Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yildirim, A. C.*; Mei, H.*; Toda, Kanako*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Saito, Takumi*
Applied Clay Science, 274, p.107853_1 - 107853_9, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Aono, Ryuji; Goto, Katsunori*; Kinase, Akari; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Haraga, Tomoko; Iseda, Hirokatsu
JAEA-Data/Code 2025-006, 24 Pages, 2025/07
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planned to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples stored at the waste storage facility L. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 12 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Co,
Co,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2020.
Am) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2020.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Ueno, Katsuhiro; Watanabe, Masayuki
Scientific Reports (Internet), 15, p.18515_1 - 18515_7, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0We first demonstrate a nonaqueous rechargeable battery using uranium and iron as active materials. This uranium-iron battery achieves an open-circuit voltage of approximately 1.3 V, exhibits stable cycling performance, and delivers a good Coulombic efficiency of 86 2%. These characteristics suggest a promising avenue for utilizing depleted uranium in innovative applications.
2%. These characteristics suggest a promising avenue for utilizing depleted uranium in innovative applications.
 Pt
Pt Ga
Ga with a honeycomb structure using extended X-ray absorption fine structure
with a honeycomb structure using extended X-ray absorption fine structureMatsumoto, Yuji*; Watabe, Yuki*; Iesari, F.*; Osumi, Masakatsu*; Ota, Kyugo*; Haga, Yoshinori; Hatada, Keisuke*; Okajima, Toshihiko*
Metals, 15(4), p.436_1 - 436_13, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe
FeNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.300 - 307, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) with
with  = 2.1 K revealed by
= 2.1 K revealed by  Te NMR
Te NMRMatsumura, Hiroki*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; 13 of others*
Physical Review B, 111(9), p.094507_1 - 094507_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Yomogida, Takumi
Hoshako, 38(1), p.19 - 25, 2025/01
High-energy-resolution fluorescence detection-X-ray absorption near-edge structure (HERFD-XANES) spectroscopy has enabled us to discuss the electronic structure of actinide compounds in more detail than with conventional XANES spectroscopy. We are conducting research with the aim of contributing to the prediction of the migration behavior of trace actinide elements in the environment by performing actinide speciation in various environmental samples. In this paper, we introduce the content of the discussion of the electronic state of U from the perspective of basic science, which is important for advancing application of HERFD-XANES spectroscopy to environmental science.
 and Fe-Zr melt
and Fe-Zr meltNakajima, Kunihisa; Takano, Masahide
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(1), p.78 - 85, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)At TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, it is estimated that considerable amounts of cesium still remain in the reactors from the analysis results using the severe accident analysis codes and the reverse analysis from contaminated water. Since cesium is known to form stable compounds with uranium and zirconium, chemisorption experiments with uranium dioxide pellets and iron-zirconium melts for cesium hydroxide vapor were carried out. As the results, formations of cesium uranate, Cs UO
UO , and cesium zirconate, Cs
, and cesium zirconate, Cs ZrO
ZrO , were confirmed, indicating that cesium was chemisorbed on both of the uranium dioxide pellets and the iron-zirconium melts in an Ar-H
, were confirmed, indicating that cesium was chemisorbed on both of the uranium dioxide pellets and the iron-zirconium melts in an Ar-H -H
-H O flow and an Ar-H
O flow and an Ar-H flow, respectively. Therefore, it was considered that cesium released from fuel might be trapped by chemisorption with fuels and/or iron-zirconium melts during light water reactor severe accidents.
flow, respectively. Therefore, it was considered that cesium released from fuel might be trapped by chemisorption with fuels and/or iron-zirconium melts during light water reactor severe accidents.
