Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yildirim, A. C.*; Mei, H.*; 戸田 賀奈子*; 青柳 登; 斉藤 拓巳*
Applied Clay Science, 274, p.107853_1 - 107853_9, 2025/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Metakaolin-based geopolymers (MKGPs) are ceramic-like materials used for nuclear waste stabilization. Therefore, understanding the sorption of ions on MKGPs is crucial where the cation exchange is considered as the main mechanism, yet the studies based on pH are limited. Thus, this study evaluates the effect of pH on the sorption mechanism of Eu(III) onto Na- and K-MKGPs. Here, time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS) combined with parallel factor analysis, TRLFS in mixed D O/H
O/H O matrices, and extended X-ray absorption fine structure analysis. Eu(III) predominantly forms surface complexes with both MKGPs in the pH range of 4
O matrices, and extended X-ray absorption fine structure analysis. Eu(III) predominantly forms surface complexes with both MKGPs in the pH range of 4  11 at the open air environment, where three distinct surface species were identified at different pH values. The Eu(III) sorption mechanisms of both MKGPs are similar, involving ternary edge-sharing bidentate or monodentate inner-sphere surface complexation of Eu(III) with MKGP and silicate ions released from the MKGP up to pH 8, followed by the precipitation of europium tri-hydroxide within the pores of MKGP. The insights gained from this study will enhance the knowledge on MKGP for pollutant immobilization, thereby mitigating the spread of contaminants in the environment and expanding the potential application areas.
11 at the open air environment, where three distinct surface species were identified at different pH values. The Eu(III) sorption mechanisms of both MKGPs are similar, involving ternary edge-sharing bidentate or monodentate inner-sphere surface complexation of Eu(III) with MKGP and silicate ions released from the MKGP up to pH 8, followed by the precipitation of europium tri-hydroxide within the pores of MKGP. The insights gained from this study will enhance the knowledge on MKGP for pollutant immobilization, thereby mitigating the spread of contaminants in the environment and expanding the potential application areas.
 Mn
Mn N and Fe
N and Fe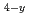 Co
Co N films
N filmsYin, W.*; 伊藤 啓太*; 坪和 優佑*; 辻川 雅人*; 白井 正文*; 梅津 理恵*; 高梨 弘毅
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 628, p.173157_1 - 173157_8, 2025/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fe N exhibits a large anomalous Nernst effect (ANE), which motivates a systematic study of enhancing the anomalous Nernst coefficient (S
N exhibits a large anomalous Nernst effect (ANE), which motivates a systematic study of enhancing the anomalous Nernst coefficient (S ) by modulating its electronic and magnetic structures. In this study, Mn and Co substitution effects for Fe in Fe
) by modulating its electronic and magnetic structures. In this study, Mn and Co substitution effects for Fe in Fe N on S
N on S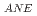 were investigated. Fe
were investigated. Fe Mn
Mn N and Fe
N and Fe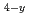 Co
Co N films in wide ranges of x and y were grown epitaxially on MgO(001) and (LaAlO
N films in wide ranges of x and y were grown epitaxially on MgO(001) and (LaAlO )
) (Sr
(Sr TaAlO
TaAlO )
) (001) substrates, respectively, using molecular beam epitaxy. The S
(001) substrates, respectively, using molecular beam epitaxy. The S value of the Fe
value of the Fe N film is suppressed by substituting Fe with Mn or Co. By measuring the ANE, Seebeck effect, and anomalous Hall effect, the transverse thermoelectric conductivity (
N film is suppressed by substituting Fe with Mn or Co. By measuring the ANE, Seebeck effect, and anomalous Hall effect, the transverse thermoelectric conductivity (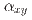 ) was evaluated. The composition dependence of S
) was evaluated. The composition dependence of S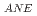 was dominated by the change of
was dominated by the change of 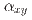 for both Fe
for both Fe Mn
Mn N and Fe
N and Fe Co
Co N films. First-principles calculations were conducted for the transverse electric conductivity (
N films. First-principles calculations were conducted for the transverse electric conductivity (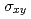 ) and
) and 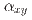 of Fe
of Fe N and Fe
N and Fe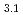 Co
Co N, and large
N, and large 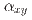 leading to large S
leading to large S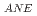 was predicted in Fe
was predicted in Fe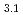 Co
Co N.
