Low-temperature structural change and magnetic anomaly in superconducting Cd Re
Re O
O
超伝導体Cd Re
Re O
O における低温の構造変化と磁気的異常
における低温の構造変化と磁気的異常
酒井 宏典; 加藤 治一; 神戸 振作 
 ; Walstedt, R. E.; 大野 浩之*; 加藤 将樹*; 吉村 一良*; 松畑 洋文*
; Walstedt, R. E.; 大野 浩之*; 加藤 将樹*; 吉村 一良*; 松畑 洋文*
Sakai, Hironori; Kato, Harukazu; Kambe, Shinsaku; Walstedt, R. E.; Ono, Hiroyuki*; Kato, Masaki*; Yoshimura, Kazuyoshi*; Matsuhata, Hirofumi*
パイロクロア型酸化物超伝導体Cd Re
Re O
O の
の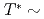 200Kにおける構造相転移についてX線・電子線回折,
200Kにおける構造相転移についてX線・電子線回折, Cd核NMR測定を用いて研究を行った。高温領域(T
Cd核NMR測定を用いて研究を行った。高温領域(T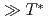 )の帯磁率は大きな負のWeiss温度をもつCurie-Weiss則に従う。このことは、この系が反強磁性的相互作用をもつ局在モーメント的に振る舞うことを示しており、幾何学的なフラストレーションを導く。X線・電子線回折測定から
)の帯磁率は大きな負のWeiss温度をもつCurie-Weiss則に従う。このことは、この系が反強磁性的相互作用をもつ局在モーメント的に振る舞うことを示しており、幾何学的なフラストレーションを導く。X線・電子線回折測定から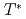 以下の温度領域において、ナノサイズのストライプ構造を誘起するReの4量体化が示唆された。
以下の温度領域において、ナノサイズのストライプ構造を誘起するReの4量体化が示唆された。 Cd核NMR測定のいわゆる
Cd核NMR測定のいわゆる -
- プロットから大きな軌道帯磁率が示唆され、また、スピン帯磁率と核磁気緩和率を温度で割った
プロットから大きな軌道帯磁率が示唆され、また、スピン帯磁率と核磁気緩和率を温度で割った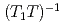 が
が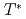 以下で鋭く減少することから、フェルミ面における状態密度の減少,部分的なエネルギーギャップの形成が示唆された。
以下で鋭く減少することから、フェルミ面における状態密度の減少,部分的なエネルギーギャップの形成が示唆された。
The structural phase transition at 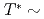 200 K in the superconducting pyrochlore oxide Cd
200 K in the superconducting pyrochlore oxide Cd Re
Re O
O has been investigated using X-ray and electron diffraction experiments and
has been investigated using X-ray and electron diffraction experiments and  Cd NMR measurements. The susceptibility for Cd
Cd NMR measurements. The susceptibility for Cd Re
Re O
O in the high temperature region (
in the high temperature region (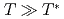 ) obeys a Curie-Weiss law with a large and negative Weiss temperature, which indicates that this system possesses a localized moment nature with antiferromagnetic interactions, leading to geometrical frustration. X-ray and electron diffraction measurements suggest the tetramerization of Re below
) obeys a Curie-Weiss law with a large and negative Weiss temperature, which indicates that this system possesses a localized moment nature with antiferromagnetic interactions, leading to geometrical frustration. X-ray and electron diffraction measurements suggest the tetramerization of Re below 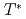 , which induces a nano-sized stripe structure. From
, which induces a nano-sized stripe structure. From  Cd NMR experiments, a large orbital susceptibility is identified by means of a
Cd NMR experiments, a large orbital susceptibility is identified by means of a  -
- plot. Both the spin susceptibility and
plot. Both the spin susceptibility and 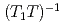 are found to decrease sharply below
are found to decrease sharply below 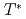 , signaling a decrease in density of states which is apparently caused by a developing partial energy gap at the Fermi surface.
, signaling a decrease in density of states which is apparently caused by a developing partial energy gap at the Fermi surface.