Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Dei, Shuntaro; Shibata, Masahito*; Negishi, Kumi*; Sugiura, Yuki; Amano, Yuki; Bateman, K.*; Wilson, J.*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kagami, Saya; Takeda, Masaki; et al.
Results in Earth Sciences (Internet), 3, p.100097_1 - 100097_16, 2025/12
Interactions between cement and host rock in geological repositories for radioactive waste will result in a chemically disturbed zone, which may potentially affect the long-term safety. This paper investigates the chemical evolution at the interface between cement (Ordinary Portland Cement: OPC and Low Alkaline Cement: LAC) and mudstone after 11 years of in situ reactions at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. The study combines various analytical techniques to identify the key reactions at the cement-rock interface, including cement dissolution, precipitation of secondary minerals such as calcite and C-(A-)S-H phases, cation exchange in montmorillonite and reduced porosity in mudstone. The study also highlights the effects of cement-mudstone interactions on radionuclide migration, such as reduction of diffusivity due to reduced porosity and enhancement of sorption due to incorporation into secondary minerals in the altered mudstone.
 C-stainless steel composites using the improved MPS method
C-stainless steel composites using the improved MPS methodAhmed, Z.*; Wu, S.*; Sharma, A.*; Kumar, R.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Pellegrini, M.*; Yokoyama, Ryo*; Okamoto, Koji*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 250, p.127343_1 - 127343_17, 2025/11
Mochizuki, Akihito; Matsui, Hiroya; Nakayama, Masashi; Sakamoto, Ryo*; Shibata, Masahito*; Motoshima, Takayuki*; Jo, Mayumi*
Case Studies in Construction Materials, 22, p.e04648_1 - e04648_20, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0The properties of low-pH cement used in the geological disposal of radioactive waste may change through atmospheric carbonation and degradation caused by groundwater during the long-term operation of a repository. In this study, we investigated the effects of atmospheric carbonation and groundwater contact on the chemical, microstructural, and transport properties of shotcrete made from low-pH, high-fly-ash silica-fume cement (HFSC) over a period of 16 years in an underground research laboratory. In both carbonated and degraded zones of the HFSC shotcrete, capillary porosity increased for pores of  300 nm in diameter, and the total porosity was higher than in undegraded zones. These changes in porosity may be associated with the decalcification of calcium-silicate-hydrate and decomposition of ettringite. Such changes were minor in altered zones of OPC shotcrete, indicating that HFSC shotcrete is less resistant to atmospheric carbonation and groundwater leaching under the studied conditions. However, the hydraulic conductivity in HFSC was low enough to fulfill the specific functional requirements of low-pH cements for geological disposal.
300 nm in diameter, and the total porosity was higher than in undegraded zones. These changes in porosity may be associated with the decalcification of calcium-silicate-hydrate and decomposition of ettringite. Such changes were minor in altered zones of OPC shotcrete, indicating that HFSC shotcrete is less resistant to atmospheric carbonation and groundwater leaching under the studied conditions. However, the hydraulic conductivity in HFSC was low enough to fulfill the specific functional requirements of low-pH cements for geological disposal.
Terada, Atsuhiko; Thwe Thwe, A.; Hino, Ryutaro*
JAEA-Review 2024-049, 400 Pages, 2025/03
In the aftermath of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, safety measures against hydrogen in severe accident has been recognized as a serious technical problem in Japan. As one of efforts to form a common knowledge base between nuclear engineers and experts on combustion and explosion, we issued the "Handbook of Advanced Nuclear Hydrogen Safety (1st edition)" in 2017. For improvement of the rational advancement of hydrogen safety measures and further reliability of hydrogen safety evaluation, a CFD analysis is highly expected to produce more precisely and quantitative results. We have been developing an integrated CFD analysis code system which can analyze hydrogen diffusion, explosion-combustion and structural integrity at the severe accident especially for pressurized water reactors (PWRs). We organized the role of LP and the CFD analyses and their utilization examples of hydrogen safety validation. Based on these results, we made the "Handbook of Advanced Nuclear Hydrogen Safety (2nd volume)". The analysis results of real scale PWR described in 2nd volume are confirmed by cross-analysis models and existing data obtained through representative small, medium and large-scale tests.
