Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Asakura, Kazuki; Shimomura, Yusuke; Donomae, Yasushi; Abe, Kazuyuki; Kitamura, Ryoichi; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Takamatsu, Misao; Sakamoto, Naoki; Isozaki, Ryosuke; Onishi, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-020, 42 Pages, 2021/10
The disposal of radioactive waste from the research facility need to calculate from the radioactivity concentration that based on variously nuclear fuels and materials. In Japan Atomic Energy Agency Oarai Research and Development Institute, the study on considering disposal is being advanced among the facilities which generate radioactive waste as well as the facilities which process radioactive waste. This report summarizes a study result in FY2020 about the evaluation method to determine the radioactivity concentration in radioactive waste on Oarai Research and Development Institute.
Ikushima, Kazuki*; Shibahara, Masakazu*; Kawajiri, Yoshitaka*; Okimi, Yui*; Uchida, Tomoki*; Akita, Koichi*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Morooka, Satoshi
Nihon Senpaku Kaiyo Kogakkai Rombunshu, (30), p.123 - 130, 2019/12
In this research, the contour method was applied to measure the residual stress distribution of a bead-on-plate specimen. The measured residual stress distribution was compared with those measured by neutron diffraction method and calculated by thermal elastic plastic finite element analysis. As a result, it was found that the residual stress distribution obtained by these three methods are in good agreement. In addition, the equilibrium of reaction force on cut plane was considered in the contour method to measure residual stresses in asymmetric cutting which is assumed in the measurement of real structures. The proposed method was applied to the measurement of the residual stress in the multi-pass welded joint. The measured results indicated that the proposed method can measure the residual stress distribution in multi-pass welded joint in asymmetric test specimen.
Xu, P. G.; Harjo, S.; Ojima, Mayumi*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Ito, Takayoshi*; Gong, W.; Vogel, S. C.*; Inoue, Junya*; Tomota, Yo*; Aizawa, Kazuya; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 51(3), p.746 - 760, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:90.58(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Ikushima, Kazuki*; Shibahara, Masakazu*; Nishikawa, Satoru*; Furukawa, Takashi*; Akita, Koichi; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Morooka, Satoshi
E-Journal of Advanced Maintenance (Internet), 9(3), p.NT87_1 - NT87_5, 2017/11
Akita, Koichi; Shibahara, Masakazu*; Ikushima, Kazuki*; Nishikawa, Satoru*; Furukawa, Takashi*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Vladimir, L.*
Yosetsu Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 35(2), p.112s - 116s, 2017/06
Ikushima, Kazuki*; Kitani, Yuji*; Shibahara, Masakazu*; Nishikawa, Satoru*; Furukawa, Takashi*; Akita, Koichi; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Morooka, Satoshi
Yosetsu Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 35(2), p.75s - 79s, 2017/06
Ojima, Mayumi*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Inoue, Junya*; Shobu, Takahisa; Xu, P. G.; Akita, Koichi; Nambu, Shoichi*; Koseki, Toshihiko*
Zairyo, 66(6), p.420 - 426, 2017/06
Ikushima, Kazuki*; Shibahara, Masakazu*; Akita, Koichi; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Morooka, Satoshi; Nishikawa, Satoru*; Furukawa, Takashi*
Welding in the World, 61(3), p.517 - 527, 2017/05
In this study, first, an analysis method to predict the behaviour of residual stress distribution on shot peening process was proposed. In the proposed method, the load distribution on the collision of shots was modelled, and it was integrated with the dynamic analysis method based on the idealized explicit FEM (IEFEM). The accuracy of the proposed analysis system was confirmed by comparing the stress distribution on the collision of a single shot with the results analyzed by ABAQUS. The thermal elastic plastic analysis method using IEFEM was applied to the analysis of residual stress distribution of multi-pass welded pipe joint. The calculated residual stress distribution was compared with the measured residual stress distribution using X-ray diffraction (XRD). As a result, it was shown that the both welding residual distribution agree well with each other. Considering the calculated welding residual stress distribution, the modification of stress distribution due to shot peening was predicted by the proposed analysis system. As a result, the similar stress distribution with measurement by XRD was obtained in case that a large number of collisions are considered.
