Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
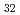 (Al, Zn)
(Al, Zn)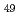 Approximant crystal; Influence of chemical disorder
Approximant crystal; Influence of chemical disorderShimizu, Kazuyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Akamaru, Satoshi*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Abe, Rion*; Sasaki, Taisuke*; Wang, Y.*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scripta Materialia, 265, p.116730_1 - 116730_7, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Ebihara, Kenichi; Fujihara, Hiro*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Toda, Hiroyuki*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 136, p.751 - 756, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0It has been experimentally reported that adding tin (Sn) to high-strength aluminum-zinc-magnesium (Al-Zn-Mg) alloys effectively suppresses hydrogen (H) embrittlement, which may be attributed to H absorption by the second-phase particles of Sn. To verify this fact, a simulation of H entry into the Sn phase in Al was performed using a model based on the reaction-diffusion equation that incorporates the solid solution energy of H evaluated by first-principles calculations. The results showed that the H solid solution site concentration of the second-phase particles must be at least five times higher than that of the Al phase for H absorption by the Sn second-phase particles to suppress H embrittlement. Therefore, the actual H embrittlement suppression effect of Sn second-phase particles is limited, and other factors may influence the suppression of H embrittlement in the experiment.
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Okamoto, Koji
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 184, p.105710_1 - 105710_10, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Very recently, Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) has been proposed as a scheme capable to inversely estimate radioactive source distributions inside reactor building rooms from air dose rate measurements together with the predicted lower bound of the measurement numbers for successful reconstructions. However, no one has ever analyzed how the uncertainty of input data including the measurement errors influences the accuracy of the inverse estimation results. In this paper, we therefore perform uncertainty analysis of the LASSO scheme and suggest an uncertainty estimation function derived based on the theory of Candes. We actually demonstrate in two types of numerical tests with different input uncertainties obtained by using Monte Carlo code, Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) that the calculated errors obey the proposed uncertainty estimation function. Thus, the LASSO scheme allows to successfully estimate radioactive distributions within the predicted uncertainty.
 path-integral simulations of hydrogen-isotope diffusion in face-centred cubic metals
path-integral simulations of hydrogen-isotope diffusion in face-centred cubic metalsKimizuka, Hajime*; Ogata, Shigenobu*; Thomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 37(19), p.193001_1 - 193001_16, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)Calculations of hydrogen isotope diffusion coefficients for face-centred cubic lattice metals using  path integral methods show that the temperature dependence of the diffusion coefficients has an unusual shape. This is due to the competition between nuclear quantum effects with different temperature dependence, which explains the unusual crossover mechanism between the normal and inverse isotope effects. We also present the results of a path integral simulation that describes approximate quantum dynamics using machine learning-based interatomic potentials with almost the same accuracy as density functional theory calculations. This computational method paves the way for understanding the quantum behaviour of hydrogen isotopes in various solid-state materials.
path integral methods show that the temperature dependence of the diffusion coefficients has an unusual shape. This is due to the competition between nuclear quantum effects with different temperature dependence, which explains the unusual crossover mechanism between the normal and inverse isotope effects. We also present the results of a path integral simulation that describes approximate quantum dynamics using machine learning-based interatomic potentials with almost the same accuracy as density functional theory calculations. This computational method paves the way for understanding the quantum behaviour of hydrogen isotopes in various solid-state materials.
Takaku, Yuhi; Kakefuda, Toyokazu*; Yashiro, Shigeo; Kimura, Hideo; Kuno, Tetsuya
JAEA-Testing 2024-006, 31 Pages, 2025/03
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has a wide variety of servers across its departments, managed by on-site server administrators who are responsible for tasks including security measures. As a result, the workload and operational cost burdens are significant. Additionally, addressing the increasing frequency of security incidents in recent years, both domestically and internationally, is essential for JAEA's operations, which involve handling sensitive information. However, it is difficult for individual server administrators to take proactive measures to mitigate these risks. To address these challenges, we carried out the migration of systems that do not contain sensitive information to an external cloud environment with a focus on cost reduction. As a result, we clarified the conditions necessary for a smooth migration to an external cloud environment while achieving significant cost savings and established a foundation for implementing measures against security incidents.
