Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suyama, Kenya; Ueki, Taro; Gunji, Satoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Araki, Shohei; Fukuda, Kodai; Yamane, Yuichi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Kikuchi, Takeo; et al.
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/10
To remove and store safely the fuel debris generated by the severe accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011 is one of the most important and challenging topics for decommissioning of the damaged reactors in Fukushima. To validate the adopted method for the evaluation of criticality safety control of the fuel debris through comparison with the experimental data obtained by the criticality experiments, the Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) of Japan funds a research and development project which was entrusted to the Nuclear Safety Research Center (NSRC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) from 2014. In this project, JAEA has been conducting such activities as i) comprehensive computation of the criticality characteristics of the fuel debris and making database (criticality map of the fuel debris), ii) development of new continuous energy Monte Carlo code, iii) evaluation of criticality accident and iv) modification of the critical assembly STACY for the experiments for validation of criticality safety control methodology. After the last ICNC2019, the project has the substantial progress in the modification of STACY which will start officially operation from May 2024 and the development of the Monte Carlo Code "Solomon" suitable for the criticality calculation for materials having spatially random distribution complies with the power spectrum. We present the whole picture of this research and development project and status of each technical topics in the session.
Saito, Shigeru; Wan, T.*; Okubo, Nariaki; Kita, Satoshi*; Obayashi, Hironari; Sasa, Toshinobu
JAEA-Technology 2021-034, 94 Pages, 2022/03
Lead-bismuth eutectic alloy (LBE) is a major candidate for a spallation target material and core coolant of an accelerator driven system (ADS) which has been developed in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to transmute high-level radioactive wastes. A proton irradiation facility to build a material irradiation database for future ADS development is under considering in the J-PARC. To realize both the ADS and the above-mentioned facility, there are many issues on operational safety of LBE to be solved. Especially, corrosion data for the major materials such as T91 (Modified 9Cr-1Mo steel) and SS316L at the temperature range between 400 and 550  C under the conditions of flowing LBE with a controlled oxygen are not sufficient to design the ADS and the facility. JAEA developed a new large-scale corrosion test loop named "OLLOCHI (Oxygen-controlled LBE LOop for Corrosion tests in HIgh-temperature)" aiming to perform the compatibility tests between the LBE and the steels, as well as to develop the LBE operation technology. OLLOCHI has a function to automatically control the oxygen concentration in LBE. The maximum temperature at the regions of high-temperature and low-temperature of the OLLOCHI are 550
C under the conditions of flowing LBE with a controlled oxygen are not sufficient to design the ADS and the facility. JAEA developed a new large-scale corrosion test loop named "OLLOCHI (Oxygen-controlled LBE LOop for Corrosion tests in HIgh-temperature)" aiming to perform the compatibility tests between the LBE and the steels, as well as to develop the LBE operation technology. OLLOCHI has a function to automatically control the oxygen concentration in LBE. The maximum temperature at the regions of high-temperature and low-temperature of the OLLOCHI are 550  C and 450
C and 450  C respectively to cover the ADS designed condition. As a result of 2,000 hours operation, it was demonstrated that the OLLOCHI showed the designed performance. In this report, outline of the OLLOCHI, details of the components, results of characteristic tests, and the future experimental plan are described.
C respectively to cover the ADS designed condition. As a result of 2,000 hours operation, it was demonstrated that the OLLOCHI showed the designed performance. In this report, outline of the OLLOCHI, details of the components, results of characteristic tests, and the future experimental plan are described.
