圧縮ベントナイト中のC, Cl, Iの拡散挙動に及ぼすケイ砂混合率及びNaNO の影響
の影響
The Effect of Silica Sand Content and NaNO Concentration on Diffusions of C, Cl and I in Compacted Bentonite
Concentration on Diffusions of C, Cl and I in Compacted Bentonite
石寺 孝充  ; 宮本 真哉*; 佐藤 治夫
; 宮本 真哉*; 佐藤 治夫
Ishidera, Takamitsu; Miyamoto, Shinya*; Sato, Haruo
TRU廃棄物処分の安全評価においては、C-14, Cl-36及びI-129といった核種のデータ取得が必要であるとともに、硝酸塩の溶出やセメント材料の溶解による地下水の高pH化の影響を評価する必要がある。よって、ケイ砂混合率及びNaNO3濃度をパラメータとして、高pH条件でCO
 , Cl
, Cl 及びI
及びI のベントナイト中の透過拡散試験を実施し、実効拡散係数(以下、De)及び見かけの拡散係数(以下、Da)の取得を行った。さらに、ベントナイト中のCO
のベントナイト中の透過拡散試験を実施し、実効拡散係数(以下、De)及び見かけの拡散係数(以下、Da)の取得を行った。さらに、ベントナイト中のCO
 , Cl
, Cl 及びI
及びI の拡散挙動について検討を行った。 その結果、CO
の拡散挙動について検討を行った。 その結果、CO
 , Cl
, Cl 及びI
及びI のDeは10
のDeは10
 10
10 m
m /s程度、CO
/s程度、CO
 のDaは10
のDaは10 m
m /s程度、Cl
/s程度、Cl 及びI
及びI のDaは10
のDaは10 m
m /s程度の値が得られた。これらのイオンのDe及びDaはケイ砂混合率の増加と共にそれぞれ増大する傾向が見られ、この変化は、スメクタイト部分密度による規格化で推定することが有効であると考えられた。また、これらのイオンのDeはNaNO
/s程度の値が得られた。これらのイオンのDe及びDaはケイ砂混合率の増加と共にそれぞれ増大する傾向が見られ、この変化は、スメクタイト部分密度による規格化で推定することが有効であると考えられた。また、これらのイオンのDeはNaNO 濃度の増加に伴ってそれぞれ増大する傾向が見られた。これは、保持因子alphaと間隙率epsilonの関係から、NaNO
濃度の増加に伴ってそれぞれ増大する傾向が見られた。これは、保持因子alphaと間隙率epsilonの関係から、NaNO 濃度の増加に伴う陰イオン排除効果の低下によるものであると考えられた。さらに、Cl
濃度の増加に伴う陰イオン排除効果の低下によるものであると考えられた。さらに、Cl , I
, I の拡散経路はスメクタイト粒子間間隙のみに限定されていると推測され、CO
の拡散経路はスメクタイト粒子間間隙のみに限定されていると推測され、CO
 はクニゲルV1中に含まれる方解石との化学平衡により、クニゲルV1中に保持されると考えられた。
はクニゲルV1中に含まれる方解石との化学平衡により、クニゲルV1中に保持されると考えられた。
For safety assessment of geological disposal of TRU waste, it is necessary to obtain the diffusivities of C-14, Cl-36 and I-129 and to estimate the effects of the dissolution of NaNO and high pH groundwater condition caused by dissolution of cementitious materials. Therefore, the effective diffusion coefficients (De) and the apparent diffusion coefficients (Da) of CO
and high pH groundwater condition caused by dissolution of cementitious materials. Therefore, the effective diffusion coefficients (De) and the apparent diffusion coefficients (Da) of CO
 , Cl
, Cl and I
and I in compacted bentonite were obtained as a function of silica sand content and NaNO
in compacted bentonite were obtained as a function of silica sand content and NaNO concentration under high pH condition by Through-diffusion method. Furthermore, the diffusion mechanisms of CO
concentration under high pH condition by Through-diffusion method. Furthermore, the diffusion mechanisms of CO
 , Cl
, Cl and I
and I were discussed.The obtained De values of CO
were discussed.The obtained De values of CO
 , Cl
, Cl and I
and I were in a range of 10
were in a range of 10 to 10
to 10 m
m /s order and Da values in a range of 10
/s order and Da values in a range of 10 to 10
to 10 m
m /s order (CO
/s order (CO
 ) and 10
) and 10 m
m /s order (Cl
/s order (Cl and I
and I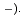 The De and Da values of CO
The De and Da values of CO
 , Cl
, Cl and I
and I increased with increasing silica sand content. The changes of De and Da values appeared to be estimated by smectite partial density. The De values of CO
increased with increasing silica sand content. The changes of De and Da values appeared to be estimated by smectite partial density. The De values of CO
 , Cl
, Cl and I
and I increased with increasing NaNO
increased with increasing NaNO concentration. The increases were interpreted by the decrease of anion exclusion effect. Furthermore, it seems that the pathways of Cl
concentration. The increases were interpreted by the decrease of anion exclusion effect. Furthermore, it seems that the pathways of Cl and I
and I were limited to the interstitial pore space. The CO
were limited to the interstitial pore space. The CO
 ions were probably retained in the Kunigel V1 as the precipitation of calcite.
ions were probably retained in the Kunigel V1 as the precipitation of calcite.