 C-SS eutectic melting and its relocation behaviour
C-SS eutectic melting and its relocation behaviourAhmed, Z.*; Sharma, A. K.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Okamoto, Koji*
Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 50(5), p.3361 - 3371, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Mitsuguchi, Takehiro; Yamano, Hiroya*
Whole history of the earth; Fragment of earth's history collected from the world, p.59 - 60, 2025/03
no abstracts in English
Ishihara, Takanori; Nishiyama, Nariaki; Kato, Yuri; Shimada, Koji
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-013, 17 Pages, 2024/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency and Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry conducted collaborative research as a part of "Establishment of Advanced Technology for Evaluating the Long-term Geosphere Stability on Geological Disposal Project of Radioactive Waste (Fiscal Years 2018-2022)" under a contract with the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. We conducted case studies of the effects of major natural phenomena (volcanic and igneous activity, deep-seated fluid, earthquakes and faulting, and uplift and erosion) required to be investigated and evaluated in relation to the selection and modeling of geological environments suitable for geological disposal in Japan, by applying techniques based on the latest research in various academic fields. Through these studies, we accumulated the knowledge necessary to solve problems and advanced our investigation and evaluation techniques. For effectively utilization of these achievements, we organized them in a Geographic Information System (GIS) and compiled them into a dataset that can be viewed in QGIS that free GIS software. This report described the procedure for creating this dataset and how to use it. With publishing this dataset, it is expected that not only seamlessly sharing information within each research field become possible, but also facilitating access and utilization of the research results by researchers in other fields and engineers involved in the geological disposal project.
Mitsuguchi, Takehiro; Okabe, Nobuaki*; Kokubu, Yoko; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 31(2), p.96 - 110, 2024/12
Geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste requires not only selecting sites appropriate for the waste repository, where its isolation ability would not be damaged by natural phenomena for several tens of thousands of years, but also rationally constructing the disposal system depending on site-specific geological environments and their anticipated long-term variability. Recently, elemental/isotopic compositions of underground fluids (deep groundwaters, hot/cold spring waters, brines associated with oil and natural gas reservoirs, and so on) in Japan have been studied for evaluating the long-term stability of the geological environments of this country. Iodine and its radioactive isotope  I (half-life = 15.7 million years) are included in the subjects of the study. The current review paper provides overviews of (i) the iodine content and iodine-129/127 ratio (
I (half-life = 15.7 million years) are included in the subjects of the study. The current review paper provides overviews of (i) the iodine content and iodine-129/127 ratio ( I/
I/ I ratio) of various materials in Earth's surface layers, (ii) relevant sample pretreatments and measurements, and (iii)
I ratio) of various materials in Earth's surface layers, (ii) relevant sample pretreatments and measurements, and (iii)  I/
I/ I data of the underground fluids in Japan, then gives (iv) some interpretations of the fluid
I data of the underground fluids in Japan, then gives (iv) some interpretations of the fluid  I/
I/ I data, along with their problems and uncertainties, and (v) some implications towards evaluating the long-term stability of geological environments.
I data, along with their problems and uncertainties, and (v) some implications towards evaluating the long-term stability of geological environments.
Miyakawa, Kazuya; Ishii, Eiichi; Imai, Hisashi*; Hirai, Satoru*; Ono, Hirokazu; Nakata, Kotaro*; Hasegawa, Takuma*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 31(2), p.82 - 95, 2024/12
no abstracts in English
 = 0.01-600
= 0.01-600 C,
C,  = 1-3000 bars,
= 1-3000 bars, 
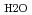 = 0.35-1.1 g cm
= 0.35-1.1 g cm , and
, and 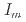 = 0
= 0
Walker, C. S.*; Arthur, R. C.*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Mihara, Morihiro
Applied Geochemistry, 175, p.106086_1 - 106086_17, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The thermodynamic properties and revised Helgeson-Kirkham-Flowers equation of state (r-H-K-F EoS) parameters of the hydrated (Si(OH) (aq), SiO(OH)
(aq), SiO(OH)
 and SiO
and SiO (OH)
(OH)
 ) and fictive dehydrated (SiO
) and fictive dehydrated (SiO (aq), HSiO
(aq), HSiO
 and SiO
and SiO
 ) monomeric silicon species are used extensively to describe the pH, composition, temperature, and pressure dependence of formation/breakdown reactions of all silicon-bearing compounds globally. Experimental log10 equilbrium constant, K values describing the formation reactions of the hydrated and dehydrated monomeric silicon species were therefore compiled from the literature, extrapolated to zero ionic strength by specific ion interaction theory as required and used to derive their thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters. Consideration of all formation reactions in the same study provides a collective, internally consistent update to the thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters of the monomeric silicon species that can provide a satisfactory match to the experimental log10 K values at
) monomeric silicon species are used extensively to describe the pH, composition, temperature, and pressure dependence of formation/breakdown reactions of all silicon-bearing compounds globally. Experimental log10 equilbrium constant, K values describing the formation reactions of the hydrated and dehydrated monomeric silicon species were therefore compiled from the literature, extrapolated to zero ionic strength by specific ion interaction theory as required and used to derive their thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters. Consideration of all formation reactions in the same study provides a collective, internally consistent update to the thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters of the monomeric silicon species that can provide a satisfactory match to the experimental log10 K values at  = 0.01-600
= 0.01-600 C,
C,  = 1-3000 bars,
= 1-3000 bars, 
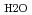 = 0.35-1.1 g cm
= 0.35-1.1 g cm , and zero ionic strength. These temperature and pressure limits comfortably bracket t=0.01-100
, and zero ionic strength. These temperature and pressure limits comfortably bracket t=0.01-100 C and P =1-270 bars relecant to the geological disposal of radioactive wastes at depths of up to 1 km.