Saito, Shigeru; Wan, T.*; Okubo, Nariaki; Obayashi, Hironari; Watanabe, Nao; Ohdaira, Naoya*; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Yamaki, Kenichi*; Kita, Satoshi*; Yoshimoto, Hidemitsu*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011041_1 - 011041_6, 2021/03
An Accelerator Driven System (ADS) for waste transmutation investigated in JAEA employs lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) as a neutron production target material and coolant. The neutrons are to be produced via the spallation with 1.5 GeV proton beam injection. As materials irradiation data are important for ADS development, JAEA plans to construct an irradiation facility with LBE neutron production target in J-PARC. There are many technical issues on LBE for practical use. In JAEA, various R&Ds are being carried out. Concerning corrosion study, conditioning operation and functional tests of OLLOCHI started. Oxygen concentration control technology has also developing. In the large scale LBE loop experiment, the operation for steady state and transient experiments was performed by using IMMORTAL. In the area of instrument, development of ultrasonic flow meter and freeze seal valve are progressing as a key technology for the LBE loop system. Investigation of behavior of impurities in LBE, which is important for design of the irradiation facility, started. In this paper, the status of the LBE studies and experimental plan will be presented.
Sugawara, Takanori; Kita, Satoshi*; Yoshimoto, Hidemitsu*; Okubo, Nariaki
JAEA-Technology 2018-008, 26 Pages, 2018/09
The oxygen sensors to measure the oxygen concentration in liquid LBE (lead-bismuth eutectic) were fabricated and tested for future use in LBE-cooled ADS (accelerator-driven system) or LBE test loops. The following tests were performed; estimation of catalyst application range, freeze seal structure and estimation of gamma-ray irradiation effect. For the estimation of the catalyst application range, it was confirmed that the measurement accuracy became worse in low LBE temperature as the application range became small. For the freeze seal structure, we realized the structure to prevent the LBE leakage with 0.5 MPa pressure condition. For the estimation of gamma-ray irradiation effect, the ex-situ test was carried out and it was observed that there was little effect by 4 MGy gamma-ray irradiation.
Kondo, Masatoshi*; Okubo, Nariaki; Irisawa, Eriko; Komatsu, Atsushi; Ishikawa, Norito; Tanaka, Teruya*
Energy Procedia, 131, p.386 - 394, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:95.25(Energy & Fuels)The chemical behaviors of lead (Pb) based coolants in the air ingress accident of fast reactors were investigated by means of the thermodynamic considerations and the static oxidation experiments for Pb alloys at various chemical compositions. The results of the static oxidation tests for lead-bismuth (Pb-Bi) alloys indicated that Pb was depleted from the alloy due to the preferential formation of PbO in air at 773K. Pb-Bi oxide and Bi O
O were formed after the enrichment of Bi in the alloys due to the Pb depletion. The oxidation rates of the alloys were much larger than that of the steels, and became larger with higher Pb concentration in the alloys. The compatibility of Pb-Bi alloys with stainless steel was worse when the Pb concentration in the alloys became low, since the dissolution type corrosion was promoted by the Bi composition in the alloy. The Pb-Li alloys were oxidized as they formed Li
were formed after the enrichment of Bi in the alloys due to the Pb depletion. The oxidation rates of the alloys were much larger than that of the steels, and became larger with higher Pb concentration in the alloys. The compatibility of Pb-Bi alloys with stainless steel was worse when the Pb concentration in the alloys became low, since the dissolution type corrosion was promoted by the Bi composition in the alloy. The Pb-Li alloys were oxidized as they formed Li PbO
PbO and Li
and Li CO
CO . Then, Li was depleted from the alloy.
. Then, Li was depleted from the alloy.
Adhi, P. M.*; Okubo, Nariaki; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kondo, Masatoshi*; Takahashi, Minoru*
Energy Procedia, 131, p.420 - 427, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.03(Energy & Fuels)The ionic conductivity of solid electrolyte may insufficient, and the sensor output signal will deviate from the theoretical one in low temperature. The performance of oxygen sensor with Ag/air reference electrode (RE) and liquid Bi/Bi O
O RE was tested in low-temperature LBE at 300
RE was tested in low-temperature LBE at 300 450
450 C and the charge transfer reactions impedance at the electrode-electrolyte interface was analyzed by electrochemical impedance analysis (EIS). After steady state condition, both of the sensors performed well and can be used at 300
C and the charge transfer reactions impedance at the electrode-electrolyte interface was analyzed by electrochemical impedance analysis (EIS). After steady state condition, both of the sensors performed well and can be used at 300 450
450 C. Bi/Bi/Bi
C. Bi/Bi/Bi O
O RE has lower impedance than Ag/air RE. Therefore, the response time of the oxygen sensor with Bi/Bi/Bi
RE has lower impedance than Ag/air RE. Therefore, the response time of the oxygen sensor with Bi/Bi/Bi O
O RE is faster than the oxygen sensor with Ag/air RE in the low-temperature region.