 -phase in
-phase in  -based titanium aluminide intermetallics
-based titanium aluminide intermetallicsLiss, K.-D.*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Dippenaar, R. J.*; Higo, Yuji*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Reid, M.*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Shobu, Takahisa; Akita, Koichi
Metals, 6(7), p.165_1 - 165_22, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:68.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Titanium aluminides find application in modern light-weight, high-temperature turbines, such as aircraft engines, but suffer from poor plasticity during manufacturing and processing. Huge forging presses enable materials processing in the 10 GPa range and hence, it is necessary to investigate the phase-diagrams of candidate materials under these extreme conditions. Here we report on an in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction study in a large-volume-press of a modern (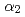 +
+  ) two-phase material, Ti-45Al-7.5Nb-0.25C, under pressures up to 9.6 GPa and temperatures up to 1686 K. At room temperature, the volume response to pressure is accommodated by the transformation
) two-phase material, Ti-45Al-7.5Nb-0.25C, under pressures up to 9.6 GPa and temperatures up to 1686 K. At room temperature, the volume response to pressure is accommodated by the transformation 

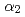 rather than volumetric strain, expressed by apparently high bulk moduli of both constituent phases. Crystallographic aspects, specifically lattice strain and atomic order are discussed in detail. It is interesting to note that this transformation takes place despite an increase in atomic volume, which is due to the high ordering energy of
rather than volumetric strain, expressed by apparently high bulk moduli of both constituent phases. Crystallographic aspects, specifically lattice strain and atomic order are discussed in detail. It is interesting to note that this transformation takes place despite an increase in atomic volume, which is due to the high ordering energy of  . Upon heating under high pressure, both the eutectoid and
. Upon heating under high pressure, both the eutectoid and  -solvus transition temperatures are elevated, and a third, cubic
-solvus transition temperatures are elevated, and a third, cubic  -phase is stabilized above 1350 K. Earlier research has shown that this
-phase is stabilized above 1350 K. Earlier research has shown that this  -phase is very ductile during plastic deformation, essential in near-conventional forging processes. Here, we were able to identify an ideal processing window for near-conventional forging, while the presence of the detrimental
-phase is very ductile during plastic deformation, essential in near-conventional forging processes. Here, we were able to identify an ideal processing window for near-conventional forging, while the presence of the detrimental  -phase is not present under operating conditions. Novel processing routes can be defined from these findings.
-phase is not present under operating conditions. Novel processing routes can be defined from these findings.
Suzuki, Ryosuke*; Matsubara, Masaaki*; Yanagihara, Seiji*; Morijiri, Mitsugu*; Omori, Atsushi*; Wakai, Takashi
Procedia Materials Science, 12, p.24 - 29, 2016/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.36(Engineering, Mechanical)In this study, the plastic collapse strength of asymmetry multiple circumferential notched stainless steel pipes subjected to combined axial tension and bending is investigated experimentally and is compared with the theoretical plastic collapse strength. In addition, the potential is discussed for the simplification of structural integrity evaluation of multiple cracked piping. The integrity of the asymmetry multiple circumferential notched stainless steel pipes subjected to combined axial tension and bending can be evaluated conservatively using the theoretical plastic collapse strength for the pipe with multiple notches calculated based on the elastic-perfectly plastic model.
Xu, P. G.; Harjo, S.; Ito, Takayoshi*; Morii, Yukio*; Gong, W.; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Akita, Koichi; Suzuki, Tetsuya*; Tomota, Yo; Lutterotti, L.*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.031022_1 - 031022_6, 2015/09
Iwata, Keiji*; Imafuku, Muneyuki*; Suzuki, Kanki*; Shobu, Takahisa; Orihara, Hideto*; Sakai, Yusuke*; Akita, Koichi; Oya, Shinichi*; Ishiyama, Kazushi*
Journal of Applied Physics, 117(17), p.17A910_1 - 17A910_4, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:27.03(Physics, Applied)Internal stress distribution for generating closure domains occurring in laser-irradiated Fe-3%Si(110) steels was investigated using high-energy X-ray analysis and domain theory based on the variational principle. The measured triaxial stresses inside the specimen were compressive and the stress in the rolling direction became more dominant than stresses in the other directions. The calculations based on the variational principle of magnetic energy for closure domains showed that the measured triaxial stresses made the closure domains more stable than the basic domain without closure domains. The experimental and calculation results reveal that the laser-introduced internal stresses result in the occurrence of the closure domains.
Akita, Koichi; Hayashi, Kengo*; Takeda, Kazuya*; Sano, Yuji*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Moriai, Atsushi; Oya, Shinichi*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 1(4), p.SMM0029_1 - SMM0029_8, 2014/08
Compressive residual stresses induced by peening techniques improve the strength properties of steels, such as fatigue and stress corrosion cracking. However, the compressive residual stress might be reduced owing to thermal and mechanical loading in-service. In this study, the behavior of surface and internal residual stresses of a laser-peened ferritic steel under quasi-static tensile loading was investigated by X-ray and neutron diffraction. The complementary use of these diffraction techniques provided decisive experimental evidence for elucidating the relaxation process. The critical applied stress of peened samples subjected to a tensile loading can be estimated from the von Misses yield criterion with the maximum tensile residual stress inside the sample.
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Harjo, S.; Abe, Jun*; Akita, Koichi
Materials Science Forum, 777, p.105 - 111, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:53.76(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Effects of beam divergence on pseudo-strains observed in time-of-flight (TOF) neutron diffraction, that overlapped with the neutron attenuation effect and the surface-effect were investigated. The through-surface strain scanning on an annealed steel plate was performed in different instrument resolutions by controlling the incident beam divergence. Typical pseudo-strain distributions were observed, but they showed different trend according to the beam divergence. Furthermore, it was demonstrated that the pseudo-strains induced in the strain scanning of coarse grain materials can be suppressed by controlling the incident beam divergence. Therefore, the incident beam divergence must be carefully considered to reduce pseudo-strains in time-of-flight neutron diffractometry.