N.
石飛 尊之
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(7), p.075001_1 - 075001_2, 2025/07
We show that superzone gap formation-phenomena usually attributed to antiferroic ordering-can also arise from ferroic orders in materials featuring sublattice structures. Through an analysis of a  -orbital tight-binding model on a zigzag chain, we reveal that ferroquadrupolar or ferromagnetic ordering, as well as external magnetic fields, can generate a Su-Schrieffer-Heeger-type gap.
-orbital tight-binding model on a zigzag chain, we reveal that ferroquadrupolar or ferromagnetic ordering, as well as external magnetic fields, can generate a Su-Schrieffer-Heeger-type gap.
久保 勝規
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(7), p.074701_1 - 074701_5, 2025/07
Surface states of a tight-binding model with nearest-neighbor hopping on a diamond lattice of finite thickness are investigated. We consider systems with (001), (110), and (111) surfaces. Even if the surface direction is fixed, there is freedom to choose the surface structure due to the two-sublattice nature of a diamond lattice. The existence of surface states is governed by the topology of the matrix elements of the bulk Hamiltonian. In this sense, the existence of surface states is determined by the bulk Hamiltonian. However, the matrix elements depend on the choice of the unit cell, which should be chosen to conform to the surface structure. Thus, the surface states depend on the surface structure. We find that for each surface direction, there are two choices of surface structure, and depending on the chosen structure, the corresponding surface states emerge in distinct regions of the surface Brillouin zone.
 nanosheets for enhancing heat storage performance
nanosheets for enhancing heat storage performance吉迫 大輝*; 岡本 範彦*; 田中 万也; 市坪 哲
Communications Chemistry (Internet), 8, p.169_1 - 169_9, 2025/06
被引用回数:0これまで層状マンガン酸化物の層間への水分子の脱挿入時の給排熱機構を利用した蓄熱材研究開発が進められてきた。本研究では、結晶子サイズの小さいマンガン酸化物を合成することで層間だけでなく表面への水分子吸着により蓄熱容量が増加することを示した。
市川 真也; Gubler, P.; 成木 恵; 四日市 悟*
Journal of Subatomic Particles and Cosmology (Internet), 3, p.100018_1 - 100018_5, 2025/06
It is important to measure the hadron spectrum at finite density to explore the origin of hadron masses. At the KEK-PS E325 experiment,  mesons inside and outside nuclei were measured by using 12GeV pA reactions and significant spectral modification was observed. In order to accurately estimate the density that the
mesons inside and outside nuclei were measured by using 12GeV pA reactions and significant spectral modification was observed. In order to accurately estimate the density that the  mesons felt during the reaction, a PHSD transport calculation of the respective reaction is currently ongoing. In this paper, PHSD and the current status of its implementation are reported.
mesons felt during the reaction, a PHSD transport calculation of the respective reaction is currently ongoing. In this paper, PHSD and the current status of its implementation are reported.
石飛 尊之
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(7), p.073703_1 - 073703_4, 2025/06
We investigate both the nonmagnetic and magnetic ordered phases of CeCoSi using Landau theory. Our analysis predicts that three successive phase transitions occur at zero magnetic field. A quadrupole order parameter that emerges below 
 = 12 K acts as a weak symmetry-breaking field on the antiferromagnetic ordering below
= 12 K acts as a weak symmetry-breaking field on the antiferromagnetic ordering below  = 9.4 K, giving rise to two-stage magnetic transitions. In the higher-temperature antiferromagnetic phase in the temperature range in
= 9.4 K, giving rise to two-stage magnetic transitions. In the higher-temperature antiferromagnetic phase in the temperature range in 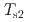 = 8 K
= 8 K 


 , an out-of-plane component of antiferromagnetic moment may be present or absent. If present, magnetic fields applied along the [100] and [110] directions induce additional magnetic phases.