RE is faster than the oxygen sensor with Ag/air RE in the low-temperature region.
Oshima, Takeshi; Yokoseki, Takashi; Murata, Koichi; Matsuda, Takuma; Mitomo, Satoshi; Abe, Hiroshi; Makino, Takahiro; Onoda, Shinobu; Hijikata, Yasuto*; Tanaka, Yuki*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 55(1S), p.01AD01_1 - 01AD01_4, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:54.92(Physics, Applied)Hijikata, Yasuto*; Mitomo, Satoshi*; Matsuda, Takuma*; Murata, Koichi*; Yokoseki, Takashi*; Makino, Takahiro; Takeyama, Akinori; Onoda, Shinobu; Okubo, Shuichi*; Tanaka, Yuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-11) (Internet), p.130 - 133, 2015/11
Yuyama, Takahiro; Ishibori, Ikuo; Kurashima, Satoshi; Yoshida, Kenichi; Ishizaka, Tomohisa; Chiba, Atsuya; Yamada, Keisuke; Yokoyama, Akihito; Usui, Aya; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; et al.
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.302 - 304, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Okubo, Ayako; Kimura, Yoshiki; Shinohara, Nobuo; Toda, Nobufumi; Funatake, Yoshio; Watahiki, Masaru; Sakurai, Satoshi; Kuno, Yusuke
JAEA-Technology 2015-001, 185 Pages, 2015/03
Nuclear forensics is the analysis of intercepted illicit nuclear or radioactive material and any associated material to provide evidence for nuclear attribution by determining origin, history, transit routes and purpose involving such material. Nuclear forensics activity includes sampling of the illicit material, analysis of the samples and evaluation of the attribution by comparing the analyzed data with database or numerical simulation. Because the nuclear forensics technologies specify the origin of the nuclear materials used illegal dealings or nuclear terrorism, it becomes possible to identify and indict offenders, hence to enhance deterrent effect against such terrorism. Worldwide network on nuclear forensics can contribute to strengthen global nuclear security regime. In this paper, the results of research and development of fundamental nuclear forensics technologies performed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency during the fiscal term of 2011-2013 were reported.
 Th and
Th and  Th distributions in mid-latitudes of the North Pacific Ocean; Effect of bottom scavenging
Th distributions in mid-latitudes of the North Pacific Ocean; Effect of bottom scavengingOkubo, Ayako; Obata, Hajime*; Gamo, Toshitaka*; Yamada, Masatoshi*
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 339-340, p.139 - 150, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:72.16(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Vertical distributions of total  Th and dissolved
Th and dissolved  Th were determined in the mid-latitudes of the North Pacific Ocean. Th in the Pacific Ocean have been described well using the reversible-scavenging model. However, we observed the depletion of total Th. The enhanced vertical eddy diffusion derived from the complex topography of the western Pacific Ocean might promote bottom scavenging and transport of the low Th in deep water to the upper layers.
Th were determined in the mid-latitudes of the North Pacific Ocean. Th in the Pacific Ocean have been described well using the reversible-scavenging model. However, we observed the depletion of total Th. The enhanced vertical eddy diffusion derived from the complex topography of the western Pacific Ocean might promote bottom scavenging and transport of the low Th in deep water to the upper layers.
