Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanigawa, Masafumi; Seya, Kazuhito*; Asakawa, Naoya*; Hayashi, Hiroyuki*; Horigome, Kazushi; Mukai, Yasunobu; Kitao, Takahiko; Nakamura, Hironobu; Henzlova, D.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-014, 63 Pages, 2025/02
The liquid waste treatment process generated sludge items at the plutonium conversion development facility. They are highly heterogeneous and contain large amounts of impurities (Na, Fe, Ni etc.). Therefore, the sludge items have very large sampling uncertainty and so the total measurement uncertainty is very large (approximately 24%). The plutonium scrap multiplicity counter (PSMC) measurement technique for sludge items was developed by joint research between the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). The technical validity for sludge items using the PSMC was evaluated using various types of sample measurements and Monte Carlo N-Particle transport code calculations. The PSMC measurement parameters were found to be valid for use with sludge items and the validity of multiplicity analysis was confirmed and demonstrated through comparisons with standard MOX powder and a standard sludge. As a result, the PSMC measurement values were shown to be consistent and reasonable and the large amount of impurity (Fe, Ni etc.) did not impact the results. Therefore, the measurement uncertainty of the improved nuclear material accountancy (NMA) procedure by combined PSMC and high-resolution gamma spectrometry was shown to be 6.5%. In addition, an acceptance test was conducted using PSMC/HRGS and IAEA benchmark equipment. Measured Pu mass by both equipment agrees within the measurement uncertainty of each method, and so the validity for Pu mass measurement by PSMC/HRGS was confirmed. The above results confirm the applicability of PSMC/HRGS as an additional NMA method for sludge and a newly designed NDA procedure based on this study is applied to sludge for NMA in PCDF.
Oizumi, Akito; Fukushima, Masahiro; Gunji, Satoshi; McKenzie, G.*; Amundson, K.*
International Criticality Safety Benchmark Evaluation Project (ICSBEP) Handbook (2022/23 edition) (Internet) , 313 Pages, 2024/11
This benchmark report was compiled to register a critical experiment using the lower-enriched uranium (LEU) system core to the International Criticality Safety Evaluation Project (ICSBEP). The LEU experiment was one of a series of joint experimental project with the Los Alamos Laboratory in the United States from 2015 to 2019 aimed at improving the design accuracy of the accelerator driven system (ADS). This core was loaded alternating highly-enriched uranium (HEU) and natural uranium (NU) to simulate LEU. In addition, a fast neutron spectrum system was constructed with not only HEU and NU but also lead which is part of coolant in the ADS. In this evaluation, it was clarified that the experimental uncertainty for the effective multiplication factor was almost 100 pcm. Moreover, the C/E-1 values of almost -70 pcm and -145 pcm were obtained by the calculation with the continuous energy Monte Carlo code MCNP and the nuclear data ENDF/B-VIII.0 and JENDL-4.0, respectively.
 compounds
compoundsFrazer, D.*; Saleh, T. A.*; Matsumoto, Taku; Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato; McClellan, K.*; White, J. T.*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 423, p.113136_1 - 113136_7, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nanoindentation based techniques can be employed on minute volumes of material to measure mechanical properties, including Young's modulus, hardness, and creep stress exponents. In this study, (U,Ce)O solid solutions samples are used to develop elevated temperature nanoindentation and nanoindentation creep testing methods for use on mixed oxide fuels. Nanoindentation testing was performed on 3 separate (Ux-1,Cex)O
solid solutions samples are used to develop elevated temperature nanoindentation and nanoindentation creep testing methods for use on mixed oxide fuels. Nanoindentation testing was performed on 3 separate (Ux-1,Cex)O compounds ranging from x equals 0.1 to 0.3 at up to 800
compounds ranging from x equals 0.1 to 0.3 at up to 800  C: their Young's modulus, hardness, and creep stress exponents were evaluated. The Young's modulus decreases in the expected linear manner while the hardness decreases in the expected exponential manner. The nanoindentation creep experiments at 800
C: their Young's modulus, hardness, and creep stress exponents were evaluated. The Young's modulus decreases in the expected linear manner while the hardness decreases in the expected exponential manner. The nanoindentation creep experiments at 800  C give stress exponent values, n=4.7-6.9, that suggests dislocation motion as the deformation mechanism.