C and P =1-270 bars relecant to the geological disposal of radioactive wastes at depths of up to 1 km.
Takayama, Yusuke; Sato, Daisuke*; Sugita, Yutaka
Kansai Geo-Symposium 2024; Chikasui Jiban Kankyo, Bosai, Keisoku Gijutsu Ni Kansuru Shinpojiumu Rombunshu, p.115 - 119, 2024/11
During the initial phases after closure of a high-level radioactive waste repository, the temperature of the buffer material will increase. Therefore, fundamental properties regarding the temperature dependence of bentonite, which is the main material of the buffer material, have been tested. The number of tests for the temperature dependence of displacement behavior is less than the number of tests for the temperature dependence of swelling pressure and permeability. In this paper, two tests were conducted using a consolidation test device that can control temperature conditions. One is a cyclic loading and unloading test under temperature conditions from room temperature to 80  C. The second is a temperature rise and fall test from room temperature to 80
C. The second is a temperature rise and fall test from room temperature to 80  C under stable loading condition. It was clarified that large deformations occur in the specimen under high temperature conditions, that the deformation associated with temperature changes is affected by the past stress path, and that irreversible deformation occurs under normal consolidation conditions.
C under stable loading condition. It was clarified that large deformations occur in the specimen under high temperature conditions, that the deformation associated with temperature changes is affected by the past stress path, and that irreversible deformation occurs under normal consolidation conditions.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Morita, Koji*
Proceedings of 13th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS13) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2024/11
Ogata, Manabu; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakanishi, Toshimichi*
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 76, p.123_1 - 123_11, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Marine terraces developed along the southeastern coast of Kii Peninsula, southwestern Japan, face a seismogenic region along the Nankai Trough. We determined the emergence age of one of these marine terraces by using feldspar OSL dating of the marine terrace sediments. The target marine terrace has previously been correlated with MIS 5e on the basis of morphostratigraphy. Samples for pIRIR dating were obtained from foreshore deposits of the marine terrace. pIRIR signals were measured at 150  C (pIRIR
C (pIRIR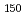 ) and 225
) and 225  C (pIRIR
C (pIRIR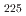 ). These results show that the surface of the marine terrace corresponds to MIS 5e rather than MIS 5c or 7, which is consistent with the chronological framework based on the morphological features of the terraces in this study area.
). These results show that the surface of the marine terrace corresponds to MIS 5e rather than MIS 5c or 7, which is consistent with the chronological framework based on the morphological features of the terraces in this study area.
Ito, Shinji*; Shimizu, Hiroyuki*; Ono, Shintaro*; Takayama, Yusuke
Doboku Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 80(8), p.24-00030_1 - 24-00030_18, 2024/08
In the design consideration of a geological disposal facility for radioactive waste, it is essential to perform a mechanical evaluation that takes into account phenomena that may occur from construction and operation to post-closure. With this background, we have developed the long-term mechanical analysis system MACBECE. In this research, we have built an analysis system that can consistently evaluate the mechanical behavior considering the thermal and hydraulic evolution after the closure of the repository by incorporating the constitutive model for unsaturated soils and coupling with the thermal-hydraulic analysis. As a validation, a mechanical analysis was conducted for the in-situ experiment for full-scale engineered barrier system performance experiment at Horonobe URL. Despite some discrepancies due to constraints in two-dimensional analysis, the extended functionality of the analysis code was confirmed to effectively repro-duce the measured data.
Morita, Koji*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 14th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation, and Safety (NTHOS-14) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2024/08
This paper describes the generalized model developed for these eutectic reactions between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as for the reactions that occur between eutectic reaction products in the solid and liquid states and SS or B
C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as for the reactions that occur between eutectic reaction products in the solid and liquid states and SS or B C. We also describe the thermophysical property model based on thermophysical property data.