Nakamura, Satoshi; Ishii, Sho*; Kato, Hitoshi*; Ban, Yasutoshi; Hiruta, Kenta; Yoshida, Takuya; Uehara, Hiroyuki; Obata, Hiroki; Kimura, Yasuhiko; Takano, Masahide
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(1), p.56 - 64, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)A dissolution method for analyzing the elemental composition of fuel debris using the sodium peroxide (Na O
O ) fusion technique has been developed. Herein, two different types of simulated debris materials (such as solid solution of (Zr,RE)O
) fusion technique has been developed. Herein, two different types of simulated debris materials (such as solid solution of (Zr,RE)O and molten core-concrete interaction products (MCCI)) were taken. At various temperatures, these debris materials were subsequently fused with Na
and molten core-concrete interaction products (MCCI)) were taken. At various temperatures, these debris materials were subsequently fused with Na O
O in crucibles, which are made of different materials, such as Ni, Al
in crucibles, which are made of different materials, such as Ni, Al O
O , Fe, and Zr. Then, the fused samples are dissolved in nitric acid. Furthermore, the effects of the experimental conditions on the elemental composition analysis were evaluated using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES), which suggested the use of a Ni crucible at 923 K as an optimum testing condition. The optimum testing condition was then applied to the demonstration tests with Three Mile Island unit-2 (TMI-2) debris in a shielded concrete cell, thereby achieving complete dissolution of the debris. The elemental composition of TMI-2 debris revealed by the proposed dissolution method has good reproducibility and has an insignificant contradiction in the mass balance of the sample. Therefore, this newly developed reproducible dissolution method can be effectively utilized in practical applications by dissolving fuel debris and estimating its elemental composition.
, Fe, and Zr. Then, the fused samples are dissolved in nitric acid. Furthermore, the effects of the experimental conditions on the elemental composition analysis were evaluated using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES), which suggested the use of a Ni crucible at 923 K as an optimum testing condition. The optimum testing condition was then applied to the demonstration tests with Three Mile Island unit-2 (TMI-2) debris in a shielded concrete cell, thereby achieving complete dissolution of the debris. The elemental composition of TMI-2 debris revealed by the proposed dissolution method has good reproducibility and has an insignificant contradiction in the mass balance of the sample. Therefore, this newly developed reproducible dissolution method can be effectively utilized in practical applications by dissolving fuel debris and estimating its elemental composition.
Maeda, Mizuho*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Haga, Yoshinori; Shirasaki, Kenji*; Kimura, Noriaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(2), p.024707_1 - 024707_6, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sudo, Ayako; Sato, Takumi; Takano, Masahide
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 9 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)During the progression of the severe accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, seawater flowed down and was predicted to react with molten corium and concrete. For the removal and storage of fuel debris, knowing the effects of seawater components on the characteristics of reaction products in the fuel debris is crucial. To understand changes in the microstructure of fuel debris, a reaction test was conducted by introducing sea salt to simulated corium and concrete under a temperature gradient. Among the components of sea salt, sulfur formed iron sulfide during metallic precipitation. Analysis of vaporized species indicated that most of Cl, some Na and K in the sea salt might volatilize during heating rather than react with simulated corium and concrete. Calcium and a small amount of Mg, Na, and K in the sea salt might be trapped in the silicate glass.
 Er(n,
Er(n, )
)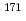 Er and
Er and  Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
) Hf reactions
Hf reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 14 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Miyata, Hokata*; Yoshida, Kenta*; Konashi, Kenji*; Du, Y.*; Kitagaki, Toru; Shobu, Takahisa; Shimada, Yusuke*
Microscopy, p.dfaf005_1 - dfaf005_10, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Microscopy)Sasaki, Yuji; Kaneko, Masashi; Ban, Yasutoshi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*
Solvent Extraction Research and Development, Japan, 32(1), p.21 - 29, 2025/00
The magnitude of the masking effect of carboxylic, amic-acidic, and amidic compounds through Ln and Am extractions by tetraoctyl diglycolamide (TODGA) is compared. The compounds used are diglycol, ethylenediamine, diethylenetriamine-type, and two other amides (dioxaoctane diamide and nitrylotriacetamide). The results show that below pH 1.2, where carboxylic acids are less dissociated, amide O atoms have higher reactivity with lanthanides than O atoms in carboxyl groups. From observing the Ln patterns (D(Ln) vs. their atomic number), the compounds primarily show high reactivity, with middle and heavy Ln having a higher charge density than light Ln. Four amide compounds are employed in this work. Those with tertiary amine N atoms have pH dependence on D(Ln) due to protonation and dissociation from amine N atoms.
