Electrical resistivity measurements of single crystalline  -Mn under high pressure
-Mn under high pressure
アルファマンガンの単結晶試料を用いた高圧下電気抵抗測定
三宅 厚志*; 金政 泰介*; 八木 良平*; 加賀山 朋子*; 清水 克哉*; 芳賀 芳範 

 ; 大貫 惇睦
; 大貫 惇睦
Miyake, Atsushi*; Kanemasa, Tsunehiro*; Yagi, Ryohei*; Kagayama, Tomoko*; Shimizu, Katsuya*; Haga, Yoshinori; Onuki, Yoshichika
アルファマンガンの単結晶試料を用いて高圧下電気抵抗測定を行った。アルファマンガンは転移温度95Kの反強磁性物質であり、結晶学的に異なる4つのマンガンサイトがある。アルファマンガンの磁気転移温度は加圧とともに低温側にシフトし、転移温度における鋭い抵抗異常は鈍いkinkへと変化し、異なる磁気秩序相が高圧下で形成されていることを示唆された。1.9GPaの相境界では、残留抵抗が急減に減少し、電気抵抗の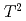 の係数Aがピークを形成することが明らかにされた。
の係数Aがピークを形成することが明らかにされた。
We have measured electrical resistivity of single crystalline  -manganese (
-manganese ( -Mn) under high pressure.
-Mn) under high pressure.  -Mn shows an antiferromagnetic ordering at
-Mn shows an antiferromagnetic ordering at  = 95 K and has four inequivalent crystal sites with different magnetic moments. With increasing pressure,
= 95 K and has four inequivalent crystal sites with different magnetic moments. With increasing pressure,  shifts toward lower temperature. At higher pressure, the shape of anomaly at
shifts toward lower temperature. At higher pressure, the shape of anomaly at  changes to a kink-like one, which may indicate different magnetic ordering from that at lower pressure. Such a difference between lower and higher pressure regions is considered to be caused by the four inequivalent magnetic moments in
changes to a kink-like one, which may indicate different magnetic ordering from that at lower pressure. Such a difference between lower and higher pressure regions is considered to be caused by the four inequivalent magnetic moments in  -Mn. At 1.9 GPa, the boundary of the ordered phases, we observe a sudden decrease of the residual resistivity and a peak of the A-coefficient of
-Mn. At 1.9 GPa, the boundary of the ordered phases, we observe a sudden decrease of the residual resistivity and a peak of the A-coefficient of 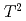 -term of the resistivity.
-term of the resistivity.