound to a specific face of nano-ice crystals, and then block the crystal growth perpendicular to that face.