Evaluation of containment failure probability by Ex-vessel steam explosion in Japanese LWR plants
日本型軽水炉における炉外水蒸気爆発による格納容器破損確率の評価
森山 清史; 高木 誠司*; 村松 健; 中村 秀夫 
 ; 丸山 結*
; 丸山 結*
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Takagi, Seiji*; Muramatsu, Ken; Nakamura, Hideo; Maruyama, Yu*
BWR Mk-II型及びPWRモデルプラントにおける炉外水蒸気爆発による格納容器破損確率を評価した。評価対象はBWRの圧力抑制プール及びペデスタル,PWRのキャビティにおける水蒸気爆発である。水蒸気爆発による負荷の確率分布を評価するために、ラテン超方格サンプリング(LHS)による確率論的手法を用い、その中で水蒸気爆発解析コードJASMINEを物理モデルとして使用した。水蒸気爆発による負荷と格納容器破損確率を関連付けるフラジリティカーブは、格納容器破損に至るシナリオについて簡略な仮定をおいて評価した。得られた条件付格納容器破損確率(CCFP)はBWR圧力抑制プールにつき6.4E-2(平均値)及び3.9E-2(中央値)、BWRペデスタルにつき2.2E-3(平均値)及び2.8E-10(中央値)、PWRにつき6.8E-2(平均値)及び1.4E-2(中央値)である。なお、これらは仮定した入力パラメータの範囲及び、保守的な簡略化により与えたフラジリティカーブに依存するものである。また、このCCFPは炉内での事故収束失敗,溶融炉心の炉外水プールへの落下、及び粗混合量が最大に近い時刻における強いトリガリングを前提条件とした確率であり、炉心損傷事象に対するCCFPはさらに小さい値となる。
The containment failure probability due to ex-vessel steam explosions was evaluated for Japanese BWR and PWR model plants. A stratified Monte Carlo technique (Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS)) was applied for the evaluation of steam explosion loads, in which a steam explosion simulation code JASMINE was used as a physics model. The evaluation was made for three scenarios: a steam explosion in the pedestal area or in the suppression pool of a BWR model plant with a Mark-II containment, and in the reactor cavity of a PWR model plant. The scenario connecting the generation of steam explosion loads and the containment failure was assumed to be displacement of the reactor vessel and pipings, and failure at the penetration in the containment boundary. The mean conditional containment failure probabilities (CCFPs) were 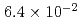 (mean) and
(mean) and 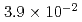 (median) for the BWR suppression pool case,
(median) for the BWR suppression pool case, 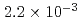 (mean) and
(mean) and 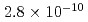 (median) for the BWR pedestal case, and
(median) for the BWR pedestal case, and 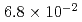 (mean) and
(mean) and 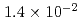 (median) for the PWR cavity case. Note that the specific values of the probability are most dependent on assumed range of melt flow rates and on fragility curves that involve conservatism and uncertainty due to simplified scenarios and limited information. Also, note that these CCFPs were based on the preconditions of failure of accident termination within the reactor vessel, relocation of the core melt into the water pool at the place in question without significant interference, and a strong triggering ofa steam explosion with maximized premixed mass for the given premixing condition. The evaluation of CCFPs on the basis of core damage needs consideration of probabilities for these preconditions. Thus, the CCFPs per core damage should be lower than the values given above.
(median) for the PWR cavity case. Note that the specific values of the probability are most dependent on assumed range of melt flow rates and on fragility curves that involve conservatism and uncertainty due to simplified scenarios and limited information. Also, note that these CCFPs were based on the preconditions of failure of accident termination within the reactor vessel, relocation of the core melt into the water pool at the place in question without significant interference, and a strong triggering ofa steam explosion with maximized premixed mass for the given premixing condition. The evaluation of CCFPs on the basis of core damage needs consideration of probabilities for these preconditions. Thus, the CCFPs per core damage should be lower than the values given above.