C give stress exponent values, n=4.7-6.9, that suggests dislocation motion as the deformation mechanism.
 Ni
Ni In
In
Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Kotegawa, Hisashi*; To, Hideki*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(23), p.235152_1 - 235152_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigate the electronic state of Ni-substituted CeCo Ni
Ni In
In by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below
by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below 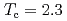 K for
K for 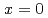 is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and
is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and  reaches zero for
reaches zero for 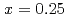 . The
. The  In NQR spectra for
In NQR spectra for 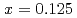 and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate
and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate  indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature (
indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature ( ) dependence of
) dependence of  for
for 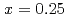 shows a maximum around
shows a maximum around 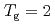 K and
K and  decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through
decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through 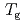 with a
with a 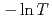 dependence. The peculiar T dependence of
dependence. The peculiar T dependence of  and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
 ;
;  In NQR/NMR and
In NQR/NMR and  Co NMR study
Co NMR studySakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Ramakrishna, S. K.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(8), p.085106_1 - 085106_12, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:30.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Antiferromagnetism in a prototypical quantum critical metal CeCoIn is known to be induced by slight substitutions of non-magnetic Zn atoms for In. In nominally 7% Zn substituted CeCoIn
is known to be induced by slight substitutions of non-magnetic Zn atoms for In. In nominally 7% Zn substituted CeCoIn , an antiferromagnetic (AFM) state coexists with heavy fermion superconductivity. Heterogeneity of the electronic states is investigated in Zn doped CeCoIn
, an antiferromagnetic (AFM) state coexists with heavy fermion superconductivity. Heterogeneity of the electronic states is investigated in Zn doped CeCoIn by means of nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonances (NQR and NMR). Site-dependent NQR relaxation rates
by means of nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonances (NQR and NMR). Site-dependent NQR relaxation rates  indicate that the AFM state is locally nucleated around Zn substituents in the matrix of a heavy fermion state, and percolates through the bulk at the AFM transition temperature
indicate that the AFM state is locally nucleated around Zn substituents in the matrix of a heavy fermion state, and percolates through the bulk at the AFM transition temperature  . At lower temperatures, an anisotropic superconducting (SC) gap below the SC transition temperature
. At lower temperatures, an anisotropic superconducting (SC) gap below the SC transition temperature  , and the SC state permeates through the AFM regions via a SC proximity effect. Applying an external magnetic field induces a spin-flop transition near 5 T, reducing the volume of the AFM regions. Consequently, a short ranged inhomogeneous AFM state survives and coexists with a paramagnetic Fermi liquid state at high fields.
, and the SC state permeates through the AFM regions via a SC proximity effect. Applying an external magnetic field induces a spin-flop transition near 5 T, reducing the volume of the AFM regions. Consequently, a short ranged inhomogeneous AFM state survives and coexists with a paramagnetic Fermi liquid state at high fields.
Lessux, G. G.*; Sakai, Hironori; Hattori, Taisuke*; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Kuhns, P. L.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Pagliuso, P. G.*; Urbano, R. R.*
Physical Review B, 101(16), p.165111_1 - 165111_6, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:42.79(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)CeRhIn is a Kondo-lattice prototype in which a magnetic field
is a Kondo-lattice prototype in which a magnetic field 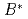
 31T induces an abrupt Fermi-surface (FS) reconstruction and pronounced in-plane electrical transport anisotropy all within its antiferromagnetic state. Here we report low-temperature nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements revealing a pronounced decrease in the
31T induces an abrupt Fermi-surface (FS) reconstruction and pronounced in-plane electrical transport anisotropy all within its antiferromagnetic state. Here we report low-temperature nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements revealing a pronounced decrease in the  In formal Knight shift, without changes in crystal or magnetic structures, of CeRhIn
In formal Knight shift, without changes in crystal or magnetic structures, of CeRhIn at fields (
at fields (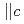 ) spanning
) spanning 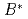 . We discuss the emergent state above
. We discuss the emergent state above 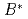 in terms of a change in Ce's 4
in terms of a change in Ce's 4 orbitals that arises from field-induced evolution of crystal-electric field (CEF) energy levels. This change in orbital character enhances hybridization between the 4
orbitals that arises from field-induced evolution of crystal-electric field (CEF) energy levels. This change in orbital character enhances hybridization between the 4 and the conduction electrons that leads ultimately to an itinerant quantum-critical point at
and the conduction electrons that leads ultimately to an itinerant quantum-critical point at 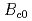
 50T.
