Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Go, G.*; Goli, D. P.*; Esaki, Nanse; Tserkovnyak, Y.*; Kim, S. K.*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 7(2), p.L022066_1 - L022066_7, 2025/06

Jin, H.*; Choi, E. S.*; Wu, H.-C.*; Curro, N. J.*; Nawa, Kazuhiro*; Sato, Taku*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ohara, Takashi; Klavins, P.*; Taufour, V.*
Physical Review B, 111(3), p.035103_1 - 035103_7, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Amano, Yuki; Sachdeva, R.*; Gittins, D.*; Anantharaman, K.*; Lei, S.*; Valentin-Alvarado, L. E.*; Diamond, S.*; Beppu, Hikari*; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Mochizuki, Akihito; et al.
Environmental Microbiome (Internet), 19, p.105_1 - 105_17, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Genetics & Heredity) archaea host diverse and interacting extrachromosomal elements
archaea host diverse and interacting extrachromosomal elementsShi, L.-D.*; West-Roberts, J.*; Schoelmerich, M. C.*; Penev, P. I.*; Chen, L.-X.*; Amano, Yuki; Lei, S.*; Sachdeva, R.*; Banfield, J. F.*
Nature Microbiology (Internet), 9(9), p.2422 - 2433, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:39.49(Microbiology)Esser, S. P.*; Rahlff, J.*; Zhao, W.*; Predl, M.*; Plewka, J.*; Sures, K.*; Wimmer, F.*; Lee, J.*; Adam, P. S.*; McGonigle, J.*; et al.
Nature Microbiology (Internet), 8(9), p.1619 - 1633, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:74.53(Microbiology) archaea
archaeaSchoelmerich, M. C.*; Oubouter, H. T.*; Sachdeva, R.*; Penev, P. I.*; Amano, Yuki; West-Roberts, J.*; Welte, C. U.*; Banfield, J. F.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.7085_1 - 7085_11, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:72.26(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Nakata, Koki
Kotai Butsuri, 56(8), p.429 - 439, 2021/08
We review the thermomagnetic relation of bosons, the Wiedemann-Franz law for magnon transport, and discuss the universality.
Jaffe, A. L.*; Thomas, A. D.*; He, C.*; Keren, R.*; Valentin-Alvarado, L. E.*; Munk, P.*; Bouma-Gregson, K.*; Farag, I. F.*; Amano, Yuki; Sachdeva, R.*; et al.
mBio, 12(4), p.e00521-21_1 - e00521-21_21, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:87.18(Microbiology)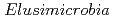 are metabolically diverse compared to gut microbiome
are metabolically diverse compared to gut microbiome 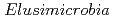 and some have a novel nitrogenase paralog
and some have a novel nitrogenase paralogM heust, R.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Matheus Carnevali, P. B.*; Farag, I. F.*; He, C.*; Chen, L.-X.*; Amano, Yuki; Hug, L. A.*; Banfield, J. F.*
heust, R.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Matheus Carnevali, P. B.*; Farag, I. F.*; He, C.*; Chen, L.-X.*; Amano, Yuki; Hug, L. A.*; Banfield, J. F.*
ISME Journal, 14(12), p.2907 - 2922, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:71 Percentile:96.30(Ecology)Al-Shayeb, B.*; Sachdeva, R.*; Chen, L.-X.*; Ward, F.*; Munk, P.*; Devoto, A.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Olm, M. R.*; Bouma-Gregson, K.*; Amano, Yuki; et al.
Nature, 578(7795), p.425 - 431, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:295 Percentile:99.46(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Atz, M.*; Salazar, A.*; Hirano, Fumio; Fratoni, M.*; Ahn, J.*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 124, p.28 - 38, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)The likelihood for criticality in the far field of a repository was evaluated for direct disposal of commercial light water reactor used nuclear fuel. Two models were used in combination for this evaluation: (1) a neutronics model to estimate the minimum critical masses of spherical, water-saturated depositions of fuel material; (2) a transport model to simulate the dissolution of fuel material from multiple canisters and the subsequent transport of the solutes through host rock to a single accumulation location. The results suggest that accumulation of a critical mass is possible under conservative conditions but that these conditions are unlikely to occur, especially in the vicinity of a carefully-arranged repository.
Kim, S. K.*; Nakata, Koki; Loss, D.*; Tserkovnyak, Y.*
Physical Review Letters, 122(5), p.057204_1 - 057204_6, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:93.53(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically study the thermal Hall effect by magnons in skyrmion crystal phases of ferrimagnets in the vicinity of the angular momentum compensation point (CP). For an experimental proposal, we predict that themagnonic thermal Hall conductivity changes its sign when the ferrimagnet is tuned across the CP, providing a way to control heat flux in spin-caloritronic devices on the one hand and a feasible way todetect the CP of ferrimagnets on the other hand.