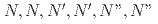 -hexahexyl-nitrilotriacetamide and electrodeposition
-hexahexyl-nitrilotriacetamide and electrodepositionMatsumiya, Masahiko*; Tokumitsu, Shun*; Mishima, Takumi*; Sasaki, Yuji
ECS Advances (Internet), 3(4), p.043001_1 - 043001_8, 2024/12
The extraction behavior of Rh(III) with Hexahexyl-nitrilotriacetamide, NTAamide(C6) was investigated in three different diluents (acetophenone, AP, 1,2-dichloroethane, DCE, and 1-octanol, OC). The electrochemical behavior of the extracted Rh(III) complex in each diluent was investigated from linear sweep voltammetry. It was revealed that Rh(III) was reduced to Rh(0) metal by a three electron transfer in NTAamide(C6)/AP, DCE and OC system. The electrodeposits can be recovered from continuous solvent extraction and direct electrodeposition. The electrodeposits were identified by XPS and XRD analyses as mainly Rh metal.
 Cs/
Cs/ Cs isotope ratio
Cs isotope ratioShimada, Asako; Tsukahara, Takehiko*; Nomura, Masao*; Takeda, Seiji
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333(12), p.6297 - 6310, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)Tokumitsu, Shun*; Mishima, Takumi*; Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Sasaki, Yuji
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 414, Part A, p.126150_1 - 126150_8, 2024/11
The coordination states of Ln(III), (Ln=Pr, Nd, Tb and Dy) in ILs were investigated by Raman spectroscopy. The thermodynamic properties for the isomerism of [TFSA]- from trans- to cis-isomer were evaluated. The cis-[TFSA]- conformer bound to Ln3+ cation was the preferred coordination state of [Ln(III)(cis-TFSA)5]2-. The bonding energies of [Ln(III)(cis-TFSA)5]2-, (Ln=Pr, Nd, Tb and Dy) were estimated from DFT calculation.
 and Eu
and Eu onto coherent and melange-type pre-neogene sedimentary rocks
onto coherent and melange-type pre-neogene sedimentary rocksHou, L.*; Toda, Kanako*; Mei, H.; Aoyagi, Noboru; Saito, Takumi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(11), p.1488 - 1498, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:75.80(Nuclear Science & Technology)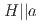 in the early-stage sample of spin-triplet superconductor UTe
in the early-stage sample of spin-triplet superconductor UTe
Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; 11 of others*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(12), p.123701_1 - 123701_5, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kitamura, Yoshimasa; Oka, Toshitaka; Seito, Hajime*; Yokozuka, Eri*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(16-18), p.1660 - 1665, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)In this work, we evaluated the applicability of hydroxyapatite, which is a main component of tooth enamel, as individual dosimeters that can detect from less than 1 Gy to several tens Gy. Commercially available hydroxyapatite was irradiated by  Co gamma-ray up to 75 Gy and ESR spectrum of the irradiated sample was observed. The relationship between the intensity of produced carbonated radical and the absorbed dose shows a good linearity (
Co gamma-ray up to 75 Gy and ESR spectrum of the irradiated sample was observed. The relationship between the intensity of produced carbonated radical and the absorbed dose shows a good linearity (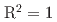 ) from 0 to 75 Gy. The detection limit of this samples was estimated to be 99.7 mGy, and the radical intensity do not change for eight month from the irradiation. These results suggest that this sample can be used as a candidate of the individual dosimeter.
) from 0 to 75 Gy. The detection limit of this samples was estimated to be 99.7 mGy, and the radical intensity do not change for eight month from the irradiation. These results suggest that this sample can be used as a candidate of the individual dosimeter.