Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Osawa, Naoki*; Kim, S.-Y.*; Kubota, Masahiko*; Wu, H.*; Watanabe, So; Ito, Tatsuya; Nagaishi, Ryuji
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 56(3), p.812 - 818, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0Yokoyama, Sumi*; Tsujimura, Norio; Hashimoto, Makoto; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Sekiguchi, Hiroshi*; Koguchi, Yasuhiro*; Ono, Koji*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 47(1), p.1 - 7, 2022/03
Background: In Japan, new regulations that revise the dose limit for the lens of the eye (the lens), operational quantities, and measurement positions for the lens dose were enforced in April 2021. Based on the international safety standards, national guidelines, the results of the Radiation Safety Research Promotion Fund of the Nuclear Regulatory Authority, and other studies, the Working Group of Radiation Protection Standardization Committee, the Japan Health Physics Society (JHPS) developed a guideline for radiation dose monitoring for the lens. Materials and Methods: The Working Group of the JHPS discussed the criteria of non-uniform exposure and the management criteria set to not exceed the dose limit for the lens. Results and Discussion: In July 2020, the JHPS guideline was published. The guideline consists of three parts: main text, explanations, and 26 questions. In the questions, the corresponding answers were prepared, and specific examples were provided to enable similar cases to be addressed. Conclusion: With the development of guideline on radiation dose monitoring of the lens, radiation managers and workers will be able to smoothly comply with revised regulations and optimise radiation protection.
Ito, Tatsuya; Osugi, Haruka*; Osawa, Naoki*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; Kim, S.-Y.*; Nagaishi, Ryuji
Analytical Sciences, 38(1), p.91 - 97, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.37(Chemistry, Analytical)A novel ionic liquid (IL) functionalized with thiodiglycol amic acid containing a soft S donor was synthesized for the effective and efficient extraction of platinum group metals (Ru, Rh, and Pd) from aqueous nitric acid solutions, such as high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW). The IL allowed a rapid extraction of Pd(II) with an extraction ratio of approximately 100%. The extractions of Ru(III) and Rh(III) by the IL were slower than that of Pd(II), but the rates were accelerated by temperature elevation. The extractions of Ru(III) and Rh(III) at 50 C reached equilibrium within 4 and 8 h, respectively, with the extraction ratios of over 90% without assisting agents or other methods for the extraction system. Furthermore, the IL could extract more than 90% of Ru(III), Rh(III), and Pd(II) from the simulated HLLW within 2 h at 50
C reached equilibrium within 4 and 8 h, respectively, with the extraction ratios of over 90% without assisting agents or other methods for the extraction system. Furthermore, the IL could extract more than 90% of Ru(III), Rh(III), and Pd(II) from the simulated HLLW within 2 h at 50 C.
C.
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Iwai, Satoshi*; Tsujimura, Norio; Hashimoto, Makoto; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Sekiguchi, Hiroshi*; Koguchi, Yasuhiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 15th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-15) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/00
Asakura, Kazuki; Shimomura, Yusuke; Donomae, Yasushi; Abe, Kazuyuki; Kitamura, Ryoichi; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Takamatsu, Misao; Sakamoto, Naoki; Isozaki, Ryosuke; Onishi, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-020, 42 Pages, 2021/10
The disposal of radioactive waste from the research facility need to calculate from the radioactivity concentration that based on variously nuclear fuels and materials. In Japan Atomic Energy Agency Oarai Research and Development Institute, the study on considering disposal is being advanced among the facilities which generate radioactive waste as well as the facilities which process radioactive waste. This report summarizes a study result in FY2020 about the evaluation method to determine the radioactivity concentration in radioactive waste on Oarai Research and Development Institute.
Nakayama, Masashi; Saiga, Atsushi; Kimura, Shun; Mochizuki, Akihito; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ono, Hirokazu; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Takeda, Masaki; Hayano, Akira; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-013, 276 Pages, 2020/03
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. The investigations will be conducted in three phases, namely "Phase 1: Surface based investigations", "Phase 2: Construction phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities) and "Phase 3: Operation phase" (research in the underground facilities). According to the research plan described in the 3rd Mid- and Long- term Plan of JAEA, "Near-field performance study", "Demonstration of repository design option", and "Verification of crustal-movement buffering capacity of sedimentary rocks" are important issues of the Horonobe URL Project, and schedule of future research and backfill plans of the project will be decided by the end of 2019 Fiscal Year. The present report summarizes the research and development activities of these 3 important issues carried out during 3rd Medium to Long-term Research Phase.
