Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

Oba, Hirofumi; Sato, Katsuya; Sghaier, H.; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Narumi, Issei
Extremophiles, 13(3), p.471 - 479, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:40.47(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology) possesses a DNA damage response mechanism that acts via the PprI protein to induce RecA and PprA proteins, both of which are necessary in conferring extreme radioresistance. In an effort to further delineate the nature of the DNA damage response mechanism in
possesses a DNA damage response mechanism that acts via the PprI protein to induce RecA and PprA proteins, both of which are necessary in conferring extreme radioresistance. In an effort to further delineate the nature of the DNA damage response mechanism in  , we set out to identify novel components of the PprI-dependent signal transduction pathway in response to radiation stress. Here we demonstrate the discovery of a novel regulatory protein, PprM (a modulator of the PprI-dependent DNA damage response), which is a homolog of cold shock protein (Csp). Disruption of the
, we set out to identify novel components of the PprI-dependent signal transduction pathway in response to radiation stress. Here we demonstrate the discovery of a novel regulatory protein, PprM (a modulator of the PprI-dependent DNA damage response), which is a homolog of cold shock protein (Csp). Disruption of the 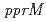 gene rendered
gene rendered  significantly sensitive to
significantly sensitive to  -rays. PprM regulates the induction of PprA but not that of RecA. PprM belongs in a distinct clade of a subfamily together with Csp homologs from
-rays. PprM regulates the induction of PprA but not that of RecA. PprM belongs in a distinct clade of a subfamily together with Csp homologs from  and
and 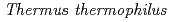 . Purified PprM is present as a homodimer under physiological conditions, as the case with
. Purified PprM is present as a homodimer under physiological conditions, as the case with  CspD. The
CspD. The 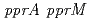 double-disruptant strain exhibited higher sensitivity than the
double-disruptant strain exhibited higher sensitivity than the  or
or 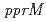 single disruptant strains, suggesting that PprM regulates other hitherto unknown protein(s) important for radioresistance besides PprA. This study strongly suggests that PprM is involved in the radiation response mediated by PprI in
single disruptant strains, suggesting that PprM regulates other hitherto unknown protein(s) important for radioresistance besides PprA. This study strongly suggests that PprM is involved in the radiation response mediated by PprI in  .
.

Oba, Hirofumi; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Sghaier, H.; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Narumi, Issei
JAEA-Review 2008-055, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2007, P. 57, 2008/11
no abstracts in English
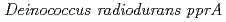 gene
geneOba, Hirofumi; Sato, Katsuya; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Narumi, Issei
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 70, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
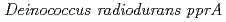 gene
geneOba, Hirofumi*; Sato, Katsuya*; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Narumi, Issei
Gene, 363, p.133 - 141, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:54.68(Genetics & Heredity)Three transcriptional start points for the 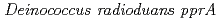 were located at positions -156, -154 and -22 upstream from the
were located at positions -156, -154 and -22 upstream from the  translation initiation site. The amount of the three extended products increased in cells exposed to 2-kGy followed by a 0.5-h post-incubation, suggesting the existence of at least two radiation responsive promoters for
translation initiation site. The amount of the three extended products increased in cells exposed to 2-kGy followed by a 0.5-h post-incubation, suggesting the existence of at least two radiation responsive promoters for  expression. A luciferase reporter assay revealed that the distal promoter is located between positions -208 and -156 from the translation initiation site, while the proximal promoter is located between positions -57 and -22. The region located between positions -57 and -38 was indispensable for proximal promoter activity. Site-directed mutagenesis of a thymine positioned at -33 resulted in severe impairment of promoter activity, and suggested that the thymine functions as a master base for the proximal radiation responsive promoter. The results also suggested that up-regulation of
expression. A luciferase reporter assay revealed that the distal promoter is located between positions -208 and -156 from the translation initiation site, while the proximal promoter is located between positions -57 and -22. The region located between positions -57 and -38 was indispensable for proximal promoter activity. Site-directed mutagenesis of a thymine positioned at -33 resulted in severe impairment of promoter activity, and suggested that the thymine functions as a master base for the proximal radiation responsive promoter. The results also suggested that up-regulation of  expression by the
expression by the  gene product is triggered at the promoter level.
gene product is triggered at the promoter level.
 in the radioresistant bacterium
in the radioresistant bacterium 
Islam, M. S.*; Hua, Y.*; Oba, Hirofumi; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Narumi, Issei
Genes and Genetic Systems, 78(5), p.319 - 327, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:27.6(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)no abstracts in English

