Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Amamiya, Hiroki*
Dai-31-Kai Shakai Chishitsugaku Shimpojiumu Rombunshu, p.19 - 22, 2021/11
A three-year monitoring of  Cs outflow associated with soil erosion from decontaminated and burnt sites using an experimental plot was conducted in a mountainous forest of Fukushima, Japan. Corresponding with recovery of the forest floor cover, such as undergrowth and litter layer, the
Cs outflow associated with soil erosion from decontaminated and burnt sites using an experimental plot was conducted in a mountainous forest of Fukushima, Japan. Corresponding with recovery of the forest floor cover, such as undergrowth and litter layer, the  Cs outflow during the monitoring period in the rainy season of Fukushima decreased from 3.24% to 0.61% and 2.79% to 0.03% in the decontaminated and burnt sites, respectively. The forest floor cover ratio of 60% or more is a threshold for an effect on the
Cs outflow during the monitoring period in the rainy season of Fukushima decreased from 3.24% to 0.61% and 2.79% to 0.03% in the decontaminated and burnt sites, respectively. The forest floor cover ratio of 60% or more is a threshold for an effect on the  Cs outflow in the monitoring sites. In the burnt site, a change of dominant outflowed materials from soil particles into litter and its fragments also contributes to the decreasing in the
Cs outflow in the monitoring sites. In the burnt site, a change of dominant outflowed materials from soil particles into litter and its fragments also contributes to the decreasing in the  Cs outflow. A protective function of forest floor cover against the soil erosion inherent in the natural forest environment is effective for the migration control of the
Cs outflow. A protective function of forest floor cover against the soil erosion inherent in the natural forest environment is effective for the migration control of the  Cs outflow.
Cs outflow.
 Cs outflow from forest floor adjacent to a residential area; Comparison of decontaminated and non-decontaminated forest floor
Cs outflow from forest floor adjacent to a residential area; Comparison of decontaminated and non-decontaminated forest floorNiizato, Tadafumi; Watanabe, Takayoshi
Global Environmental Research (Internet), 24(2), p.129 - 136, 2021/06
The 3-years monitoring of  Cs outflow associated with soil erosion in the decontaminated and no decontaminated sites using experimental plot was conducted in the forest of Fukushima during the rainy season. The
Cs outflow associated with soil erosion in the decontaminated and no decontaminated sites using experimental plot was conducted in the forest of Fukushima during the rainy season. The  Cs outflow in the decontaminated site was 10 to 14 times larger than that of no decontaminated site. However, the outflow in the decontaminated site decreased from 3.24% to 0.61% in corresponding with the recovery of the forest floor cover. When reaching of the forest floor cover to 60% and over, the
Cs outflow in the decontaminated site was 10 to 14 times larger than that of no decontaminated site. However, the outflow in the decontaminated site decreased from 3.24% to 0.61% in corresponding with the recovery of the forest floor cover. When reaching of the forest floor cover to 60% and over, the  Cs outflow in the decontaminated site turned into relatively minor fluctuations and similar level to the no decontaminated site. The decrease in the
Cs outflow in the decontaminated site turned into relatively minor fluctuations and similar level to the no decontaminated site. The decrease in the  Cs outflow corresponding to the restoration of the forest floor cover was owing to the recovering of the protective effect of forest floor against the raindrop splash and decrease in ratio of the soil component with relatively high
Cs outflow corresponding to the restoration of the forest floor cover was owing to the recovering of the protective effect of forest floor against the raindrop splash and decrease in ratio of the soil component with relatively high  Cs activity in the particulate matter.
Cs activity in the particulate matter.
Nagao, Fumiya; Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ito, Satomi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Dohi, Terumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Funaki, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Research 2020-007, 249 Pages, 2020/10
The accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. occurred due to the Great East Japan Earthquake, Sanriku offshore earthquake, of 9.0 magnitude and the accompanying tsunami. As a result, large amount of radioactive materials was released into the environment. Under these circumstances, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting "Long-term Assessment of Transport of Radioactive Contaminants in the Environment of Fukushima" concerning radioactive materials released in environment, especially migration behavior of radioactive cesium since November 2012. This report is a summary of the research results that have been obtained in environmental dynamics research conducted by JAEA in Fukushima Prefecture.
 Cs on paved surfaces affected by the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident
Cs on paved surfaces affected by the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accidentYoshimura, Kazuya; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Kurikami, Hiroshi
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 217, p.106213_1 - 106213_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:25.07(Environmental Sciences)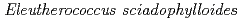 ).