Onoue, Tetsuji*; Sato, Honami*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Noguchi, Takaaki*; Hidaka, Yoshihiro*; Shirai, Naoki*; Ebihara, Mitsuru*; Osawa, Takahito; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Toh, Yosuke; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(47), p.19134 - 19139, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:72.55(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The 34 million year (My) interval of the Late Triassic is marked by the formation of several large impact structures on Earth. As with the Chicxulub impact event at the Cretaceous/Paleogene boudary, the Late Triassic impact events have been considered a factor in biotic extinction events in the Late Triassic (e.g., the Triassic/Jurassic boundary). However, the causal link between these impact events and a mass extinction event in the Late Triassic remains controversial because of a lack of stratigraphic records of their ejecta deposits. Here we report evidence for an impact event (platinum group elements anomaly, nickel-rich magnetite and microspherules) deposited within a Paleo-Pacific basin in the middle Norian (Upper Triassic) deep-sea sediment in Japan. This includes anomalously high abundances of iridium, up to 41.5 parts per billion (ppb), in the ejecta deposit, which suggests that the iridium anomaly may be found on a global scale. The middle Norian age of the ejecta deposit suggests that the impact event that produced the 100-km-wide Manicouagan crater in Canada8 is most likely related to its deposition. Our analysis of siliceous microfossils shows no evidence of a mass extinction event across the impact event horizon, and no contemporaneous faunal turnover is seen in other marine fossils. However, such an event has been reported among terrestrial tetrapods and floras in North America. We therefore hypothesize that the Manicouagan impact caused the catastrophic collapse of terrestrial ecosystems near the impact site, but not within the marine realm.
Shibata, Masahiro; Sawada, Atsushi; Tachi, Yukio; Makino, Hitoshi; Hayano, Akira; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Taniguchi, Naoki; Oda, Chie; Kitamura, Akira; Osawa, Hideaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2012-032, 298 Pages, 2012/09
JAEA and NUMO have conducted a collaborative research work which is designed to enhance the methodology of repository design and performance assessment in preliminary investigation phase. The topics and the conducted research are follows; (1) Study on selection of host rock: in terms of hydraulic properties, items for assessing rock property, and assessment methodology of groundwater travel time has been organized with interaction from site investigation. (2) Study on development of scenario: the existing approach has been embodied, in addition, the phenomenological understanding regarding dissolution of and nuclide release from vitrified waste, corrosion of the overpack, long-term performance of the buffer are summarized. (3) Study on setting nuclide migration parameters: the approach for parameter setting has been improved for sorption and diffusion coefficient of buffer/rock, and applied and tested for parameter setting of key radionuclides. (4) Study on ensuring quality of knowledge: framework for ensuring quality of knowledge has been studied and examined aimed at the likely disposal facility condition.
Takasaki, Koji; Sagawa, Naoki; Kurosawa, Shigeyuki; Mizuniwa, Harumi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(6), p.911 - 918, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:66.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)An autoradiographical method using an imaging plate (IP) was developed to analyze the plutonium contamination in the plutonium handling facility and was applied to the monitoring of the workplace in a practical uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel fabrication facility. A good relationship between the photo stimulated luminescence (PSL) intensities of IP and radioactivities measured by a radiation counter was obtained by the least-square fitting, taking the fading effect into consideration. The  -radioactivities of plutonium contamination were derived from the PSL image in this IP method, and their relative errors were evaluated from exposure time.
-radioactivities of plutonium contamination were derived from the PSL image in this IP method, and their relative errors were evaluated from exposure time.
Sagawa, Naoki; Yamazaki, Takumi; Kurosawa, Shigeyuki*; Izaki, Kenji; Mizuniwa, Harumi; Takasaki, Koji
JAEA-Technology 2010-051, 35 Pages, 2011/03
The image analysis method using a imaging plate (IP) is recent technique, and this method can get the information of radioactivity distribution by the unit of Photo Simulated Luminescence (PSL). We have investigated the PSL images obtained by measuring some plutonium samples which are radiation protection samples in order to apply imaging plate to the radiation protection at the MOX fuel facility. Plutonium spots were extracted from the PSL image extracted by the threshold, in which about 99% of the back ground was excluded, and identified by the additional requirement that the spot size is more than 40 pixels. The average background is subtracted from PSL strength of the spot area identified as Pu, and the radioactivity of the Pu spot was evaluated by multiplying the conversion calculation that is in consideration of fading.