Yoshida, M.*; McDermott, R. M.*; Angioni, C.*; Camenen, Y.*; Citrin, J.*; Jakubowski, M.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Mantica, P.*; Mariani, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 65(3), p.033001_1 - 033001_132, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:95.90(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Progress in physics understanding and theoretical model development of plasma transport and confinement in the ITPA Transport and Confinement Topical Group since the publication of the ITER Physics Basis was summarized focusing on the contributions to ITER and burning plasma prediction and control. This paper provides a general and streamlined overview on the advances that were mainly led by the ITPA TC joint experiments and joint activities for the last 15 years. This paper starts with the scientific strategy and scope of the ITPA TC Topical group and overall picture of the major progress, followed by the progress of each research field: particle transport, impurity transport, ion and electron thermal turbulent transport, momentum transport, impact of 3D magnetic fields on transport, confinement mode transitions, global confinement, and reduced transport modeling.
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Okumura, Masahiko; Kawamura, Naomi*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Science of the Total Environment, 964, p.178585_1 - 178585_13, 2025/02
There are many unresolved issues in the adsorption reactions of clay minerals. One of the reasons is the existence of multiple adsorption sites. It is known that the contribution of each adsorption site depends on the concentration of adsorbed ions, and there is a challenge in comprehensively correlate the results of atomic-level simulations that employ limited number of atoms and inevitably deal high-concentration samples with actual environmental samples where concentrations are orders of magnitude lower. In this study, we combined experiments using synchrotron radiation and first-principles calculations to comprehensively elucidate the systematic changes in the local structure of adsorption sites and adsorbed ions based on the adsorption concentration at the atomic level, and demonstrated that the interaction between adsorbed ions and clay minerals involves ionic bonding.
HPC Technology Promotion Office, Center for Computational Science & e-Systems
JAEA-Review 2024-044, 121 Pages, 2025/01
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) conducts research and development (R&D) in various fields related to nuclear power as a comprehensive institution of nuclear energy R&Ds, and utilizes computational science and technology in many activities. Over the past 10 years or so, the publication of papers utilizing computational science and technology at JAEA has accounted for about 20 percent of the total publications each fiscal year. The supercomputer system of JAEA has become an important infrastructure to support computational science and technology. In FY2023, the system was utilized in R&D activities that were prioritized in the Fourth Medium- to Long-Term Plan, including contributing to carbon neutrality through the development of innovative technologies such as improving safety, creating innovation by promoting diverse R&D related to nuclear science and technology, promoting R&D in response to the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, steadily implementing technological developments for the treatment and disposal of high-level radioactive waste, and supporting nuclear safety regulatory administration and nuclear disaster prevention by promoting safety research for these purposes. This report presents a great number of R&D results accomplished by using the system in FY2023, as well as user support, operational records and overviews of the system, and so on.
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Tsuru, Tomohito
Scripta Materialia, 255, p.116366_1 - 116366_5, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Reduction of grain boundary cohesive energy by hydrogen has been considered as one of the candidate causes of grain boundary fracture in steels and aluminum alloys. Recently, the effects of grain boundary segregation elements have been investigated by first-principles calculations, but there are few studies that quantitatively estimate the grain boundary cohesive energy. In this study, we describe a quantitative evaluation method using first-principles calculation results and show some examples of experimental calculations.
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Okumura, Masahiko
Isotope News, (796), p.21 - 23, 2024/12
Clay minerals are abundant in soils and control the environmental behavior of various elements because they adsorb many cations. Since the strength of adsorption of clay minerals depends on the adsorption structure at the molecular level, a systematic understanding of what determines the adsorption structure at the molecular level is important. In this study, we systematically elucidated the adsorption structures of many cations, including radium, using extensive X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) measurements and first-principles simulations. The results show that the size and hydration enthalpy of adsorbed ions are important in determining the adsorption structure.
Fujisawa, Yuita*; Krishnadas, A*; Nakamura, Tomonori*; Hsu, C.-H.*; Smith, B. R. M.*; Pardo-Almanza, M*; Hiyane, Hoshu*; Nagai, Yuki; Machida, Tadashi*; Okada, Yoshinori*
Physical Review B, 110(22), p.224511_1 - 224511_5, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Understanding the nature of vortices in type-II superconductors has been vital for deepening the physics of exotic superconductors and applying superconducting materials to future electronic devices. A recent study has shown that the LiTi O
O (111) thin film offers a unique experimental platform to unveil the nature of the vortex along the curved Josephson junction. This study successfully visualized individual Josephson vortices along the curved Josephson junctions using in-situ spectroscopic scanning tunneling microscopy on LiTi
(111) thin film offers a unique experimental platform to unveil the nature of the vortex along the curved Josephson junction. This study successfully visualized individual Josephson vortices along the curved Josephson junctions using in-situ spectroscopic scanning tunneling microscopy on LiTi O
O (111) epitaxial thin films. Notably, the local curvature of the Josephson junction was discovered to control the position of Josephson vortices. Furthermore, the numerical simulation reproduces the critical role of the curvature of the Josephson junction. This study provides guidelines to control Josephson vortices through geometrical ways, such as mechanical controlling of superconducting materials and their devices.