).Ito, Satomi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Niizato, Tadafumi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Mitachi, Katsuaki*
KEK Proceedings 2019-2, p.132 - 137, 2019/11
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Takayoshi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Niizato, Tadafumi; Mitachi, Katsuaki*; Ito, Satomi
KEK Proceedings 2019-2, p.114 - 119, 2019/11
no abstracts in English
Nagao, Fumiya; Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ito, Satomi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Dohi, Terumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Funaki, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-002, 235 Pages, 2019/08
The accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (hereinafter referred to 1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. occurred due to the Great East Japan Earthquake, Sanriku offshore earthquake, of 9.0 magnitude and the accompanying tsunami. As a result, large amount of radioactive materials was released into the environment. Under these circumstances, JAEA has been conducting Long-term Environmental Dynamics Research concerning radioactive materials released in environment, especially migration behavior of radioactive cesium since November 2012. This report is a summary of the research results that have been obtained in environmental dynamics research conducted by JAEA in Fukushima Prefecture.
Watanabe, Takayoshi; Oyama, Takuya; Ishii, Yasuo; Niizato, Tadafumi; Abe, Hironobu; Mitachi, Katsuaki; Sasaki, Yoshito
KEK Proceedings 2017-6, p.122 - 126, 2017/11
no abstracts in English
Sasaki, Yoshito; Ishii, Yasuo; Abe, Hironobu; Mitachi, Katsuaki; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Niizato, Tadafumi
The Horticulture Journal, 86(2), p.139 - 144, 2017/04
To examine the translocation of radiocesium (Cs) scattered by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident that occurred in March 2011 to the Japanese chestnut, we investigated the autoradiography and radiocesium concentration in each part of the Japanese chestnut. The Japanese chestnut fruit has a thin skin between the kernel (cotyledons) and shell; the kernel of the fruit is edible.  Cs concentration in each part of the fruit was found to be almost the same at about 1.0
Cs concentration in each part of the fruit was found to be almost the same at about 1.0 10
10 Bq
Bq kg
kg . Radiocesium concentration in chestnut weevil larvae found on the fruit was approximately one-seventh of that in the kernel.
. Radiocesium concentration in chestnut weevil larvae found on the fruit was approximately one-seventh of that in the kernel.
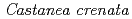 ) contaminated by radionuclides from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident
) contaminated by radionuclides from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accidentSasaki, Yoshito; Abe, Hironobu; Mitachi, Katsuaki; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Ishii, Yasuo; Niizato, Tadafumi
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 161, p.58 - 65, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:43.99(Environmental Sciences)We report the behavior of radiocesium on the tree bark and its transfer into the stemflow of chestnut in a forest in Fukushima. The radiocesium concentration is greatest in  2-cm stem, less in
2-cm stem, less in 
 5-mm stem, and least in the leaves. In the
5-mm stem, and least in the leaves. In the  2-cm stem, the radiocesium concentration of the bark was approximately 10 times that of wood. The average Cs-137 concentration of the dissolved fraction of stem flow was about 10 Bq/L; the pH was nearly constant at 5.8. A strong positive correlation was observed between the radiocesium concentration and the electrical conductivity of the dissolved fraction of stemflow; this result suggests that radiocesium and electrolytes have the same elution mechanism from the tree. Some of the particles in the particulate fraction of the stem flow was strongly adsorbed radiocesium.
2-cm stem, the radiocesium concentration of the bark was approximately 10 times that of wood. The average Cs-137 concentration of the dissolved fraction of stem flow was about 10 Bq/L; the pH was nearly constant at 5.8. A strong positive correlation was observed between the radiocesium concentration and the electrical conductivity of the dissolved fraction of stemflow; this result suggests that radiocesium and electrolytes have the same elution mechanism from the tree. Some of the particles in the particulate fraction of the stem flow was strongly adsorbed radiocesium.
Niizato, Tadafumi; Abe, Hironobu; Mitachi, Katsuaki; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ishii, Yasuo; Watanabe, Takayoshi
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 161, p.11 - 21, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:67.86(Environmental Sciences)Estimations of radiocesium input and output budgets concerning the forest floor in a mountain forest region have been conducted in the north and central part of the Abukuma Mountains of Fukushima, after 2 to 3 year period following the TEPCO Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. The radiocesium input and output associated with surface washoff, throughfall, stemflow, and litterfall processes at the experimental plots have been monitored on a forest floor of evergreen Japanese cedar and deciduous Konara oak forests. The results at both monitoring locations show the radiocesium input to be 4-50 times higher than the output during the rainy season in Fukushima. These results indicate that the radiocesium tend to be preserved in the forest ecosystem due to extremely low output ratios. Thus, the associated fluxes throughout the circulation process are key issues for the projecting the environmental fate of the radiocesium levels.
Niizato, Tadafumi; Abe, Hironobu; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Yasue, Kenichi; Oda, Yoshihiro; Sato, Haruo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Niizato, Tadafumi; Abe, Hironobu; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Sato, Haruo; Yasue, Kenichi; Oda, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Niizato, Tadafumi; Abe, Hironobu; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Sato, Haruo; Yasue, Kenichi; Oda, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
An understanding of the environmental fate of the radiocaesium released from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant is a crucial issue for remediation of the Fukushima environment because it is the main radionuclide which contributes to population dose within the contaminated area. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency launched a new research project, which aims to develop a system for evaluation of radiation exposure, taking into consideration the transport, deposition, and reworking behaviour of radiocaesium from the highest contaminated mountain forests down through the biosphere to eventual deposition in the sea. In addition, the project aims to propose counter measures for reduction in dose from the most significant exposure pathways. In this paper, we present the current status and preliminary results on the investigation of the Fukushima forest.
