Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Saha, P. K.; Takeda, Osamu*; Saeki, Riuji*; Muto, Masayoshi*
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.937 - 941, 2023/11
In the J-PARC 3GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS), the 400MeV H beam is changed to H+ beam by a charge exchange foil and accelerated to 3GeV. So far, RCS had used two types of charge exchange foil. One is the HBC (Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon) foil and the other is the Kaneka GTF (Graphene Thin Film). HBC foil is a patented deposition method developed at KEK for the stable production of thick carbon foil. Initially, the RCS used HBC foil produced atKEK. However, in 2017, JAEA had started HBC foil production and has been using it since then. Recently, we have succeeded in depositing thick pure carbon foil, which had been considered difficult to produce by the arc deposition method. As a new challenge, this pure carbon foil was used in the user operation from March 2023. As a result, Pure carbon foils showed less deformation and more stable charge exchange performance than HBC and GTF.
beam is changed to H+ beam by a charge exchange foil and accelerated to 3GeV. So far, RCS had used two types of charge exchange foil. One is the HBC (Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon) foil and the other is the Kaneka GTF (Graphene Thin Film). HBC foil is a patented deposition method developed at KEK for the stable production of thick carbon foil. Initially, the RCS used HBC foil produced atKEK. However, in 2017, JAEA had started HBC foil production and has been using it since then. Recently, we have succeeded in depositing thick pure carbon foil, which had been considered difficult to produce by the arc deposition method. As a new challenge, this pure carbon foil was used in the user operation from March 2023. As a result, Pure carbon foils showed less deformation and more stable charge exchange performance than HBC and GTF.
Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Saha, P. K.; Takeda, Osamu*; Saeki, Riuji*; Muto, Masayoshi*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.629 - 633, 2023/01
In the J-PARC 3-GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS), a 400 MeV H- beam injected from the linac is exchange to an H+ beam by a charge exchange foil and accelerated to 3 GeV. The charge exchange foils mainly used in the RCS are HBC foil (Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon stripper foil), which are made by adding a small amount of boron to carbon rods and using them as electrodes by the arc deposition method. Since 2018, foils produced by JAEA have been used for user operation. So far, no major problems have occurred due to the foils. Meanwhile, the beam power of the RCS has been gradually increased from 500 kW to 830 kW since 2018. As beam power increases, the foil issues were identified to achieve the RCS design power of 1 MW. In this paper, we will report on the recent foil usage status and issue in the user operation.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
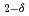 CoGa
CoGa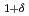 films
filmsKubota, Takahide*; Takano, Daichi*; Kota, Yohei*; Mohanty, S.*; Ito, Keita*; Matsuki, Mitsuhiro*; Hayashida, Masahiro*; Sun, M.*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Saito, Yuji; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(4), p.044405_1 - 044405_12, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:59.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Kamiya, Junichiro; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Tani, Norio; Kotoku, Hirofumi*; Horino, Koki*; Yanagibashi, Toru*; Takeda, Osamu*; Yamamoto, Kazami
JAEA-Technology 2021-019, 105 Pages, 2021/11
Since a user operation startup, the 3 GeV synchrotron accelerator (Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron: RCS) gradually reinforced the beam power. As a result, the surface dose rate of the apparatus located at the beam injection area of the RCS, such as the magnet, vacuum chambers, beam monitors, etc., increases year by year. The beam injection area has many apparatuses which required manual maintenance, so reducing worker's dose is a serious issue. To solve this problem, we have organized a task force for the installation of the shield. The task force has aimed to optimize the structure of the radiation shield, construct the installation procedure with due consideration of the worker's dose suppression. As the examination result of the shield design, we have decided to adopt removal shielding that could be installed quickly and easily when needed. We carried out shield installation work during the 2020 summer maintenance period. The renewal work required to install the shielding has been carried out in a under high-dose environment. For this reason, reducing the dose of workers was an important issue. So, we carefully prepared the work plan and work procedure in advance. During the work period, we implemented various dose reduction measures and managed individual dose carefully. As a result, the dose of all workers could be kept below the predetermined management value. We had installed removal shielding at the beam injection area in the 2020 summer maintenance period. We confirmed that this shield can contribute to the reduction of the dose during work near the beam injection area. It was a large-scale work to occupy the beam injection area during almost of the summer maintenance period. However, it is considered very meaningful for dose suppression in future maintenance works.
Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Kamiya, Junichiro; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Tani, Norio; Kotoku, Hirofumi*; Horino, Koki*; Yanagibashi, Toru*; Takeda, Osamu*; Yamamoto, Kazami
Proceedings of 18th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.238 - 242, 2021/10
Since a user operation startup, the 3GeV synchrotron accelerator (Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron: RCS) gradually reinforced the beam power. As a result, the surface dose rate of the apparatus located at the beam injection area of the RCS increases year by year. The beam injection area has many apparatuses which required manual maintenance, so reducing worker's dose is a serious issue. To solve this problem, we have decided to adopt removal shielding that could be installed quickly and easily when needed. We carried out shield installation work during the 2020 summer maintenance period. The installation work of the shield has been carried out in a under high-dose environment. For this reason, reducing the dose of workers was an important issue. So, we carefully prepared the work plan and work procedure in advance. During the work period, we implemented various dose reduction measures and managed individual dose carefully. As a result, the dose of all workers could be kept below the predetermined management value. We had installed removal shielding at the beam injection area in the 2020 summer maintenance period. We confirmed that this shield can contribute to the reduction of the dose during work near the beam injection area.