(111) epitaxial thin films. Notably, the local curvature of the Josephson junction was discovered to control the position of Josephson vortices. Furthermore, the numerical simulation reproduces the critical role of the curvature of the Josephson junction. This study provides guidelines to control Josephson vortices through geometrical ways, such as mechanical controlling of superconducting materials and their devices.
Okada, Kazuho*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Kimura, Yuji*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 280, p.120288_1 - 120288_14, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:36.18(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) and machine learning potentials for modeling nuclear quantum effects in water
and machine learning potentials for modeling nuclear quantum effects in waterThomsen, B.; Nagai, Yuki*; Kobayashi, Keita; Hamada, Ikutaro*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Journal of Chemical Physics, 161(20), p.204109_1 - 204109_18, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:37.13(Chemistry, Physical)We introduce the self-learning path integral hybrid Monte Carlo with mixed  and machine learning potentials (SL-PIHMC-MIX) method which allows the application of hybrid Monte Carlo for both path integrals and for larger system sizes. The method shows savings of an order of magnitude with respect to the number of
and machine learning potentials (SL-PIHMC-MIX) method which allows the application of hybrid Monte Carlo for both path integrals and for larger system sizes. The method shows savings of an order of magnitude with respect to the number of  DFT calculations needed to calculate and converge the structure of room temperature water when using SL-PIHMC-MIX over ab initio path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD).
DFT calculations needed to calculate and converge the structure of room temperature water when using SL-PIHMC-MIX over ab initio path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD).
Nagai, Yuki; Tomiya, Akio*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(11), p.114007_1 - 114007_8, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:43.84(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We proposed a new self-learning Monte Carlo method using Transformer, a key technology in generative AI. By using Transformer's Attention mechanism, which can infer the relevance of distant words in a sentence, we have constructed an effective model that can efficiently capture the long-range correlations that are important in the phase transitions in electronic systems. Furthermore, we reduce the number of parameters by incorporating symmetries that the system must satisfy, such as spin rotation and spatial translation, into the network. We also found a scaling law that the loss decreases as the number of layers is increased.
Catumba, G.*; Hiraguchi, Atsuki; Hou, W.-S.*; Jansen, K.*; Kao, Y.-J.*; David Lin, C.-J.*; Ramos, A.*; Sarkar, M.*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(4), p.043172_1 - 043172_12, 2024/11
Gauge theories with matter fields in various representations play an important role in different branches of physics. Recently, it was proposed that several aspects of the interesting pseudogap phase of cuprate superconductors near optimal doping may be explained by an emergent SU(2) gauge symmetry. Around the transition with positive hole-doping, one can construct a (2+1)-dimensional SU(2) gauge theory coupled to four adjoint scalar fields which gives rise to a rich phase diagram with a myriad of phases having different broken symmetries. We study the phase diagram of this model on the Euclidean lattice using the Hybrid Monte Carlo algorithm. We find the existence of multiple broken phases as predicted by previous mean field studies. Depending on the quartic couplings, the SU(2) gauge symmetry is broken down either to U(1) or 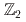 in the perturbative description of the model. We further study the confinement-deconfinement transition in this theory, and find that both the broken phases are deconfining in the range of volumes that we studied. However, there exists a marked difference in the behavior of the Polyakov loop between the two phases.
in the perturbative description of the model. We further study the confinement-deconfinement transition in this theory, and find that both the broken phases are deconfining in the range of volumes that we studied. However, there exists a marked difference in the behavior of the Polyakov loop between the two phases.
Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Proceedings of 31st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE31) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2024/11
Efficiency and safety improvements in nuclear fuel development demand a comprehensive understanding of the thermal properties of PuO . Because of difficulty of experiments at high temperatures, they have been supplemented by numerical simulations, such as density functional theory (DFT). While DFT struggles to replicate the nonmagnetic insulating ground state of PuO
. Because of difficulty of experiments at high temperatures, they have been supplemented by numerical simulations, such as density functional theory (DFT). While DFT struggles to replicate the nonmagnetic insulating ground state of PuO , DFT+U can reproduce nonmagnetic insulating state. However, the obtained state remains less stable than magnetic states and is not the ground state. Adiabatic connection fluctuation-dissipation theory (ACFDT) is expected to be a promising solution, addressing higher-order correlations and exact exchange energies. In this study, we evaluate the ground state energy using ACFDT and find that the nonmagnetic state can be the ground state. This result successfully reproduces the observed nonmagnetic ground state of PuO
, DFT+U can reproduce nonmagnetic insulating state. However, the obtained state remains less stable than magnetic states and is not the ground state. Adiabatic connection fluctuation-dissipation theory (ACFDT) is expected to be a promising solution, addressing higher-order correlations and exact exchange energies. In this study, we evaluate the ground state energy using ACFDT and find that the nonmagnetic state can be the ground state. This result successfully reproduces the observed nonmagnetic ground state of PuO and has the potential to improve predictions of the thermal properties of nuclear fuel materials.
and has the potential to improve predictions of the thermal properties of nuclear fuel materials.
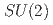 gauge fields
gauge fieldsCatumba, G.*; Hiraguchi, Atsuki; W.-S. Hou, G.*; Jansen, K.*; Kao, Y.-J.*; David Lin, C.-J.*; Ramos, A.*; Sarkar, M.*
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 453, p.87_1 - 87_9, 2024/11
We study the most general Two Higgs Doublet Model with 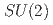 gauge fields on the lattice. The phase space is probed through the computation of gauge-invariant global observables serving as proxies for order parameters. In each phase, the spectrum of the theory is analysed for different combinations of bare couplings and different symmetry breaking patterns. The scale setting and determination of the running gauge coupling are performed through the Wilson flow computation of the action density.
gauge fields on the lattice. The phase space is probed through the computation of gauge-invariant global observables serving as proxies for order parameters. In each phase, the spectrum of the theory is analysed for different combinations of bare couplings and different symmetry breaking patterns. The scale setting and determination of the running gauge coupling are performed through the Wilson flow computation of the action density.
Catumba, G.*; Hiraguchi, Atsuki; W.-S. Hou, G.*; Jansen, K.*; Kao, Y.-J.*; David Lin, C.-J.*; Ramos, A.*; Sarkar, M.*
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 453, p.362_1 - 362_7, 2024/11
We study a 3-dimensional SU(2) gauge theory with 4 Higgs fields which transform under the adjoint representation of the gauge group, that has been recently proposed by Sachdev et al. to explain the physics of cuprate superconductors near optimal doping. The symmetric confining phase of the theory corresponds to the usual Fermi-liquid phase while the broken (Higgs) phase is associated with the interesting pseudogap phase of cuprates. We employ the Hybrid Monte-Carlo algorithm to study the phase diagram of the theory. We find the existence of a variety of broken phases in qualitative accordance with earlier mean-field predictions and discuss their role in cuprates. In addition, we investigate the behavior of Polyakov loop to probe the confinement/deconfinement phase transition, and find that the Higgs phase hosts a stable deconfining phase consistent with previous studies.
Tomiya, Akio*; Nagai, Yuki
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 453, p.001_1 - 001_7, 2024/11
Machine learning, deep learning, has been accelerating computational physics, which has been used to simulate systems on a lattice. Equivariance is essential to simulate a physical system because it imposes a strong induction bias for the probability distribution described by a machine learning model. However, imposing symmetry on the model sometimes occur a poor acceptance rate in self-learning Monte-Carlo (SLMC). On the other hand, Attention used in Transformers like GPT realizes a large model capacity. We introduce symmetry equivariant attention to SLMC. To evaluate our architecture, we apply it to our proposed new architecture on a spin-fermion model on a two-dimensional lattice. We find that it overcomes poor acceptance rates for linear models and observe the scaling law of the acceptance rate in machine learning.
Uno, Koichiro*; Okumura, Masahiko; Nakao, Atsushi*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Yanai, Junta*
Science of the Total Environment, 949, p.175012_1 - 175012_8, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Frayed edge sites (FES), formed by the partial weathering of mica minerals, selectively adsorb Cs ions. However, the detailed mechanism of this adsorption has not been fully clarified. In this study, cation extraction and Cs adsorption experiments were conducted on mica. It was found that potassium-adsorbed mica adsorbed more Cs than rubidium-adsorbed mica. To elucidate the cause of this, the stability of Cs, rubidium, and potassium adsorbed on FES was evaluated using first-principles calculations. It was determined that the presence of potassium as the cation species prior to Cs adsorption is important for the stability of Cs on the FES.