Taguchi, Shigeo; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Surugaya, Naoki; Kurosawa, Akira; Hiyama, Toshiaki; Tanaka, Tatsuhiko*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 288(2), p.435 - 441, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.16(Chemistry, Analytical)Yamamoto, Masahiko; Ishibashi, Atsushi; Nagayama, Tetsuya; Surugaya, Naoki; Kurosawa, Akira; Hiyama, Toshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2010-040, 28 Pages, 2010/12
Precise analysis of plutonium is necessary for material control and safeguards in nuclear facility. Thus, controlled-potential coulometry, which yields absolute results and high precision, was applied for the determination of plutonium. The coulometry system and sample pretreatment procedures were optimized following ISO12183:2005. Plutonium sample prepared from NBL CRM-126 Pu metal was measured and agreed well with certified value. For spike preparation of isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS), plutonium solution was prepared from MOX powder. Plutonium content was 15.5995 mgPu/g. The uncertainty was calculated by ISO/BIPM Guide to the Expression of Uncertainties in Measurements. The relative expanded uncertainty was 0.023% with confidence interval of 95%. The results were in good agreement with those obtained by IDMS. Thus the proposed coulometry method was successfully applied for the determination of plutonium at the highest level of precision and accuracy.
Sumi, Mika; Surugaya, Naoki; Kurosawa, Akira; Suzuki, Toru; Kuno, Yusuke
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-31-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/12
For the long-term stable operation of nuclear fuel cycle facilities, it is essential to satisfy the requirements of IAEA safeguards agreement. The requirements to maintain and improve the precision of DA are supposed to grow along with nuclear fuel cycle fully in progress and Pu handling amount increases. In order to maintain long-term stability of quality level of accountancy analysis for safeguards, a special committee on "Quality Assurance (QA) for Accountancy / Safeguards analysis" was established at Atomic Energy Society Japan supported by INNN-Japan. Experts for safeguards analysis, reference materials, statistics and QA were gathered and drafted the committee standard document for isotope dilution mass spectrometry, the major accountancy analysis technique for Pu and U, supported Pu standard preparation at JAEA and summarized the items needed for QA of DA.
Taguchi, Shigeo; Surugaya, Naoki; Kurosawa, Akira; Hiyama, Toshiaki; Tanaka, Tatsuhiko*
Bunseki Kagaku, 59(11), p.1035 - 1041, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.69(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
 Hex-BTP/SiO
Hex-BTP/SiO -P resin
-P resinSurugaya, Naoki; Sano, Yuichi; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Kurosawa, Akira; Hiyama, Toshiaki
Nuclear Energy and the Environment; ACS Symposium Series 1046, p.131 - 139, 2010/10
Taguchi, Shigeo; Surugaya, Naoki; Kurosawa, Akira; Hiyama, Toshiaki; Tanaka, Tatsuhiko*
Bunseki Kagaku, 58(10), p.901 - 907, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)An on-line analysis system using a solid-phase extraction column coupled to electrochemical detection has been developed for rapid determination of small amounts of uranium in liquid wastes of spent nuclear-fuel reprocessing plants. A sample solution with a concentration of 3 M HNO was loaded onto the column: packed with U/TEVA
was loaded onto the column: packed with U/TEVA resin. The interference elements were rinsed by passing 3 M HNO
resin. The interference elements were rinsed by passing 3 M HNO through the column. The adsorbed uranium was eluted with 0.1 M HNO
through the column. The adsorbed uranium was eluted with 0.1 M HNO . The eluate was directly introduced into a flow-electrolysis cell. The result of five repeated analyses for a standard solution containing 2.5
. The eluate was directly introduced into a flow-electrolysis cell. The result of five repeated analyses for a standard solution containing 2.5  g (0.1 mL at 25
g (0.1 mL at 25  g mL
g mL ) of uranium was found to be 2.5
) of uranium was found to be 2.5  0.025
0.025  g (mean
g (mean  1
1  ). The detection limit calculated from 3 times the standard deviation of background current was 56 ng. The analysis time required for one sample was within 5 min. The recoveries of uranium in actual nuclear waste reprocessing solutions were 92%
). The detection limit calculated from 3 times the standard deviation of background current was 56 ng. The analysis time required for one sample was within 5 min. The recoveries of uranium in actual nuclear waste reprocessing solutions were 92%  112%.
112%.