Abe, Hironobu; Niizato, Tadafumi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Yasue, Kenichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Niizato, Tadafumi; Abe, Hironobu; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Yasue, Kenichi; Sato, Haruo
no journal, ,
This paper presents the status on the research of the dynamic behavior of radiocaesium in the Fukushima forest.
Niizato, Tadafumi; Abe, Hironobu; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Ishii, Yasuo; Sasaki, Yoshito
no journal, ,
This paper discusses the predominant factor in the depth profiles of radiocaesium, released by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant Accident, in the forest soil developed under the evergreen coniferous and broadleaved deciduous forests in the valley-head of mountain area of Fukushima, northeast Japan. The samples were obtained from ridge, slope, and bottomland in the forest by drilling with soil sampler and scraping with scraper plate to the depth about 40 cm and 20 cm, respectively. The investigation of soil horizon, tree census, and topographical surveying was also carried out for characterization of the study area. The results show that the concentration profile of radiocaesium in the uppermost soil horizon is related to the distribution of depositional and erosional area in the forest, that is, the concentration profile trends to be higher in the depositional area than in the erosional area. Additionally, the decrease rate of the concentration from the ground surface to the depth direction is related to the soil composition, such as organic, clay minerals and clastics of parent rock. Therefore, not only soil type but also geomorphological aspects should be taken into consideration in the elucidation of the dynamics of radiocaesium in the mountain forests of Fukushima.
Ishii, Yasuo; Sasaki, Yoshito; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Oyama, Takuya; Abe, Hironobu; Niizato, Tadafumi; Sato, Haruo
no journal, ,
As part of the project entitled "Long-Term Assessment of Transport of Radioactive Contaminant in the Environment of Fukushima" (F-TRACE project), JAEA has researched since November 2012 to predict the transport behavior of radioactive caesium, which now Cs-134 and Cs137 are the main radiological contribution, from contaminated mountain forests to estuary and coast through dam, pond, river etc. based on their investigated data survey data in the Fukushima prefecture. In this study, we report characterization and radio assay of the surface run-off substances obtained (or collected) at the forest observation plots in the Ogi district of Kawauchi-mura and the Yamakiya district of Kawamata-machi, and at the soil-saving dam in the Ogaki district of Namie-machi, Fukishima prefecture, Japan. The air dose rates measured at 1m in height were about 2-3  Sv/h at the forest observation plots in Ogi and Yamakiya, and about 10
Sv/h at the forest observation plots in Ogi and Yamakiya, and about 10  Sv/h at the soil-saving dam in Ogaki. Both Cs-134 and Cs-137 were detected from soil samples taken in these areas, and their concentrations were high particularly in the muddy substances (silts and clay). This tendency was similar to the sediment samples taken in dam and river areas in Fukushima.
Sv/h at the soil-saving dam in Ogaki. Both Cs-134 and Cs-137 were detected from soil samples taken in these areas, and their concentrations were high particularly in the muddy substances (silts and clay). This tendency was similar to the sediment samples taken in dam and river areas in Fukushima.
Watanabe, Takayoshi; Mitachi, Katsuaki; Abe, Hironobu; Niizato, Tadafumi
no journal, ,
Radionuclides such as radioactive cesium, now the main radiological contributor, were released in the environment by the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Japan Atomic Energy Agency initiated a project entitled "Long-Term Assessment of Transport of Radioactive Contaminant in the Environment of Fukushima" (F-TRACE project) in November 2012. To understand radioactive cesium transport in forest, we have conducted forest investigation at Ogi district, Kawauchi Village and Yamakiya district, Kawamata Town, Fukushima Prefecture since December 2012. As a part of the investigation, we carried out geophysical exploration of soil structure with ground penetrating radar (GPR) with 100 MHz and 500 MHz radio wave. In this presentation, we report correlation between imaging of soil structure obtained by GPR survey and depth profile of radioactive cesium in soil.
Niizato, Tadafumi; Ishii, Yasuo; Abe, Hironobu; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Sasaki, Yoshito
no journal, ,
Understanding the environmental dynamics of the radiocaesium (particularly Cs-134 and 137) released from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant provides the firm foundation for a remediation of the Fukushima environment because it is the main radionuclide to radiological dose within the contaminated area. One of the main sources of radiocaesium under the current situation is a mountain forest, where the decontamination work has not been carried out as yet. Therefore, transport process, flux and chemical form of the radiocaesium flowing from the mountain forest are crucial issues for an evaluation of a radiation exposure, taking into a dynamics behavior of radiocaesium from the highest contaminated mountain forests down through the river to eventual deposition in the sea. This paper discusses the predominant process of the radiocaesium transport in the mountainous region, Fukushima, Japan.