Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
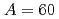
Tamii, Atsushi*; Pellegri, L.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 59(9), p.208_1 - 208_21, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.66(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Nemoto, Miho*; Ebine, Noriya; Okamoto, Akiko; Hosaka, Yasuhisa*; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Terada, Hiroaki; Hayakawa, Tsuyoshi; Togawa, Orihiko
JAEA-Technology 2021-013, 41 Pages, 2021/08
When North Korea has carried out nuclear tests, Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) predicts atmospheric dispersion of radionuclides by using the WSPEEDI-II upon requests from Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) and submits the predicted results to NRA in cooperation with Nuclear Science and Engineering Center (NSEC). This is a part of the activity of NEAT supporting the Japanese Government in emergency responses. The WSPEEDI-II automatic calculation system specialized for responses to nuclear tests by North Korea was developed by NSEC and was used for responses to three nuclear tests from February 2013 to September 2017. This report describes the transfer and installation of the calculation system to NEAT, and the subsequent maintenance and operation. Future issues for responses to nuclear tests are also described in this report.
 Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta intermetallic compounds induced by energetic ion beam irradiation
Ta intermetallic compounds induced by energetic ion beam irradiationKojima, Hiroshi*; Yoshizaki, Hiroaki*; Kaneno, Yasuyuki*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Hori, Fuminobu*; Saito, Yuichi; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 372, p.72 - 77, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:64.39(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ni Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta intermetallic compounds, which show the complicated lattice structures were irradiated with 16 MeV Au
Ta intermetallic compounds, which show the complicated lattice structures were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions at room temperature. The X-ray diffraction measurement revealed that the lattice structure of these intermetallic compounds changed from the ordered structures to the amorphous state by the ion irradiation. The irradiation-induced amorphization caused the increase in Vickers hardness. The result was compared with our previous results for Ni
ions at room temperature. The X-ray diffraction measurement revealed that the lattice structure of these intermetallic compounds changed from the ordered structures to the amorphous state by the ion irradiation. The irradiation-induced amorphization caused the increase in Vickers hardness. The result was compared with our previous results for Ni Al and Ni
Al and Ni V, and was discussed in terms of the intrinsic lattice structures of the samples.
V, and was discussed in terms of the intrinsic lattice structures of the samples.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Ochi, Eiji*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
Denki Kagaku Oyobi Kogyo Butsuri Kagaku, 81(7), p.543 - 546, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:17.86(Electrochemistry)The molten state of simulated high-level waste glass and the behavior of ruthenium element in the melt were investigated by using synchrotron radiation based X-ray imaging technique. Melting, generating and moving of bubbles, condensation and sedimentation of ruthenium element were observed dynamically in continuous 12-bit gray-scale images from the CCD camera. X-ray intensity was obtained easily by digitizing gray-scale values in the image. The existence of ruthenium element is emphasized as a black color in the CCD image at X-ray energy higher than the Ru K-absorption edge. Position sensitive imaging X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurement was also performed to clarify the chemical state of ruthenium element in the melt.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Ochi, Eiji*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
Proceedings of 4th Asian Conference on Molten Salt Chemistry and Technology & 44th Symposium on Molten Salt Chemistry, Japan, p.47 - 52, 2012/09
The molten state of the simulated high-level waste glass and the behavior of ruthenium element in the melt were investigated by using synchrotron radiation based X-ray imaging technique. Melting, generating and moving of bubbles, condensation and sedimentation of ruthenium element were observed dynamically in continuous 12-bit gray-scale images from the CCD camera. The existence of ruthenium in the X-ray CCD image was emphasized over the energy of Ru K-absorption edge. X-ray intensity was obtained easily by digitalizing gray-scale values in the image. Position sensitive imaging X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurement was performed to clarify the chemical state of ruthenium element in the melt.
Kondo, Takeo*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Goriely, S.*; Daoutidis, I.*; Iwamoto, Chihiro*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Okamoto, Akiyuki*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Kamata, Masaki*; Ito, Osamu*; et al.
Physical Review C, 86(1), p.014316_1 - 014316_7, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:86.82(Physics, Nuclear)Using quasi-monochromatic laser-Compton scattering  rays, total photoneutron cross sections were measured for
rays, total photoneutron cross sections were measured for 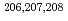 Pb near neutron threshold with a high-efficiency 4
Pb near neutron threshold with a high-efficiency 4 neutron detector. Partial
neutron detector. Partial  1 and
1 and  1 photoneutron cross sections along with total cross sections were determined for
1 photoneutron cross sections along with total cross sections were determined for 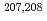 Pb at four energies near threshold by measuring anisotropies in photoneutron emission with linearly-polarized
Pb at four energies near threshold by measuring anisotropies in photoneutron emission with linearly-polarized  rays. The
rays. The  1 strength dominates over the
1 strength dominates over the  1 strength in the neutron channel where
1 strength in the neutron channel where  1 photoneutron cross sections show extra strength of the pygmy dipole resonance in
1 photoneutron cross sections show extra strength of the pygmy dipole resonance in 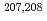 Pb near the neutron threshold corresponding to 0.32-0.42% of the Thomas-Reiche-Kuhn sum rule. Several
Pb near the neutron threshold corresponding to 0.32-0.42% of the Thomas-Reiche-Kuhn sum rule. Several 
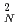 units of B(
units of B( 1)
1)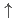 strength were observed in
strength were observed in 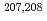 Pb just above neutron threshold, which correspond to an
Pb just above neutron threshold, which correspond to an  1 cross section less than 10% of the total photoneutron cross section.