50T.
Sekine, Megumi; Matsuki, Takuya; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Tsutagi, Koichi; Nishida, Naoki; Kitao, Takahiko; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Nakamura, Hironobu; LaFleur, A.*; Browne, M.*
JAEA-Technology 2019-023, 160 Pages, 2020/03
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has proposed in its Research and Development plan (STR-385), the development of technology to enable real-time flow measurement of nuclear material as a part of an advanced approach to effective and efficient safeguards for reprocessing facilities. To address this, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been tackling development of a new detector to enable monitoring of Pu in solutions with numerous FPs as a joint research program with U.S. DOE to cover whole reprocessing process. In this study, High Active Liquid Waste (HALW) Storage Facility in Tokai Reprocessing Plant was used as the test field. At first, the design information of HALW storage tank and radiation (type and intensity) were investigated to develop a Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport Code (MCNP) model. And then, dose rate distribution outside/ inside of the concrete cell where the HALW tank is located was measured to design new detectors and check MCNP model applicability. Using the newly designed detectors, gamma rays and neutron were continuously measured at the outside/ inside of the concrete cell to assess the radiation characteristics and to optimize detector position. Finally, the applicability for Pu monitoring technology was evaluated based on the simulation results and gamma-ray/neutron measurement results. We have found that there is possibility to monitor the change of Pu amount in solution by combination both of gamma-ray and neutron measurement. The results of this study suggested the applicability and capability of the Pu motoring to enhance safeguards for entire reprocessing facility which handles Pu with FP as a feasibility study. This is final report of this project.
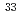 S nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of uranium disulfide
S nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of uranium disulfide  -US
-US
Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Ramakrishna, S. K.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Rosa, P. F. S.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Fisk, Z.*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 30, p.011169_1 - 011169_6, 2020/03
Uranium disulfide  -US
-US showing a semimetal-to-semiconductor crossover has been investigated by the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technique for
showing a semimetal-to-semiconductor crossover has been investigated by the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technique for 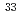 S nuclei with the nuclear spin of
S nuclei with the nuclear spin of 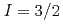 . Since the natural concentration 0.76% of NMR active
. Since the natural concentration 0.76% of NMR active 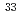 S nuclei is too dilute, the isotopic enrichment to
S nuclei is too dilute, the isotopic enrichment to  50% has been carried out for the single crystal growth. The
50% has been carried out for the single crystal growth. The 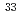 S NMR spectra have been successfully obtained using a single crystal of
S NMR spectra have been successfully obtained using a single crystal of  -US
-US with external fields along the crystallographic
with external fields along the crystallographic  axis. The S sites assignments have been made based on these NMR spectra.
axis. The S sites assignments have been made based on these NMR spectra.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Goda, J.*; Oizumi, Akito; Bounds, J.*; Cutler, T.*; Grove, T.*; Hayes, D.*; Hutchinson, J.*; McKenzie, G.*; McSpaden, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 194(2), p.138 - 153, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:53.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)To validate lead (Pb) nuclear cross sections, a series of integral experiments to measure lead void reactivity worth was conducted systematically in three fast spectra with different fuel compositions on the Comet critical assembly of the National Criticality Experiments Research Center. Previous experiments in a high-enriched uranium (HEU)/Pb and a low-enriched uranium (LEU)/Pb systems had been performed in 2016 and 2017, respectively. A follow-on experiment in a plutonium (Pu)/Pb system has been completed. The Pu/Pb system was constructed using lead plates and weapons grade plutonium plates that had been used in the Zero Power Physics Reactor (ZPPR) of Argonne National Laboratory until the 1990s. Furthermore, the HEU/Pb system was re-examined on the Comet critical assembly installed newly with a device that can guarantee the gap reproducibility with a higher accuracy and precision, and then the experimental data was re evaluated. Using the lead void reactivity worth measured in these three cores with different fuel compositions, the latest nuclear data libraries, JENDL 4.0 and ENDF/B VIII.0, were tested with the Monte Carlo calculation code MCNP version 6.1. As a result, the calculations by ENDF/B-VIII.0 were confirmed to agree with lead void reactivity worth measured in all the cores. It was furthermore found that the calculations by JENDL 4.0 overestimate by more than 20% for the Pu/Pb core while being in good agreements for the HEU/Pb and LEU/Pb cores.