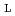 -lactic acid) using electron beam nanoimprint lithography
-lactic acid) using electron beam nanoimprint lithographyOkubo, Satoshi*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Kobayashi, Akinobu*; Oyama, Tomoko*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Oshima, Akihiro*; Tagawa, Seiichi*; Washio, Masakazu*
Applied Physics Express, 5(2), p.027303_1 - 027303_3, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:18.19(Physics, Applied)Electron beam nanoimprint lithography was proposed for fabricating the micro-/nanostructures of cross-linked poly(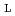 -lactic acid) (RX-PLLA). PLLA with triallyl isocyanurate (TAIC) solutions were dropped on the Si-molds fabricated by the conventional EB lithography technique. PLLA/TAIC on Si-molds were imprinted and cross-linked with doses from 10 to 500 kGy at room temperature under vacuum. The micro-/nanostructures of RX-PLLA were successfully obtained with high accuracy. Hence, it was found that the imprinted structures of RX-PLLA (100 kGy irradiation) show low line edge roughness and high thermal durability at 120
-lactic acid) (RX-PLLA). PLLA with triallyl isocyanurate (TAIC) solutions were dropped on the Si-molds fabricated by the conventional EB lithography technique. PLLA/TAIC on Si-molds were imprinted and cross-linked with doses from 10 to 500 kGy at room temperature under vacuum. The micro-/nanostructures of RX-PLLA were successfully obtained with high accuracy. Hence, it was found that the imprinted structures of RX-PLLA (100 kGy irradiation) show low line edge roughness and high thermal durability at 120  C.
C.
Nogiwa, Kimihiro; Nishimura, Akihiko; Yokoyama, Atsushi; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji; Inoue, Masaki; Okubo, Tadakatsu*; Hono, Kazuhiro*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417(1-3), p.201 - 204, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:53.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Du se 9Cr-ODS (oxide dispersion-strengthened) steel consisting of residual- ferrite and
ferrite and  prime martensite has excellent high-temperature strength. This study describes the microstructure of dual-phase 9Cr-ODS steels characterized by atom-probe tomography in order to compare oxide-particle dispersion states in each phase. This revealed that nano-size oxide particles were of the same chemical composition and that their mean size was about 3 nm in each phase. On the other hand, the number density in the residual-
prime martensite has excellent high-temperature strength. This study describes the microstructure of dual-phase 9Cr-ODS steels characterized by atom-probe tomography in order to compare oxide-particle dispersion states in each phase. This revealed that nano-size oxide particles were of the same chemical composition and that their mean size was about 3 nm in each phase. On the other hand, the number density in the residual- phase was about four times higher than that of the
phase was about four times higher than that of the  prime phase. These results indicate that the dense distribution of the oxide particles in the residual-
prime phase. These results indicate that the dense distribution of the oxide particles in the residual- phase contribute to the excellent high-temperature strength of 9Cr-ODS steel.
phase contribute to the excellent high-temperature strength of 9Cr-ODS steel.
Yamada, Keisuke; Nara, Takayuki; Ishibori, Ikuo; Kurashima, Satoshi; Yoshida, Kenichi; Yuyama, Takahiro; Ishizaka, Tomohisa; Agematsu, Takashi; Uno, Sadanori; Chiba, Atsuya; et al.
Proceedings of 8th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), 3 Pages, 2011/08
no abstracts in English
Okubo, Satoshi*; Takahashi, Tomohiro*; Takasawa, Yuya*; Gowa, Tomoko*; Sasaki, Takashi*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Tamada, Masao; Oshima, Akihiro*; Tagawa, Seiichi*; Washio, Masakazu*
Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology, 23(3), p.393 - 397, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:13.82(Polymer Science)Microfabrication of biodegradable polymers such as poly(butylene succinate-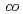 -adipate) (PBSA) and poly(
-adipate) (PBSA) and poly( -caprolactone) (PCL) were demonstrated using focused ion beam (FIB) with maskless direct etching. As the result, the micro structures of PBSA and PCL were obtained. The etching depth of both PBSA and PCL were increased with increasing FIB fluence, and the etching rates were estimated to be about 1.3
-caprolactone) (PCL) were demonstrated using focused ion beam (FIB) with maskless direct etching. As the result, the micro structures of PBSA and PCL were obtained. The etching depth of both PBSA and PCL were increased with increasing FIB fluence, and the etching rates were estimated to be about 1.3  10
10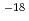
 m/(ions cm
m/(ions cm ) and 1.2
) and 1.2  10
10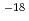
 m/(ions cm
m/(ions cm ), respectively. Moreover, very thin films of PBSA and PCL were made by spin-coating method. The thicknesses of the spin-coated samples were about 200 nm, and the surface roughness was less than 10 nm (RMS). The fine structures such as micro-gear of PBSA and PCL were obtained without solid debris. The line width of the fabricated structure was about 250 nm.