Sato, Katsuya; Narumi, Issei; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Kitayama, Shigeru; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Yamamoto, Kazuo; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Journal of Biochemistry, 131(1), p.121 - 129, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:38.61(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)RecA protein is considered to be the most important participant in the radiation resistance of  . We identified a new
. We identified a new  mutation (
mutation (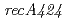 ) in the DNA-repair deficient mutant strain KI696, the phenotype of which is remarkably different from mutant strain rec30 carrying
) in the DNA-repair deficient mutant strain KI696, the phenotype of which is remarkably different from mutant strain rec30 carrying 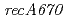 . In vitro, neither RecA424 nor RecA670 could promote DNA strand exchange, indicating that both RecA424 and Rec670 are defective in recombination activity. RecA424 promoted the autocleavage reaction of LexA in vitro, whereas RecA670 did not. The LexA level in KI696 was decreased following
. In vitro, neither RecA424 nor RecA670 could promote DNA strand exchange, indicating that both RecA424 and Rec670 are defective in recombination activity. RecA424 promoted the autocleavage reaction of LexA in vitro, whereas RecA670 did not. The LexA level in KI696 was decreased following  -irradiation. However, the LexA level in strain rec30 was constant irrespective of irradiation. These results indicate that RecA424 retains co-protease activity, whereas RecA670 does not. While strain rec30 is extremely radiation sensitive, strain KI696 is only slightly sensitive. Together, these observations suggest that the co-protease activity rather than the recombination activity of RecA contributes to the radiation resistance in
-irradiation. However, the LexA level in strain rec30 was constant irrespective of irradiation. These results indicate that RecA424 retains co-protease activity, whereas RecA670 does not. While strain rec30 is extremely radiation sensitive, strain KI696 is only slightly sensitive. Together, these observations suggest that the co-protease activity rather than the recombination activity of RecA contributes to the radiation resistance in  .
.
 is not involved in RecA induction following
is not involved in RecA induction following  irradiation
irradiationNarumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuo
Journal of Bacteriology, 183(23), p.6951 - 6956, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:89 Percentile:83.76(Microbiology)The involvement of LexA in induction of RecA was investigated in  . As in the wild-type strain, an increase in RecA protein synthesis following
. As in the wild-type strain, an increase in RecA protein synthesis following  irradiation was detected in a
irradiation was detected in a 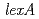 disruptant, indicating that LexA is not involved in the induction of RecA in
disruptant, indicating that LexA is not involved in the induction of RecA in  .
.
Narumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Kitayama, Shigeru; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuo
Mutation Research; DNA Repair, 435(3), p.233 - 243, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
 gene
geneOba, Hirofumi*; Sato, Katsuya*; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
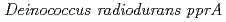 gene
geneOba, Hirofumi*; Sato, Katsuya*; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 ; A Novel key protein "PprM"
; A Novel key protein "PprM"Oba, Hirofumi; Sghaier, H.; Sato, Katsuya; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
PprI, which is unique to  , is invoked by present data as the most important protein for radiation response mechanism. However, despite the interest in mechanism underlying the radiation response in
, is invoked by present data as the most important protein for radiation response mechanism. However, despite the interest in mechanism underlying the radiation response in 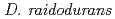 , little is known about the exact function of PprI protein. In this study, functional analysis of PprI protein was performed. Western blot analysis and gel shift assay suggested that PprI itself does not control directly the expression of
, little is known about the exact function of PprI protein. In this study, functional analysis of PprI protein was performed. Western blot analysis and gel shift assay suggested that PprI itself does not control directly the expression of  and
and  . We identified a novel regulatory protein PprM by 2D-PAGE.
. We identified a novel regulatory protein PprM by 2D-PAGE. 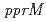 -disruptant strain showed significant sensitivity to
-disruptant strain showed significant sensitivity to  -rays. Western blot analysis revealed that PprM involves in RecA and PprA induction. By reporter assay it was found that PprM protein regulates the
-rays. Western blot analysis revealed that PprM involves in RecA and PprA induction. By reporter assay it was found that PprM protein regulates the  expression at the promoter level. These results suggest that PprM is involved in the unique radiation response mechanism controlled by PprI in
expression at the promoter level. These results suggest that PprM is involved in the unique radiation response mechanism controlled by PprI in  .
.
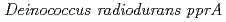 gene
geneOba, Hirofumi; Sato, Katsuya; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Oba, Hirofumi; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Narumi, Issei; Sghaier, H.*; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English