Suzuki, Kiichi; Kato, Masato; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Uno, Hiroki*; Carvajal-Nunez, U.*; Nelson, A. T.*; McClellan, K. J.*
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 102(4), p.1994 - 2008, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:93.21(Materials Science, Ceramics)The fundamental properties of CeO were assessed using a range of experimental techniques. The oxygen potential of CeO
were assessed using a range of experimental techniques. The oxygen potential of CeO was measured by the thermogravimetric technique, and a numerical fit for the oxygen potential of CeO
was measured by the thermogravimetric technique, and a numerical fit for the oxygen potential of CeO is derived based on defect chemistry. Mechanical properties of CeO
is derived based on defect chemistry. Mechanical properties of CeO were obtained using sound velocity measurement, resonant ultrasound spectroscopy and nanoindentation. The obtained mechanical properties of CeO
were obtained using sound velocity measurement, resonant ultrasound spectroscopy and nanoindentation. The obtained mechanical properties of CeO are then used to evaluate the Debye temperature and Gruneisen constant. The heat capacity and thermal conductivity of CeO
are then used to evaluate the Debye temperature and Gruneisen constant. The heat capacity and thermal conductivity of CeO were also calculated using the Debye temperature and the Gruneisen constant. Finally, the thermal conductivity was calculated based upon laser flash analysis measurements. This result demonstrates that the thermal conductivity has strong dependence upon material purity.
were also calculated using the Debye temperature and the Gruneisen constant. Finally, the thermal conductivity was calculated based upon laser flash analysis measurements. This result demonstrates that the thermal conductivity has strong dependence upon material purity.
 Pu nuclear magnetic resonance in the candidate topological insulator PuB
Pu nuclear magnetic resonance in the candidate topological insulator PuB
Dioguardi, A. P.*; Yasuoka, Hiroshi*; Thomas, S. M.*; Sakai, Hironori; Cary, S. K.*; Kozimor, S. A.*; Albrecht-Schmitt, T. E.*; Choi, H. C.*; Zhu, J.-X.*; Thompson, J. D.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 99(3), p.035104_1 - 035104_6, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:42.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a detailed nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) study of  Pu in bulk and powdered single-crystal plutonium tetraboride (PuB
Pu in bulk and powdered single-crystal plutonium tetraboride (PuB ), which has recently been investigated as a potential correlated topological insulator. The
), which has recently been investigated as a potential correlated topological insulator. The  Pu NMR spectra are consistent with axial symmetry of the shift tensor showing for the first time that
Pu NMR spectra are consistent with axial symmetry of the shift tensor showing for the first time that  Pu NMR can be observed in an anisotropic environment and up to room temperature. The temperature dependence of the
Pu NMR can be observed in an anisotropic environment and up to room temperature. The temperature dependence of the  Pu shift, combined with a relatively long spin-lattice relaxation time (
Pu shift, combined with a relatively long spin-lattice relaxation time ( ), indicate that PuB
), indicate that PuB adopts a nonmagnetic state with gaplike behavior consistent with our density functional theory calculations. The temperature dependencies of the NMR Knight shift and
adopts a nonmagnetic state with gaplike behavior consistent with our density functional theory calculations. The temperature dependencies of the NMR Knight shift and 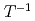 imply bulk gaplike behavior confirming that PuB
imply bulk gaplike behavior confirming that PuB is a good candidate topological insulator.
is a good candidate topological insulator.