1 cross section less than 10% of the total photoneutron cross section.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Ochi, Eiji*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 11(2), p.127 - 132, 2012/06
Distribution and the chemical state of Ru element in the simulated high-level waste glass were examined by using the synchrotron radiation based X-ray imaging technique. In this technique, a direct X-ray CCD camera is used in place of an ion chamber. Position sensitive X-ray absorption spectra were obtained by analyzing gray scale in images of the X-ray CCD camera. At first, we measured a test sample containing RuO and Ru metal powder. We successfully obtained information on the Ru distribution in the sample. In addition, the chemical state (oxide or metal ?) of each small Ru-rich spot was evaluated by the corresponding position sensitive XAFS spectrum. The imaging XAFS technique was applied to some simulated high-level waste glass samples. The Ru distribution of the glass sample and their chemical state were confirmed by image analyses. It can be seen that Ru element scattered in the glass sample exists as oxide RuO
and Ru metal powder. We successfully obtained information on the Ru distribution in the sample. In addition, the chemical state (oxide or metal ?) of each small Ru-rich spot was evaluated by the corresponding position sensitive XAFS spectrum. The imaging XAFS technique was applied to some simulated high-level waste glass samples. The Ru distribution of the glass sample and their chemical state were confirmed by image analyses. It can be seen that Ru element scattered in the glass sample exists as oxide RuO .
.
Kondo, Takeo*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Okamoto, Akiyuki*; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Shima, Tatsushi*; Horikawa, Ken*; Miyamoto, Shuji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 659(1), p.462 - 466, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:89.07(Instruments & Instrumentation)We measured pulse-height spectra of 16.7 MeV laser-Compton scattering photons with a 6" 5" NaI(Tl) detector for blank and three lead materials of 75.8, 50.9, and 25.9% transmissions at the NewSUBARU facility to investigate how the original Poisson distribution of the pulsed photons is modified after passing through thick-target materials. We present a well-prescribed method of determining the number of incident photons within 3.5% accuracy based on the response of the NaI(Tl) detector to the pulsed photon beams.
5" NaI(Tl) detector for blank and three lead materials of 75.8, 50.9, and 25.9% transmissions at the NewSUBARU facility to investigate how the original Poisson distribution of the pulsed photons is modified after passing through thick-target materials. We present a well-prescribed method of determining the number of incident photons within 3.5% accuracy based on the response of the NaI(Tl) detector to the pulsed photon beams.
 SF method
SF methodUtsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Goriely, S.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Kondo, Takeo*; Iwamoto, Chihiro*; Okamoto, Akiyuki*; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Goko, Shinji*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1377, p.255 - 259, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.05(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Kureta, Masatoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Kume, Etsuo; Someya, Satoshi*; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of 3rd International Workshop on Process Tomography (IWPT-3) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2009/04
Dynamic neutron tomography velocimetry has been developed in order to obtain the 3-D velocity distribution and flow profile data of liquid metal flow in a heated rod bundle for development of an advanced nuclear reactor. In this paper, data processing methods for the 3-D velocimetry is focused on. The data processing is started from the reading images recorded by the three high-speed video cameras, and is finished to the visualization of velocity of the tracers and the profiles. Basic experiments were carried out using the research reactor JRR-4 and the dynamic neutron tomography system. As the results, it was confirmed that the 3-D velocity distribution and flow profile could be visualized by the new data processing methods.
Kureta, Masatoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki*; Kume, Etsuo; Someya, Satoshi*; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 147, p.012087_1 - 012087_14, 2009/03
The aim of this development is to visualize and measure the velocity distribution in liquid metal flow using the neutron beam with the high-speed imaging technique, computer tomography (CT) technique and particle tracking velocimetry (PTV). Final research purpose is to obtain the velocity distribution and flow profile data of liquid metal flow in a heated rod bundle for development of the FBR core. In this paper, visualization and measurement method using the JRR-4, spring model PTV method for this technique and results of the fundamental PTV experiment were reported. The fundamental experiment was conducted. As the result, cadmium tracers buried in the aluminum column with the speed of 1.5 revolving per second could be visualized as the 3D movie under 125Hz and 250Hz sampling conditions, the profile of the tracer could be traced, and fundamental velocity distribution measurement method could be conformed.