Kobayashi, Masaki*; Anh, L. D.*; Suzuki, Masahiro*; Kaneta-Takada, Shingo*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Fujimori, Shinichi; Shibata, Goro*; Tanaka, Arata*; Tanaka, Masaaki*; Oya, Shinobu*; et al.
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 15(6), p.064019_1 - 064019_10, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:27.71(Physics, Applied)Takai, Shizuka; Kimura, Hideo*; Uchikoshi, Emiko*; Munakata, Masahiro; Takeda, Seiji
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-007, 174 Pages, 2020/09
The MIG2DF computer code is a computer program that simulates groundwater flow and radionuclide transport in porous media for the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The original version of MIG2DF was released in 1992. The original code employs a two-dimensional (vertical or horizontal cross-section, or an axisymmetric configuration) finite-element method to approximate the governing equations for density-dependent saturated-unsaturated groundwater flow and radionuclide transport. Meanwhile, for geological disposal of radioactive wastes, landscape evolution such as uplift and erosion needs to be assessed as a long-term geological and climate events, considering site conditions. In coastal areas, the impact to groundwater flow by change of salinity distribution to sea level change also needs to be considered. To deal with these events in the assessment, we have revised the original version of MIG2DF and developed the external program which enables MIG2DF to consider unsteady landscape evolution. In these developments, this report describes an upgrade of MIG2DF (Version 2) and presents the configuration, equations, methods, and verification. This reports also give the explanation external programs of MIG2DF: PASS-TRAC (the particle tracking code), PASS-PRE (the code for dataset preparation), and PASS-POST (the post-processing visualization system).
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:56.2(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Takeda, Osamu*; Saeki, Riuji*; Muto, Masayoshi*
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.545 - 549, 2019/07
In the 3 GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research complex (J-PARC), we adopted the carbon stripper foil for the multi-turn H- charge exchange injection. The charge exchange foil which use in RCS is fabricated by the arc discharge method with the boron doped carbon electrode. The foil fabricated this method is called HBC foil (Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon stripper foil). HBC foil had been developed at KEK. It has high durability for the beam irradiation damage. In past days, the foil fabrication process was conducted in KEK Tsukuba-site and the foil preparation process was conducted in JAEA Tokai-site. In 2017, the foil deposition apparatus has been relocated from KEK to JAEA, and we started both processes in Tokai-site. We carried out the offline beam irradiation test for the new HBC foil which fabricated in JAEA, and we confirmed that its performance is equivalent to the original HBC foil. Next we tested a new HBC foil with actual beam in RCS and we confirmed it could withstand 1 week beam irradiation. After that, we started user operation with the new HBC foil in 2018. So far we accomplished stable user operation for one year by using the new HBC foil only.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Yamakawa, Emi*; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Miki, Nobuharu*; Kamiya, Junichiro; Saha, P. K.; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Yanagibashi, Toru*; Horino, Koki*; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; et al.
ANS RPSD 2018; 20th Topical Meeting of the Radiation Protection and Shielding Division of ANS (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2018/08
The existing beam power of the J-PARC Rapid Cycling Synchrotron is up to 500 kW, and higher radiation doses are concentrated in the injection area. These activations are caused by the interaction between the foil and the beam. To reduce dose exposure to workers near the injection point, we study a new design of the injection scheme. Experience has shown that eddy currents are generated in the metal flange near the magnet owing to the pulsed magnetic field, and the temperature exceeds 100 degrees C. The shield installed in the new injection system needs to have a layer structure, in which an insulator is inserted between iron shields to reduce the eddy current. From the results of the shielding calculation, even if 1 mm of polyethylene was inserted between two 9-mm-thick SUS 316 plates, which serve as shielding material, the shielding performance was reduced only about 5%, and we confirmed that it would function well.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kamiya, Junichiro; Saha, P. K.; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Takeda, Osamu*; Miki, Nobuharu*
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.374 - 378, 2017/12
The 3-GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) aims to deliver 1-MW proton beam to the neutron target and Main Ring synchrotron. Present beam power of the Rapid Cycling Synchrotron is up to 500-kW and the higher radiation doses were concentrated in the injection area. These activations were caused by the interaction between the foil and the beam. To reduce the worker dose near the injection point, we have studied a new design of the injection scheme to secure enough space for radiation shielding and bellows. In the new system, two of four injection pulse bump magnets are replaced and we are able to ensure the additional space around the injection foil chamber. So far, new injection system seems not impossible. However, preliminary study result indicated that temperature of the duct and shielding metals would be slightly higher. The eddy current due to the shift bump magnet field generates heat. Thus we have to study details of above effect.
Okabe, Kota; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kamiya, Junichiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takeda, Osamu*; Horino, Koki*; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Yanagibashi, Toru*; et al.