, an out-of-plane component of antiferromagnetic moment may be present or absent. If present, magnetic fields applied along the [100] and [110] directions induce additional magnetic phases.
門野 良典*; 伊藤 孝
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(6), p.064601_1 - 064601_11, 2025/06
We extend the previously published model that distinguishes between the diffusive motion of diamagnetic muons and the dynamics of ions around the muon in matter, and propose a generalized model for 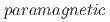
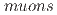 (Mu
(Mu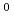 s, bound states of a muon and an unpaired electron) observed in non-metallic host materials. The new model distinguishes among the independent motion of unpaired electron associated with Mu
s, bound states of a muon and an unpaired electron) observed in non-metallic host materials. The new model distinguishes among the independent motion of unpaired electron associated with Mu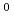 , the self-diffusive motion of Mu
, the self-diffusive motion of Mu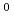 as single atomic entity, and that of the ions surrounding Mu
as single atomic entity, and that of the ions surrounding Mu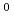 , where the muon spin relaxation is induced by dynamical fluctuations of the hyperfine (HF) field exerted from the unpaired electron (e.g., due to spin/charge exchange reaction) and/or that of the nuclear hyperfine (NHF) interactions between the unpaired electron and the surrounding ions. We have applied this model to the muonated radicals (Mu
, where the muon spin relaxation is induced by dynamical fluctuations of the hyperfine (HF) field exerted from the unpaired electron (e.g., due to spin/charge exchange reaction) and/or that of the nuclear hyperfine (NHF) interactions between the unpaired electron and the surrounding ions. We have applied this model to the muonated radicals (Mu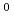 s in a polaron state) in conducting polymers, and examined the validity of the interpretations claimed in the earlier literature that the spin relaxation is induced by quasi-one dimensional jump motion of the unpaired electron. The result suggests that experimental support for such a claim is still inadequate and needs to be reexamined, including the possibility of other origins for the fluctuations. It is expected that our model will prove a useful guide for
s in a polaron state) in conducting polymers, and examined the validity of the interpretations claimed in the earlier literature that the spin relaxation is induced by quasi-one dimensional jump motion of the unpaired electron. The result suggests that experimental support for such a claim is still inadequate and needs to be reexamined, including the possibility of other origins for the fluctuations. It is expected that our model will prove a useful guide for  SR studies of various local dynamics involving paramagnetic muon states.
SR studies of various local dynamics involving paramagnetic muon states.