 Sr
Sr )MnO
)MnO and (Ba
and (Ba Sr
Sr )(Co
)(Co Fe
Fe )O
)O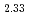 through rietveld refinement and MEM analysis
through rietveld refinement and MEM analysisIto, Takanori*; Shirasaki, Saori*; Fujie, Yoshinori*; Kitamura, Naoto*; Idemoto, Yasushi*; Osaka, Keiichi*; Hirosawa, Ichiro*; Igawa, Naoki
Denki Kagaku Oyobi Kogyo Butsuri Kagaku, 77(2), p.161 - 168, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:8.2(Electrochemistry)We analyzed the mechanism of mixed conduction due to electrons and oxygen ions in (La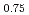 Sr
Sr )MnO
)MnO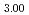 and (Ba
and (Ba Sr
Sr )(Co
)(Co Fe
Fe )O
)O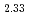 through the Rietveld refinement and maximum entropy method analyses of neutron and synchrotron X-ray diffractions. It was found that Mn-O plane in (La
through the Rietveld refinement and maximum entropy method analyses of neutron and synchrotron X-ray diffractions. It was found that Mn-O plane in (La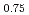 Sr
Sr )MnO
)MnO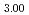 has a strong, isotropic covalent bond that enables conduction of electrons. The (Co, Fe)-O2 plane with a covalent bond and a low concentration of oxygen vacancies in (Ba
has a strong, isotropic covalent bond that enables conduction of electrons. The (Co, Fe)-O2 plane with a covalent bond and a low concentration of oxygen vacancies in (Ba Sr
Sr )(Co
)(Co Fe
Fe )O
)O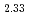 can also conduct electrons. On the other hand, the (Ba, Sr)-O1 plane in (Ba
can also conduct electrons. On the other hand, the (Ba, Sr)-O1 plane in (Ba Sr
Sr )(Co
)(Co Fe
Fe )O
)O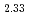 , which has a high concentration of oxygen vacancies, large isotropic displacement parameter, and a strong ionic bond, is responsible for the diffusion of oxygen ions.
, which has a high concentration of oxygen vacancies, large isotropic displacement parameter, and a strong ionic bond, is responsible for the diffusion of oxygen ions.
 Sr
Sr )(Co
)(Co Fe
Fe )O
)O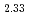 by Rietveld refinement and maximum entropy method analysis
by Rietveld refinement and maximum entropy method analysisIto, Takanori*; Nishida, Yuki*; Tomita, Aya*; Fujie, Yoshinori*; Kitamura, Naoto*; Idemoto, Yasushi*; Osaka, Keiichi*; Hirosawa, Ichiro*; Igawa, Naoki
Solid State Communications, 149(1-2), p.41 - 44, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:77.53(Physics, Condensed Matter)The crystal structure and charge density of (Ba Sr
Sr )(Co
)(Co Fe
Fe )O
)O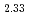 were investigated by the Rietveld refinement method and the maximum entropy method by using neutron and synchrotron X-ray diffraction. The crystal structure was refined by using the split atom model to cation sites with the space group,
were investigated by the Rietveld refinement method and the maximum entropy method by using neutron and synchrotron X-ray diffraction. The crystal structure was refined by using the split atom model to cation sites with the space group,  . The site occupancies of O1(4
. The site occupancies of O1(4 ) and O2(8
) and O2(8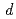 ) sites were 0.59 and 0.87, respectively. It was found that the (Co, Fe)-O2 plane in the sample has anisotropic covalent and ionic bands, and that the (Ba, Sr)-O1 bond was ionic with a low charge density.
) sites were 0.59 and 0.87, respectively. It was found that the (Co, Fe)-O2 plane in the sample has anisotropic covalent and ionic bands, and that the (Ba, Sr)-O1 bond was ionic with a low charge density.
Takasaki, Koji; Sagawa, Naoki; Kurosawa, Shigeyuki*; Shioya, Satoshi; Suzuki, Kazunori; Horikoshi, Yoshinori; Mizuniwa, Harumi
JAEA-Technology 2008-028, 73 Pages, 2008/03
Recently, an imaging plate (IP) was developed. Pu analysis by an IP was studied in the JAEA Cooperative Research Scheme on the Nuclear Fuel Cycle, and the availability about detection of Pu and discrimination with radon progenies was shown. In order to apply these results to the radiation control, this research aims at evaluation of radioactivity, discrimination with radon progenies, and evaluation of AMAD by an IP. In the conventional autoradiography (ARG) by a ZnS and Polaroid film, Contamination of Pu can only be grasped by viewing. Since the digital data of the radiation and location is obtained by an IP, Pu can be detected quantitatively and radioactivity can be evaluated. As a result of this research, the image of alpha emitter on an IP is the same as that of the conventional ARG, and can be applied also to the ARG of beta and  emitter. In measurement of Pu, the function of Image J (image-analysis software) was very available. Pu radioactivity was evaluated by an IP.
emitter. In measurement of Pu, the function of Image J (image-analysis software) was very available. Pu radioactivity was evaluated by an IP.
Umeda, Koji; Oi, Takao; Osawa, Hideaki; Oyama, Takuya; Oda, Chie; Kamei, Gento; Kuji, Masayoshi*; Kurosawa, Hideki; Kobayashi, Yasushi; Sasaki, Yasuo; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-050, 82 Pages, 2007/12
This report shows the annual report which shows the summarized results and topic outline of each project on geological disposal technology in the fiscal year of 2006.