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.853 - 857, 2017/12
The most important issue is to reduce the uncontrolled beam loss in the high intensity hadron accelerator such as J-PARC proton accelerators. The J-PARC 3 GeV Synchrotron (RCS) has a collimator system which narrows a high intensity beam in the RCS. After startup of RCS in 2007, the collimator system of the RCS worked well. However, in April 2016, vacuum leakage at the collimator system occurred during the maintenance operation. To investigate a cause of the failure, we took apart iron shields of the collimator reducing exposed dose of operators. As a result of inspection, we succeeded to identify the cause of the vacuum leakage failure. In this presentation, we report the failure investigation of the beam collimator system in the RCS.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kamiya, Junichiro; Saha, P. K.; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Takeda, Osamu*; Miki, Nobuharu*
Proceedings of 8th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '17) (Internet), p.579 - 581, 2017/05
The 3-GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron of Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex aims to deliver 1-MW proton beam to the neutron target and Main Ring synchrotron. Present beam power of the Rapid Cycling Synchrotron is up to 500-kW and the higher radiation doses were concentrated in the injection area. These activations were caused by the interaction between the foil and the beam. To reduce the worker dose near the injection point, we have studied a new design of the injection scheme to secure enough space for radiation shielding and bellows. In the new system, two of four injection pulse bump magnets are replaced and we are able to ensure the additional space around the injection foil chamber. So far, new injection system seems not impossible. However, preliminary study result indicated that temperature of the duct and shielding metals would be slightly higher. The eddy current due to the shift bump magnet field generates heat. Thus we have to study details of above effect.
Takai, Shizuka; Takeda, Seiji; Sakai, Ryutaro*; Shimada, Taro; Munakata, Masahiro; Tanaka, Tadao
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 16(1), p.34 - 48, 2017/03
In geological disposal, direct effect on geological repositories by active faults is avoided at a stage of site characterization; however, uncertainty remains for avoidance of faults derived from the active faults, which are concealed deep under the ground and difficult to detect in advance. In this research, the influence of growth of undetected splay faults on natural barrier in a geological disposal system, which will caused by attack of the faults in the future, was evaluated. We investigated examples of splay faults in Japan and set conditions for growth of splay faults. Furthermore, we assumed a disposal site composed of sedimentary rocks and made a hydrogeological model of growth of splay faults. We carried out groundwater flow analyses, changing parameters such as location and depth of repository and growth velocity of splay faults. The results indicate that main flow path from the repository is changed into upward flow along the splay fault due to its growth and the average velocity to the ground surface becomes one or two orders of magnitude higher than that before its growth. The results also suggest that the splay fault growth leads into the possibility of downward flow of oxidizing groundwater from ground surface area.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Okabe, Kota; Kamiya, Junichiro; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takeda, Osamu; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Yamamoto, Masanobu
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.314 - 318, 2016/11
The 3 GeV Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) project generates 1MW proton beam for the neutron experiments and Main ring accelerator. In case of such high intensity hadron accelerator, the most important issue is to reduce the uncontrolled loss. The beam collimation system is designed for this purpose. In the present design, the physical aperture is 1.5 times wider than the primary collimator aperture and the beam loss can be enough localized on this condition. After a startup of RCS in 2007, the collimator system of RCS worked well. But vacuum leakage occurred during the maintenance period in April, 2016. Since it was expected that the beam collimator was radio-activated very much, we took the influence of radiation into consideration and designed the collimator (ie. a remote clamp system to connect/take off it with a vacuum flange away from itself). Therefore, during the recovery work of the collimator, we were able to reduce the worker dose to less than 60 micro Sv though the collimator block had a residual dose of 40 mSv/h.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takeda, Osamu; Harada, Hiroyuki; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1097 - 1101, 2016/11
In the 3 GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), a beam collimation system which aims to localize the beam loss at the collimators and to reduce the level of residual doses at the other devices is installed in the ring to achieve a 1MW high power beam operation. However vacuum leakage due to the collimator trouble occurred in April, 2016. Therefore an absorber No.5 in the collimation system had to be removed from the ring. Before resuming the beam operation, a new beam loss situation was simulated by using the particle tracking code. In the beam tuning, the transition of the beam loss distribution was measured by the beam loss monitors. We verified that the new beam situation was permissible, and the beam operation can be resumed. By following-up the transition of the residual dose distribution along the ring, the detailed beam loss structure can be understood. In this presentation, we report an influence of ring-collimator malfunction on beam loss localization in the J-PARC RCS.
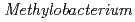 sp. ME121, isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with
sp. ME121, isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with 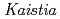 sp. 32K
sp. 32KFujinami, Shun*; Takeda, Kiyoko*; Onodera, Takefumi*; Sato, Katsuya; Shimizu, Tetsu*; Wakabayashi, Yu*; Narumi, Issey*; Nakamura, Akira*; Ito, Masahiro*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 3(5), p.e01005-15_1 - e01005-15_2, 2015/09
Tobita, Norimitsu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takeda, Osamu; Saeki, Riuji; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Kinsho, Michikazu; Muto, Masayoshi*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1350 - 1354, 2015/09
no abstracts in English