 Co
Co )Sn studied by
)Sn studied by  SR
SRCai, Y.*; Yoon, S.*; Sheng, Q.*; Zhao, G.*; Seewald, E. F.*; Ghosh, S.*; Ingham, J.*; Pasupathy, A. N.*; Queiroz, R.*; Lei, H.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(21), p.214412_1 - 214412_17, 2025/06
被引用回数:0We study the magnetic properties of the metallic kagome system (Fe Co
Co )Sn by a combination of muon spin relaxation (
)Sn by a combination of muon spin relaxation ( SR), magnetic susceptibility, and scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) measurements in single crystal specimens with Co concentrations
SR), magnetic susceptibility, and scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) measurements in single crystal specimens with Co concentrations  = 0, 0.11, 0.8. In the undoped antiferromagnetic compound FeSn, we find possible signatures for a previously unidentified phase that sets in at
= 0, 0.11, 0.8. In the undoped antiferromagnetic compound FeSn, we find possible signatures for a previously unidentified phase that sets in at 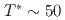 ~K, well beneath the Neel temperature
~K, well beneath the Neel temperature 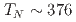 ~K as indicated by a peak in the relaxation rate 1/
~K as indicated by a peak in the relaxation rate 1/ observed in zero field (ZF) and longitudinal field (LF)
observed in zero field (ZF) and longitudinal field (LF)  SR measurements, with a corresponding anomaly in the ac and dc susceptibility, and an increase in the static width 1/
SR measurements, with a corresponding anomaly in the ac and dc susceptibility, and an increase in the static width 1/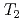 in ZF-
in ZF- SR measurements. No signatures of spatial symmetry breaking are found in STM down to 7~K. Related to the location and motion of muons in FeSn, we confirmed a previous report that about 40% of the implanted muons reside at a field-cancelling high symmetry site at
SR measurements. No signatures of spatial symmetry breaking are found in STM down to 7~K. Related to the location and motion of muons in FeSn, we confirmed a previous report that about 40% of the implanted muons reside at a field-cancelling high symmetry site at 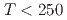 ~K, while an onset of thermal hopping changes the site occupancy at higher temperatures. In Fe
~K, while an onset of thermal hopping changes the site occupancy at higher temperatures. In Fe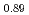 Co
Co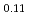 Sn, where disorder eliminated the field-cancellation effect, all the implanted muons exhibit precession and/or relaxation in the ordered state. In Fe
Sn, where disorder eliminated the field-cancellation effect, all the implanted muons exhibit precession and/or relaxation in the ordered state. In Fe Co
Co Sn, we find canonical spin glass behavior with freezing temperature
Sn, we find canonical spin glass behavior with freezing temperature 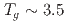 ~K; the ZF and LF-
~K; the ZF and LF- SR time spectra exhibit results similar to those observed in dilute alloy spin glasses CuMn and AuFe, with a critical behavior of
SR time spectra exhibit results similar to those observed in dilute alloy spin glasses CuMn and AuFe, with a critical behavior of  at
at 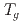 and
and 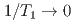 as
as 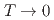 . The absence of spin dynamics at low temperatures makes a clear contrast to the spin dynamics observed by
. The absence of spin dynamics at low temperatures makes a clear contrast to the spin dynamics observed by  SR in many geometrically frustrated spin systems on insulating kagome, pyrochlore, and triangular lattices. The spin glass behavior of CoSn doped with dilute Fe moments is shown to originate primarily from the randomness of doped Fe moments rather than due to geometrical frustration of the underlying lattice.
SR in many geometrically frustrated spin systems on insulating kagome, pyrochlore, and triangular lattices. The spin glass behavior of CoSn doped with dilute Fe moments is shown to originate primarily from the randomness of doped Fe moments rather than due to geometrical frustration of the underlying lattice.
松下 太樹*; 小沢 耀弘*; 荒木 康史; 藤本 純治*; 佐藤 昌利*
Physical Review B, 111(24), p.245131_1 - 245131_11, 2025/06
被引用回数:0We investigate the intrinsic spin Nernst effect (SNE), a transverse spin current induced by temperature gradients, in topological Dirac semimetals (TDSMs) and magnetic Weyl semimetals (MWSMs) with Ising spin-orbit coupling. The intrinsic SNE is described by the spin Berry curvature, which reflects the geometric nature of TDSMs and MWSMs. We clarified that the intrinsic SNE becomes significant when the Fermi energy is near, but slightly deviates from, the energy of the point nodes. In this situation, Bloch electrons with strong spin Berry curvature contribute to the SNE while avoiding carrier compensation between electrons and holes. We found that in TDSMs with small Fermi surfaces, the spin Nernst angle, which measures the efficiency of the SNE, is larger than that observed in heavy metals. This suggests that TDSMs with small Fermi surfaces can achieve efficient heat-to-spin current conversion. In MWSMs, variation in the magnitude of the exchange coupling with magnetic moments significantly changes the SNE, affecting both the direction and magnitude of the spin Nernst current. This implies that ferromagnetic transitions can be used to reverse the spin Nernst current. These results provide the fundamentals for future topological spin caloritronics.