Kureta, Masatoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Kume, Etsuo; Someya, Satoshi*; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of 6th International Symposium on Measurement Techniques for Multiphase Flows (ISMTMF 2008) (USB Flash Drive), 14 Pages, 2008/12
The aim of this development is to visualize and measure the velocity distribution in liquid metal flow using the neutron beam with the high-speed imaging technique, computer tomography (CT) technique and particle tracking velocimetry (PTV). Final research purpose is to obtain the velocity distribution and flow profile data of liquid metal flow in a heated rod bundle for development of the FBR core. In this paper, visualization and measurement method using the JRR-4, spring model PTV method for this technique and results of the fundamental PTV experiment were reported. The fundamental experiment was conducted. As the result, cadmium tracers buried in the aluminum column with the speed of 1.5 revolving per second could be visualized as the 3D movie under 125 Hz and 250 Hz sampling conditions, the profile of the tracer could be traced, and fundamental velocity distribution measurement method could be conformed.
 electrons in Ce
electrons in Ce In
In (
( =Rh, Ir)
=Rh, Ir)Fujimori, Shinichi; Okane, Tetsuo; Okamoto, Jun; Mamiya, Kazutoshi; Muramatsu, Yasuji; Fujimori, Atsushi*; Harima, Hisatomo*; Aoki, Dai*; Ikeda, Shugo*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 67(14), p.144507_1 - 144507_5, 2003/04
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:79.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have performed angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (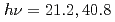 ~eV) and 3
~eV) and 3 -4
-4 resonant photoemission spectroscopy (
resonant photoemission spectroscopy (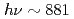 ~eV) studies on the layered cerium compounds Ce
~eV) studies on the layered cerium compounds Ce In
In (
( =Rh and Ir), which show competition between superconductivity and antiferromagnetism. The results suggest that the Ce~4
=Rh and Ir), which show competition between superconductivity and antiferromagnetism. The results suggest that the Ce~4 electrons in both compounds are nearly localized. We have found that although the Ce~4
electrons in both compounds are nearly localized. We have found that although the Ce~4 electrons in the superconducting CeIrIn
electrons in the superconducting CeIrIn are more delocalized than those in the antiferromagnetic CeRhIn
are more delocalized than those in the antiferromagnetic CeRhIn , their electronic structures are very similar to each other.
, their electronic structures are very similar to each other.
Sayano, Akio*; Kano, Fumihisa*; Saito, Norihisa*; Abe, Hiroaki*; Okamoto, Koji*; Takamasa, Tomoji*; Furuya, Masahiro*; Miyano, Masami*; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kureta, Masatoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Kume, Etsuo; Someya, Satoshi*; Okamoto, Koji*
no journal, ,
Development of the Dynamic Neutron Computer Tomography (DNCT) technique is started as the new 4D thermal-hydraulic measurement technique in order to provide the detailed database for thermal-hydraulic evaluation methods on liquid metal cooled FBR core. In this presentation, development of the DNCT system and fundamental tests carried out in the JRR-4 are reported. Basic principal of the DNCT, that is, six neutron radiography projection images are recorded with high speed at the same time was confirmed.
Oba, Yojiro; Okamoto, Hiroaki*; Sato, Tetsuya*; Nakamura, Tetsuya*; Osawa, Hitoshi*; Muro, Takayuki*; Shinohara, Takenao; Suzuki, Junichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Okamoto, Koji*; Someya, Satoshi*; Kureta, Masatoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Kume, Etsuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kureta, Masatoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Kume, Etsuo; Someya, Satoshi*; Okamoto, Koji*
no journal, ,
The paper proposes a new measurement technique named as dynamic neutron computer tomography (CT). The purpose of the development is to visualize and measure the three-dimensional velocity distribution in liquid metal flow based on high-speed neutron radiography and CT techniques. The dynamic neutron CT system generates six neutron beams and neutron radiography images at the same time. And the images are recorded by three set of high-speed video camera systems in the neutron irradiation room of the research reactor JRR-4. Consecutive instantaneous CT value 3D distributions were visualized using a fundamental rotating test section for the dynamic neutron CT test with the developed system.
Kureta, Masatoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Kume, Etsuo; Someya, Satoshi*; Okamoto, Koji*
no journal, ,
Development of the Dynamic Neutron Computer Tomography (DNCT) technique is conducted as the new 4D thermal-hydraulic measurement technique in order to provide the detailed database for thermal-hydraulic evaluation methods on liquid metal cooled FBR core. We studied the data analysis method to be realized a velocity measurement by the DNCT, and developed the velocity and locus measurement techniques by expanding the spring model particle trace velocimetry. In this presentation, velocity measurement technique installed in the DNCT analysis system and test results taken at the JRR-4 are reported.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Minato, Kazuo; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
Chemical state analysis of Ru element scattered in an imitative glass matrix was performed by using the Imaging XAFS technique. Information on distribution of Ru element in the matrix was obtained from contrast values of CCD images before and after the Ru K-absorption edge. It is confirmed that the feature of the distributed element can be examined by getting XAFS spectra from the contrast information. We can get two kinds of XAFS spectra corresponding to Ru metal and oxide separately in the Imaging XAFS analysis.