Sekine, Megumi; Matsuki, Takuya; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Tsutagi, Koichi; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Nakamura, Hironobu; LaFleur, A.*; Browne, M.*
Proceedings of IAEA Symposium on International Safeguards; Building Future Safeguards Capabilities (Internet), 8 Pages, 2018/11
The IAEA has proposed, in its Research and Development plan (STR-385), the development of technology to enable real-time flow measurement of nuclear material as part of an advanced approach to effective and efficient safeguards for reprocessing facilities. To address this, JAEA and JNFL had previously designed and developed a neutron coincidence based non-destructive assay system to monitor Pu in solution directly after a purification process. To enhance this technology for entire reprocessing facilities, as a feasibility study, JAEA has been tackling development of a new detector to enable monitoring of Pu in solutions with numerous fission products (FPs) as a joint research program with the U.S. DOE. In this study, the High Active Liquid Waste (HALW) Storage Facility in Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) was used as the test bed. The design information of the HALW storage tank and radiation (type and intensity) were investigated, to develop a Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport Code (MCNP) model. Then, dose rate distribution inside the concrete cell where the HALW tank is located was measured, to enable design of new detectors and check the integrity of the MCNP model and its applicability. Using the newly-designed detectors,  -rays and neutrons could be measured continuously at the outside/inside of the concrete cell, to optimize detector position and the radiation characteristics. The applicability as a Pu-monitoring technology was evaluated, based on the simulation results and
-rays and neutrons could be measured continuously at the outside/inside of the concrete cell, to optimize detector position and the radiation characteristics. The applicability as a Pu-monitoring technology was evaluated, based on the simulation results and  -ray/neutron measurement results. We have found that there is a possibility to monitor the change of Pu amount in solution by combination of
-ray/neutron measurement results. We have found that there is a possibility to monitor the change of Pu amount in solution by combination of  -ray and neutron measurements. The results of this study suggest a feasibility study into the applicability and capability of Pu monitoring to enhance the entire reprocessing facility handling Pu with FPs. In this paper, a summary of the project will be presented.
-ray and neutron measurements. The results of this study suggest a feasibility study into the applicability and capability of Pu monitoring to enhance the entire reprocessing facility handling Pu with FPs. In this paper, a summary of the project will be presented.
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Talou, P.*; Plompen, A. J.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 148, p.189 - 213, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:78 Percentile:98.03(Physics, Nuclear)The CIELO collaboration has studied neutron cross sections on nuclides that significantly impact criticality in nuclear facilities -  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Fe,
Fe,  O and
O and  H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Goda, J.*; Bounds, J.*; Cutler, T.*; Grove, T.*; Hutchinson, J.*; James, M.*; McKenzie, G.*; Sanchez, R.*; Oizumi, Akito; et al.
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 189, p.93 - 99, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:60.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)To validate lead (Pb) nuclear cross sections, a series of integral experiments to measure lead void reactivity worths was conducted in a high-enriched uranium (HEU)/Pb system and a low enriched uranium (LEU)/Pb system using the Comet Critical Assembly at NCERC. The critical experiments were designed to provide complementary data sets having different sensitivities to scattering cross sections of lead. The larger amount of the  U present in the LEU/Pb core increases the neutron importance above 1 MeV compared with the HEU/Pb core. Since removal of lead from the core shifts the neutron spectrum to the higher energy region, positive lead void reactivity worths were observed in the LEU/Pb core while negative values were observed in the HEU/Pb core. Experimental analyses for the lead void reactivity worths were performed with the Monte Carlo calculation code MCNP6.1 together with nuclear data libraries, JENDL 4.0 and ENDF/B VII.1. The calculation values were found to overestimate the experimental ones for the HEU/Pb core while being consistent for the LEU/Pb core.
U present in the LEU/Pb core increases the neutron importance above 1 MeV compared with the HEU/Pb core. Since removal of lead from the core shifts the neutron spectrum to the higher energy region, positive lead void reactivity worths were observed in the LEU/Pb core while negative values were observed in the HEU/Pb core. Experimental analyses for the lead void reactivity worths were performed with the Monte Carlo calculation code MCNP6.1 together with nuclear data libraries, JENDL 4.0 and ENDF/B VII.1. The calculation values were found to overestimate the experimental ones for the HEU/Pb core while being consistent for the LEU/Pb core.