C. We also describe the thermophysical property model based on thermophysical property data.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Emura, Yuki; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Morita, Koji*; Nakamura, Kinya*; Ahmed, Z.*; Pellegrini, M.*
Proceedings of 14th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation, and Safety (NTHOS-14) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2024/08
This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2022. A specific result in this paper is to obtain first experimental data of B C-SS eutectic freezing.
C-SS eutectic freezing.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Futagami, Satoshi; Higurashi, Koichi*
Proceedings of 14th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation, and Safety (NTHOS-14) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2024/08
This paper describes the application of safety design criteria (SDC) and safety design guidelines (SDG) developed in the Generation-IV International Forum on the natural circulation of sodium to sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs) recently designed in Japan.
 C-stainless steel using the Moving Particle Semi-Implicit (MPS) Method
C-stainless steel using the Moving Particle Semi-Implicit (MPS) MethodAhmed, Z.*; Wu, S.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Okamoto, Koji*; Sharma, A.*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 14th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation, and Safety (NTHOS-14) (Internet), 14 Pages, 2024/08
The analysis show that once eutectic reaction occurs, the boron diffuses into the stainless steel (SS) wall. Melting initiates at the B C and SS interface, with melt flow following SS cladding penetration. Also, we observed that as temperature rises, a proportional increase in the boron concentration within the melt. The updated MPS method indicated a computational capability of the eutectic reaction model used to effectively analyze control rod eutectic reactions, simulating severe accidents, and its subsequent relocation to understand the effect of B
C and SS interface, with melt flow following SS cladding penetration. Also, we observed that as temperature rises, a proportional increase in the boron concentration within the melt. The updated MPS method indicated a computational capability of the eutectic reaction model used to effectively analyze control rod eutectic reactions, simulating severe accidents, and its subsequent relocation to understand the effect of B C ingress into the core.
C ingress into the core.
Kikuchi, Shin; Kondo, Toshiki; Doi, Daisuke; Seino, Hiroshi; Ogawa, Kengo*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*
Proceedings of 14th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation, and Safety (NTHOS-14) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2024/08
Nakajima, Toru; Fukuda, Shoma; Sueoka, Shigeru; Niki, Sota*; Kawakami, Tetsuo*; Danhara, Toru*; Tagami, Takahiro*
Geochronology (Internet), 6(3), p.313 - 323, 2024/07
In this study, we explored the impacts of radiation damage and chemical composition on the etching time of fission tracks in monazite. Despite the potential of monazite fission-track (MFT) dating as an ultralow-temperature thermochronology, the comprehensive effects of radiation damage and non-formula elements, especially on the etching rate of MFTs, remain unexplored, and established analytical procedures are lacking. We quantified the degree of radiation damage (dFHWM) in Cretaceous to Quaternary monazites distributed in the Japan arc through Raman spectroscopy and chemical composition analyses. Subsequently, MFT etching was performed to examine the correlation between these parameters and the etching time. Estimation of the degree of radiation damage showed an increase in radiation damage corresponding to the cooling age of each geological unit. For example, the Toya ignimbrite (ca. 0.1 Ma) and the Kurobegawa granodiorite ( 0.8 Ma), both of which are types of monazite from Quaternary geological units, have dFHWM values of 0.27 and 0.55 cm
0.8 Ma), both of which are types of monazite from Quaternary geological units, have dFHWM values of 0.27 and 0.55 cm , respectively. In contrast, the Muro ignimbrite (ca. 15 Ma) has a dFHWM value of 4.01 cm
, respectively. In contrast, the Muro ignimbrite (ca. 15 Ma) has a dFHWM value of 4.01 cm , while the Kibe granite and the Sagawa granite, both of which are Cretaceous granitoids, yielded 7.35 and 6.31 cm
, while the Kibe granite and the Sagawa granite, both of which are Cretaceous granitoids, yielded 7.35 and 6.31 cm , respectively. MFT etching of these samples according to the existing recipe (6M HCl at 90
, respectively. MFT etching of these samples according to the existing recipe (6M HCl at 90 C for 60-90 min) was completed at 1200, 860, 210, 120, and 90 min for the Toya ignimbrite, Kurobegawa granodiorite, Muro ignimbrite, Sagawa granite, and Kibe granite, respectively.
C for 60-90 min) was completed at 1200, 860, 210, 120, and 90 min for the Toya ignimbrite, Kurobegawa granodiorite, Muro ignimbrite, Sagawa granite, and Kibe granite, respectively.