Sud, A.*; 山本 慧; 飯浜 賢志*; 石橋 一晃*; 深見 俊輔*; 紅林 秀和*; 水上 成美*
Physical Review Letters, 134(24), p.246704_1 - 246704_7, 2025/06
被引用回数:1We investigate the nonlinear coupling between acoustic (ac) and optical (op) modes in the coupled magnetization dynamics of synthetic antiferromagnets (SyAFs), utilizing current-driven resonance spectroscopy. A clear spectral splitting is evident in the ac mode when strongly excited by the radio frequency (RF) current at the driving frequency half that of the op mode resonance. The Landau-Lifshitz phenomenology aligns with the experimental observations, affirming the coupling of the RF-excited ac and op modes through three-magnon mixing. The nonlinearity enables a Rabi-like splitting in in-plane magnetized SyAF without breaking its natural symmetries. This discovery holds potential for advancing our understanding of nonlinear antiferromagnetic dynamics.
Go, G.*; Goli, D. P.*; 江崎 蘭世; Tserkovnyak, Y.*; Kim, S. K.*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 7(2), p.L022066_1 - L022066_7, 2025/06
It remains an open question whether or not the scalar spin chirality itself can exhibit a Hall-type transport. In this work, we show that the answer is yes: The scalar spin chirality is Hall-transported in Kagome ferromagnets and antiferromagnets under an external bias, engendering a phenomenon which we dub the scalar spin chirality Nernst effect. Our findings call for the need to lift the conventional assumption that the scalar spin chirality is a static quantity in order to discover the active roles of the scalar spin chirality in transport properties.
目黒 智成*; 小沢 耀弘*; 小林 浩二*; 荒木 康史; 野村 健太郎*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 7(2), p.L022065_1 - L022065_8, 2025/06
We theoretically find a topological spin-orbit torque (SOT) in the compensated ferrimagnetic Weyl semimetal Ti MnAl. The topological SOT arises from all the occupied states, which is free from dissipation. However, it is negligible in metallic magnets and was not reported in Weyl semimetals. We show the enhancement of the topological SOT from the mixed Berry curvature around the Weyl points in Ti
MnAl. The topological SOT arises from all the occupied states, which is free from dissipation. However, it is negligible in metallic magnets and was not reported in Weyl semimetals. We show the enhancement of the topological SOT from the mixed Berry curvature around the Weyl points in Ti MnAl. This finding provides a guiding principle for designing highly efficient SOT devices using the topological nature of ferrimagnetic Weyl semimetals.
MnAl. This finding provides a guiding principle for designing highly efficient SOT devices using the topological nature of ferrimagnetic Weyl semimetals.
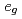 orbital system on a simple cubic lattice
orbital system on a simple cubic lattice久保 勝規
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(5), p.054703_1 - 054703_7, 2025/05
A tight-binding model for 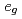 orbitals on a simple cubic lattice with finite thickness is investigated. The hopping integrals for nearest-neighboring sites are considered. We examine the electronic band structures for systems with (001), (110), and (111) surfaces. Electronic states well localized around the surfaces are found for the (110) and (111) surfaces. In particular, the surface state is flat and extends in the entire Brillouin zone for the (111) surface, provided the bulk band projected onto the surface Brillouin zone is gapped. We also find that these surface states possess octupole moments in both the (110) and (111) surface cases.
orbitals on a simple cubic lattice with finite thickness is investigated. The hopping integrals for nearest-neighboring sites are considered. We examine the electronic band structures for systems with (001), (110), and (111) surfaces. Electronic states well localized around the surfaces are found for the (110) and (111) surfaces. In particular, the surface state is flat and extends in the entire Brillouin zone for the (111) surface, provided the bulk band projected onto the surface Brillouin zone is gapped. We also find that these surface states possess octupole moments in both the (110) and (111) surface cases.