Swinhoe, M. T.*; Menlove, H. O.*; Marlow, J. B.*; Makino, Risa; Nakamura, Hironobu
LA-UR-17-23474, 28 Pages, 2017/04
The Inventory Verification Sample system (INVS) has been used for IAEA verification measurement at the Plutonium Conversion Development Facility for MOX powder and Pu solution samples (measurement uncertainty: about 3-5%). If the measurement uncertainty can be improved (to  1%), it is expected that the range of usage can be extended and it could reduce the number of destructive analyses. In order to improve the measurement uncertainty for solution samples, we conducted three different types of calibration method that are passive calibration curve method, known-
1%), it is expected that the range of usage can be extended and it could reduce the number of destructive analyses. In order to improve the measurement uncertainty for solution samples, we conducted three different types of calibration method that are passive calibration curve method, known- method and multiplicity method after optimization of detector parameter and sample position. In the range of concentration of typical solution samples, a good correlation was found between measured doubles and
method and multiplicity method after optimization of detector parameter and sample position. In the range of concentration of typical solution samples, a good correlation was found between measured doubles and  Pu effective mass in the three methods. Especially, the result of the conventional calibration curve method and known-
Pu effective mass in the three methods. Especially, the result of the conventional calibration curve method and known- method met our target uncertainty within 1% (22 hours measurement). Since it is thought that background singles change may affect measurement uncertainty, an additional shielding was installed around the INVS to reduce those effects. This shielding improved measurement uncertainty in known-
method met our target uncertainty within 1% (22 hours measurement). Since it is thought that background singles change may affect measurement uncertainty, an additional shielding was installed around the INVS to reduce those effects. This shielding improved measurement uncertainty in known- method. The results with this shielding suggests passive calibration method and known-
method. The results with this shielding suggests passive calibration method and known- method could achieve the target uncertainty within 1% less than 1 hour measurement time.
method could achieve the target uncertainty within 1% less than 1 hour measurement time.
Nakamura, Hironobu; Nakamichi, Hideo; Mukai, Yasunobu; Hosoma, Takashi; Kurita, Tsutomu; LaFleur, A. M.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics & Computational Methods Applied to Nuclear Science & Engineering (M&C 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2017/04
In order to maintain facility nuclear material accountancy (NMA) and safeguards properly, to understand where and how much holdup deposit in the process is presence is very important for the cleanout before PIT. JAEA and LANL developed a GloveBox Cleanout Assistance Tool (BCAT) to help cleanout (MOX powder recovering in a glovebox) for invisible holdup effectively by computational approach which is called distributed source-term approach (DSTA). The BCAT tool is a simple neutron measurement slab detectors and helps operator to find locations of holdup. To know the holdup location and the activity from the neutron measurements, the relation between BCAT measurements results at predetermined positions (57 positions) and source voxels (53 voxels) that we want to know the holdup activity was mathematically defined as a matrix by the MCNPX simulation. The model of MCNPX for entire process is very precisely established. We have implemented and experimentally proved that the BCAT tool can direct the operator to recoverable holdup that would otherwise be accounted for as MUF. Reducing facility MUF results in a direct improvement of the facility NMA. The BCAT enables the staff to significantly improve their knowledge of the locations of residual holdup in the process area. JAEA would like to use this application for dismantling of the glovebox with transparency in the future.
 He replacement technologies; Development of HLNB counter
He replacement technologies; Development of HLNB counterTanigawa, Masafumi; Mukai, Yasunobu; Nakamura, Hironobu; Kurita, Tsutomu; Henzlova, D.*; Menlove, H. O.*
Dai-37-Kai Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nihon Shibu Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2017/02
no abstracts in English
 He-alternative HLNC-type counter; High Level Neutron counter-Boron (HLNB)
He-alternative HLNC-type counter; High Level Neutron counter-Boron (HLNB)Henzlova, D.*; Menlove, H. O.*; Tanigawa, Masafumi; Mukai, Yasunobu; Nakamura, Hironobu
EUR-28795-EN (Internet), p.313 - 323, 2017/00
Facing the depletion of  He gas supply and the continuing uncertainty of options for future resupply, Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) designed and built a
He gas supply and the continuing uncertainty of options for future resupply, Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) designed and built a  He free full scale thermal neutron coincidence counter based on boron-lined parallel-plate proportional technology. The counter was designed as a direct alternative to High Level Neutron Coincidence counter (HLNC-II). This paper provides a summary of performance evaluation of HLNB under realistic field conditions at Plutonium Conversion Development Facility (PCDF) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The field test included a range of small to large mass MOX materials that represent realistic process samples and provided key insight on and validation of the feasibility of HLNB as a safeguards instrument in realistic facility environment. In particular, the results of verification measurements demonstrate that HLNB is capable to satisfy ITV expected for HLNC-II-type counter of 2.1% in 300s measurement time.