), respectively. Moreover, very thin films of PBSA and PCL were made by spin-coating method. The thicknesses of the spin-coated samples were about 200 nm, and the surface roughness was less than 10 nm (RMS). The fine structures such as micro-gear of PBSA and PCL were obtained without solid debris. The line width of the fabricated structure was about 250 nm.
Yoshida, Kenichi; Nara, Takayuki; Ishibori, Ikuo; Kurashima, Satoshi; Yuyama, Takahiro; Ishizaka, Tomohisa; Agematsu, Takashi; Uno, Sadanori; Chiba, Atsuya; Yamada, Keisuke; et al.
Proceedings of 7th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (DVD-ROM), p.23 - 26, 2010/08
no abstracts in English
Okano, Yasushi; Kobayashi, Noboru*; Ogawa, Takashi; Oki, Shigeo; Naganuma, Masayuki; Okubo, Tsutomu; Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Ogata, Takanari*; Ueda, Nobuyuki*; Nishimura, Satoshi*
JAEA-Research 2009-025, 105 Pages, 2009/10
A metal fuel core has specific features on high heavy metal density, hard neutron spectrum, and efficient neutron utilization. Enlarged applicable design envelops would improve core performances and features: higher breeding ratio, compacted reactor core, and, smaller amount of Pu-fissile inventory. A joint study on "Reactor Core and Fuel Design of Metal Fuel Core of Sodium Cooled Fast Reactor" by Japan Atomic Energy Agency and Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry has been conducted during Japanese fiscal years of 2007 and 2008. This report shows the results on (1) the study on applicable design ranges of metal fuel specifications, (2) the study on conceptual core designs for high breeding ratio, and (3) the safety study on metal fuel core designed in the Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development (FaCT) Project.
Saito, Yuichi; Yokota, Wataru; Nara, Takayuki; Agematsu, Takashi; Okumura, Susumu; Uno, Sadanori; Ishibori, Ikuo; Kurashima, Satoshi; Yoshida, Kenichi; Yuyama, Takahiro; et al.
Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-8), p.95 - 98, 2008/12
Yokota, Wataru; Nara, Takayuki; Ishibori, Ikuo; Kurashima, Satoshi; Yoshida, Kenichi; Yuyama, Takahiro; Ishizaka, Tomohisa; Agematsu, Takashi; Uno, Sadanori; Chiba, Atsuya; et al.
Proceedings of 5th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 33rd Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan (CD-ROM), p.22 - 24, 2008/08
no abstracts in English
Iwamura, Takamichi; Okubo, Tsutomu; Akie, Hiroshi; Kugo, Teruhiko; Yonomoto, Taisuke; Kureta, Masatoshi; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Araya, Fumimasa; Okajima, Shigeaki; et al.
JAERI-Research 2004-008, 383 Pages, 2004/06
The present report contains the achievement of "Research and Development on Reduced-Moderation Light Water Reactor with Passive Safety Features", which was performed by Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), Hitachi Ltd., Japan Atomic Power Company and Tokyo Institute of Technology in FY2000-2002 as the innovative and viable nuclear energy technology (IVNET) development project operated by the Institute of Applied Energy (IAE). In the present project, the reduced-moderation water reactor (RMWR) has been developed to ensure sustainable energy supply and to solve the recent problems of nuclear power and nuclear fuel cycle, such as economical competitiveness, effective use of plutonium and reduction of spent fuel storage. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as high burnup, long operation cycle, multiple recycling of plutonium (Pu) and effective utilization of uranium resources based on accumulated LWR technologies.