大井川 宏之
低温工学, 60(3), P. 59, 2025/05
「エネルギー基本計画」改定の原案では、超電導技術を駆使する核融合エネルギーは、高速炉、高温ガス炉と並び、次世代革新炉に位置付けられ開発研究を精力的に進めることになっている。また、エネルギー需要を抑制するための省エネや、大容量の蓄電システムの開発においても超電導技術は期待される。さらに、放射性廃棄物の核変換技術においても超電導陽子加速器の開発が期待されている。この他、ウラン・テルル化合物も超電導物質として特徴ある性質を示すことが最近分かってきた。広く連携を活性化してエネルギー問題の解決、地球環境の保全、新たな技術革新の創出などに取り組んでいくことが必要である。
 SRによるイオンダイナミクス解析の精密化に向けた動的久保-鳥谷部モデルの拡張
SRによるイオンダイナミクス解析の精密化に向けた動的久保-鳥谷部モデルの拡張伊藤 孝; 門野 良典*
固体物理, 60(4), p.197 - 206, 2025/04
 SRを用いた固体内イオンダイナミクス解析法が抱える深刻な矛盾を解消するために、その根幹をなす動的久保・鳥谷部モデルの拡張を試みた。我々の新しいモデルは、ミュオン静止描像の上での定量的な解析を可能にするだけでなく、この前提の妥当性を評価する手段を同時に提供する。
SRを用いた固体内イオンダイナミクス解析法が抱える深刻な矛盾を解消するために、その根幹をなす動的久保・鳥谷部モデルの拡張を試みた。我々の新しいモデルは、ミュオン静止描像の上での定量的な解析を可能にするだけでなく、この前提の妥当性を評価する手段を同時に提供する。
 Pt
Pt Ga
Ga with a honeycomb structure using extended X-ray absorption fine structure
with a honeycomb structure using extended X-ray absorption fine structure松本 裕司*; 渡部 悠貴*; Iesari, F.*; 大角 将勝*; 太田 玖吾*; 芳賀 芳範; 畑田 圭介*; 岡島 敏浩*
Metals, 15(4), p.436_1 - 436_13, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A heavy fermion system Ce Pt
Pt Ga
Ga is studied by the extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS). The spectra show that cerium is in trivalent state. On the other hand, EXAFS result is well explained by the proposed structure model with the honeycomb arrangement.
is studied by the extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS). The spectra show that cerium is in trivalent state. On the other hand, EXAFS result is well explained by the proposed structure model with the honeycomb arrangement.
Sheng, L.*; 山本 慧; 他18名*
Nature Physics, 8 Pages, 2025/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:82.94(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Controlling the spin current lies at the heart of spintronics and its applications. In ferromagnets, the sign of spin currents is fixed once the current direction is determined. However, spin currents in antiferromagnets can possess opposite polarizations, but this requires enormous magnetic fields to lift the degeneracy between the two modes. Therefore, controlling spin currents with opposite polarization is still a challenge. Here we demonstrate the control of spin currents at room temperature by magnon interference in a canted antiferromagnet, namely, haematite that has recently been classified as an altermagnet. Magneto-optical characterization by Brillouin light scattering reveals that the spatial periodicity of the beating patterns is tunable via the microwave frequency. We further observe that the inverse spin Hall voltage changes sign as the frequency is tuned, evincing a frequency-controlled switching of polarization of pure spin currents. Our work highlights the use of antiferromagnetic magnon interference to control spin currents, which substantially extends the horizon for the emerging field of coherent antiferromagnetic spintronics.