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Katsuyama, Jinya; Akita, Koichi
Materials Science Forum, 772, p.33 - 38, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:53.76(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)When measuring residual strain distributions of thick structural components such as thick butt-welds using neutron diffraction, it is required to make a gauge volume larger as well as to shorten neutron path length in a material to obtain sufficient diffraction intensity. In this study, neutron attenuation effect on the strain measurement with a large gauge volume was discussed on the normal strain measurement of a thick butt-weld. Influences of neutron attenuation like an apparent strain change were observed, and it was more noticeable when the gauge volume becomes larger. Therefore, the neutron attenuation effect should be considered in the strain measurement with a large gauge volume, and the neutron absorption corrections certainly play an important role for improvement of reliabilities of strain measurement using neutron diffraction with a large gauge volume.
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Harjo, S.; Abe, Jun; Xu, P. G.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Akita, Koichi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 715, p.28 - 38, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:64.2(Instruments & Instrumentation)Effects of gauge volume on pseudo-strains induced in neutron strain measurements using the time-of-flight neutron diffraction due to influences of the neutron attenuation, the surface-effect and a strain distribution were discussed on strain measurements in an annealed and a bent ferritic steel bars. An average strain in a gauge volume was weighted towards a neutron-weighted center of gravity (ncog) position, and the weighted average strain was apparently changed following change in the ncog position with an increase of the gauge volume. On the other hand, typical pseudo-strains due to the surface-effect were appeared in near-surface strain measurements when a gauge volume is incompletely filled in a sample. Furthermore, a pseudo-strain due to change in the ncog position was observed even when perfectly immersing the gauge volume in a sample, and it was increased with an increase of the gauge volume. These pseudo-strains measured were well simulated by taking into account an incident neutron beam divergence additionally in the conventional model. Therefore, it was clarified that the incident neutron beam divergence must be an important parameter to make a modeling of pseudo-strains induced in the strain measurement using the TOF engineering diffractometer.
Xu, P. G.; Akita, Koichi; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Moriai, Atsushi
Keikinzoku Gakkai Heisei-24-Nendo Dai-2-kai Kako To Netsu Shori Ni Yoru Yusen Hoi Seigyo Kenkyu Bukai Kokai Koenkai Shiryo, p.19 - 20, 2012/10
Xu, P. G.; Akita, Koichi; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Moriai, Atsushi; Suzuki, Tetsuya*; Yukutake, Eitaro*
Nihon Zairyo Gakkai Dai-46-Kai X Sen Zairyo Kyodo Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.24 - 27, 2012/07
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Akita, Koichi
Zairyo, 61(7), p.604 - 611, 2012/07
It is required to evaluate a strain-free reference, 
 , to perform accurate stress measurement using neutron diffraction. In this study, accuracy of neutron stress measurement was quantitatively discussed from
, to perform accurate stress measurement using neutron diffraction. In this study, accuracy of neutron stress measurement was quantitatively discussed from 
 evaluations on a dissimilar metal butt-weld between a type 304 austenitic stainless steel and an A533B low alloy ferritic steel. In the lattice constant evaluation using a standard specimen and a sliced specimen taken from the dissimilar metal butt-weld, average lattice constant derived from multiple
evaluations on a dissimilar metal butt-weld between a type 304 austenitic stainless steel and an A533B low alloy ferritic steel. In the lattice constant evaluation using a standard specimen and a sliced specimen taken from the dissimilar metal butt-weld, average lattice constant derived from multiple 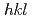 reflections was evaluated as the stress-free reference with cancelling out an intergranular strain, and ferrite-211 and austenite-311 reflections were judged as a suitable reflection for neutron strain measurement to reduce intergranular strain effects. Residual stress distribution in the sliced specimen evaluated using
reflections was evaluated as the stress-free reference with cancelling out an intergranular strain, and ferrite-211 and austenite-311 reflections were judged as a suitable reflection for neutron strain measurement to reduce intergranular strain effects. Residual stress distribution in the sliced specimen evaluated using 
 measured here exhibited higher accuracy than that measured using strain gauges. As a conclusion of this study, it was confirmed that accurate
measured here exhibited higher accuracy than that measured using strain gauges. As a conclusion of this study, it was confirmed that accurate 
 evaluation, optimization of the measurement condition, and multiple evaluations on the results play an important role to improve accuracy of the residual stress measurement using neutron diffraction.
evaluation, optimization of the measurement condition, and multiple evaluations on the results play an important role to improve accuracy of the residual stress measurement using neutron diffraction.
Kisohara, Naoyuki; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Akita, Koichi; Kasahara, Naoto*
Proceedings of 2012 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '12) (CD-ROM), p.621 - 630, 2012/06