He free full scale thermal neutron coincidence counter based on boron-lined parallel-plate proportional technology. The counter was designed as a direct alternative to High Level Neutron Coincidence counter (HLNC-II). This paper provides a summary of performance evaluation of HLNB under realistic field conditions at Plutonium Conversion Development Facility (PCDF) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The field test included a range of small to large mass MOX materials that represent realistic process samples and provided key insight on and validation of the feasibility of HLNB as a safeguards instrument in realistic facility environment. In particular, the results of verification measurements demonstrate that HLNB is capable to satisfy ITV expected for HLNC-II-type counter of 2.1% in 300s measurement time.
Sekine, Megumi; Matsuki, Takuya; Suzuki, Satoshi; Tanigawa, Masafumi; Yasuda, Takeshi; Yamanaka, Atsushi; Tsutagi, Koichi; Nakamura, Hironobu; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; LaFleur, A. M.*; et al.
EUR-28795-EN (Internet), p.788 - 796, 2017/00
The IAEA has proposed in its long-term R&D plan, the development of technology to enable real-time flow measurement of nuclear material as a part of an advanced approach to effective and efficient safeguards for reprocessing facilities. To address this, JAEA has designed and developed a neutron coincidence based nondestructive assay system to monitor Pu directly in solutions which is after purification process and contains very little fission products (FPs). A new detector to enable monitoring of Pu in solutions with numerous FPs is being developed as a joint research program with U.S. DOE at the High Active Liquid Waste (HALW) Storage Facility in Tokai Reprocessing Plant. As the first step, the design information of HALW tank was investigated and samples of HALW was taken and analyzed for Pu concentration and isotope composition, density, content of dominant nuclides emitting  ray or neutron, etc. in order to develop a Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport Code (MCNP) of the HALW tank. In addition,
ray or neutron, etc. in order to develop a Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport Code (MCNP) of the HALW tank. In addition,  ray source spectra simulated by Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) was developed by extracting peaks from the analysis data with germanium detector. These outputs are used for the fundamental data in the MCNP model which is then used to evaluate the type of detector, shielding design and measurement positions. In order to evaluate available radiations to measure outside the cell wall, continuous
ray source spectra simulated by Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) was developed by extracting peaks from the analysis data with germanium detector. These outputs are used for the fundamental data in the MCNP model which is then used to evaluate the type of detector, shielding design and measurement positions. In order to evaluate available radiations to measure outside the cell wall, continuous  ray and neutron measurement were carried out and the results were compared to the simulation results. The measurement results showed that there are no FP peaks above 3 MeV. This paper presents an overview of the research plan, characteristics of HALW, development of source term for MCNP, simulation of radiation dose from the HALW tank and radiation measurement results at outside of cell wall.
ray and neutron measurement were carried out and the results were compared to the simulation results. The measurement results showed that there are no FP peaks above 3 MeV. This paper presents an overview of the research plan, characteristics of HALW, development of source term for MCNP, simulation of radiation dose from the HALW tank and radiation measurement results at outside of cell wall.
 Th-
Th- U age dating of bulk uranium for nuclear forensics
U age dating of bulk uranium for nuclear forensicsGaffney, A.*; Hubert, A.*; Kinman, W. S.*; Magara, Masaaki; Okubo, Ayako; Pointurier, F.*; Schorzman, K. C.*; Steiner, R. E.*; Williams, R. W.*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 307(3), p.2055 - 2060, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:90.18(Chemistry, Analytical)In and inter-laboratory measurement comparison study, four laboratories (LLNL, LANL, CEA, JAEA) determined  Th-
Th- U model ages of uranium certified reference material NBL U050 using isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The model dates determined by the participating laboratories range from 9 March 1956 to 19 October 1957, and are indistinguishable given the associated measurement uncertainties. These model ages are concordant with to slightly older than the known production age of NBL U050, indicating unsufficient purification of U050.
U model ages of uranium certified reference material NBL U050 using isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The model dates determined by the participating laboratories range from 9 March 1956 to 19 October 1957, and are indistinguishable given the associated measurement uncertainties. These model ages are concordant with to slightly older than the known production age of NBL U050, indicating unsufficient purification of U050.