 Md produced in the
Md produced in the  He +
He +  Es reaction
Es reaction西尾 勝久; 廣瀬 健太郎; 牧井 宏之; Orlandi, R.; Kean, K. R.*; 塚田 和明; 豊嶋 厚史*; 浅井 雅人; 佐藤 哲也; Chiera, N. M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 111(4), p.044609_1 - 044609_12, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)In spontaneous fission (SF) it is found that the mass-asymmetric fission of well-known actinides suddenly changes to the symmetric fission when nucleus has a mass number 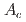 larger than 257. We have measured for the first time fission-fragment mass and total-kinetic-energy (TKE) distributions of the excited compound nucleus
larger than 257. We have measured for the first time fission-fragment mass and total-kinetic-energy (TKE) distributions of the excited compound nucleus  Md, populated in the reaction
Md, populated in the reaction  He+
He+ Es, using the rare isotope
Es, using the rare isotope  Es with a short half-life,
Es with a short half-life, 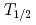 =276 days. The fission of
=276 days. The fission of  Md can be interpreted as involving 3 fission modes: an mass-asymmetric mode and two modes of mass-asymmetric fissions, the latter two are manifested by different TKE values. Predominantly symmetric fission was obtained at the excitation energy of 15.0 MeV. By increasing the energy to 18.0 MeV, the asymmetric fission mode dominates. Both such a strong change of fission modes within a small increase of excitation energy and the enhancement of asymmetric split are new phenomena in fission.
Md can be interpreted as involving 3 fission modes: an mass-asymmetric mode and two modes of mass-asymmetric fissions, the latter two are manifested by different TKE values. Predominantly symmetric fission was obtained at the excitation energy of 15.0 MeV. By increasing the energy to 18.0 MeV, the asymmetric fission mode dominates. Both such a strong change of fission modes within a small increase of excitation energy and the enhancement of asymmetric split are new phenomena in fission.
Huang, Y.-C.*; 吉川 貴史; 他5名*
Applied Physics Letters, 126(9), p.092403_1 - 092403_6, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)The application of spin-current volume effect (SVE) with volume magnetostriction of iron gallium (FeGa) films is examined for micro-diaphragm actuation. A silicon diaphragm measuring 1.5 1.5 mm
1.5 mm is coated with Pt (100-nm-thick) and FeGa (100-nm-thick) thin films. An alternating charge current passed through the FeGa/Pt/Si diaphragm under a magnetic field perpendicular to the charge current generates an alternating spin current via the spin Hall effect in the Pt film, transferring angular momentum from the Pt film to the FeGa film. The injected spin current provides energy and changes the effective temperature, thereby varying the thermal fluctuation of the magnetic moments. In a magnetic material with volume magnetostriction, the thermal fluctuation of the magnetic moments affects its volume. When the spin fluctuations change, the volume magnetostriction induces a corresponding expansion or contraction of the material. Both electrodeposited and ion-beam sputter-deposited FeGa films are investigated, and it is observed that the FeGa film exhibits SVE. The force generated by the SVE is evaluated based on the vibration amplitude at the fundamental resonant mode. This study demonstrates that the force generated by the SVE is correlated with the volume magnetostriction and the deposition process.
is coated with Pt (100-nm-thick) and FeGa (100-nm-thick) thin films. An alternating charge current passed through the FeGa/Pt/Si diaphragm under a magnetic field perpendicular to the charge current generates an alternating spin current via the spin Hall effect in the Pt film, transferring angular momentum from the Pt film to the FeGa film. The injected spin current provides energy and changes the effective temperature, thereby varying the thermal fluctuation of the magnetic moments. In a magnetic material with volume magnetostriction, the thermal fluctuation of the magnetic moments affects its volume. When the spin fluctuations change, the volume magnetostriction induces a corresponding expansion or contraction of the material. Both electrodeposited and ion-beam sputter-deposited FeGa films are investigated, and it is observed that the FeGa film exhibits SVE. The force generated by the SVE is evaluated based on the vibration amplitude at the fundamental resonant mode. This study demonstrates that the force generated by the SVE is correlated with the volume magnetostriction and the deposition process.