Matheus Carnevali, P. B.*; Schulz, F.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Kantor, R. S.*; Shih, P.*; Sharon, I.*; Santini, J.*; Olm, M. R.*; Amano, Yuki; Thomas, B. C.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.463_1 - 463_15, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:88.33(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Okumura, Masahiko; Kerisit, S.*; Bourg, I. C.*; Lammers, L. N.*; Ikeda, Takashi*; Sassi, M.*; Rosso, K. M.*; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 189, p.135 - 145, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:87.43(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
Li, B.; Wang, H.*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Zhang, Q.*; Feygenson, M.*; Yu, H. L.*; Wu, D.*; Ohara, Koji*; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Shibata, Kaoru; et al.
Nature Materials, 17(3), p.226 - 230, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:161 Percentile:97.18(Chemistry, Physical)Liu, X.*; Fratoni, M.*; Ahn, J.*; Hirano, Fumio
Proceedings of 2017 International High-Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM 2017) (CD-ROM), p.595 - 599, 2017/04
Atz, M.*; Liu, X.*; Fratoni, M.*; Ahn, J.*; Hirano, Fumio
Proceedings of 2017 International High-Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM 2017) (CD-ROM), p.608 - 614, 2017/04
Salazar, A.*; Fratoni, M.*; Ahn, J.*; Hirano, Fumio
Proceedings of 2017 International High-Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM 2017) (CD-ROM), p.600 - 607, 2017/04
 and metal transformations associated with novel bacteria and archaea in deep terrestrial subsurface sediments
and metal transformations associated with novel bacteria and archaea in deep terrestrial subsurface sedimentsHernsdorf, A. W.*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Ise, Kotaro; Suzuki, Yohei*; Anantharaman, K.*; Probst, A. J.*; Burstein, David*; Thomas, B. C.*; Banfield, J. F.*
ISME Journal, 11, p.1915 - 1929, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:107 Percentile:96.15(Ecology)To evaluate the potential for interactions between microbial communities and disposal systems, we explored the structure and metabolic function of a sediment-hosted subsurface ecosystem associated with Horonobe Underground Research Center, Hokkaido, Japan. Overall, the ecosystem is enriched in organisms from diverse lineages and many are from phyla that lack isolated representatives. The majority of organisms can metabolize H , often via oxidative [NiFe] hydrogenases or electron-bifurcating [FeFe] hydrogenases that enable ferredoxin-based pathways, including the ion motive Rnf complex. Many organisms implicated in H
, often via oxidative [NiFe] hydrogenases or electron-bifurcating [FeFe] hydrogenases that enable ferredoxin-based pathways, including the ion motive Rnf complex. Many organisms implicated in H metabolism are also predicted to catalyze carbon, nitrogen, iron, and sulfur transformations. Notably, iron-based metabolism was predicted in a bacterial lineage where this function has not been predicted previously and in an ANME-2d archaeaon that is implicated in methane oxidation. We infer an ecological model that links microorganisms to sediment-derived resources and predict potential impacts of microbial activity on H
metabolism are also predicted to catalyze carbon, nitrogen, iron, and sulfur transformations. Notably, iron-based metabolism was predicted in a bacterial lineage where this function has not been predicted previously and in an ANME-2d archaeaon that is implicated in methane oxidation. We infer an ecological model that links microorganisms to sediment-derived resources and predict potential impacts of microbial activity on H accumulation and radionuclide migration.
accumulation and radionuclide migration.
Hug, L. A.*; Baker, B. J.*; Anantharaman, K.*; Brown, C. T.*; Probst, A. J.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Butterfield, C. N.*; Hernsdorf, A. W.*; Amano, Yuki; Ise, Kotaro; et al.
Nature Microbiology (Internet), 1(5), p.16048_1 - 16048_6, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:1378 Percentile:99.96(Microbiology)The tree of life is one of the most important organizing principles in biology. Gene surveys suggest the existence of an enormous number of branches, but even an approximation of the full scale of The Tree has remained elusive. Here, we use newly available information from genomes of uncultivated organisms, along with other published sequences, to present a new version of the Tree of life, with Bacteria, Archaea and Eukaryotes included. The depiction is both a global overview and a snapshot of the diversity within each major lineage. The results imply the predominance of bacterial diversification and underline the importance of organisms lacking isolated representatives, with substantial evolution concentrated in a major radiation of such organisms.