Neutrino-nucleus reaction cross sections for light element synthesis in supernova explosions
超新星爆発における軽元素合成に用いるニュートリノ・原子核反応断面積
吉田 敬*; 鈴木 俊夫*; 千葉 敏; 梶野 敏貴*; 横枕 英和*; 木村 恵一*; 高村 明*; Hartmann, D.*
Yoshida, Takashi*; Suzuki, Toshio*; Chiba, Satoshi; Kajino, Toshitaka*; Yokomakura, Hidekazu*; Kimura, Keiichi*; Takamura, Akira*; Hartmann, D.*
新しい殻模型ハミルトニアンを用いて Heと
Heと Cのニュートリノ反応断面積を求めた。超新星ニュートリノに対してLi, BeとB同位体を生成する崩壊比を導出した。今回求めた断面積を使うと太陽質量の16.2倍の星が超新星を起こした場合に生成する
Cのニュートリノ反応断面積を求めた。超新星ニュートリノに対してLi, BeとB同位体を生成する崩壊比を導出した。今回求めた断面積を使うと太陽質量の16.2倍の星が超新星を起こした場合に生成する Liと
Liと Bの量が以前の結果のそれぞれ1.3, 1.2倍になることがわかった。それに対して
Bの量が以前の結果のそれぞれ1.3, 1.2倍になることがわかった。それに対して Bの量は三分の一になるなど、顕著な違いのあることもわかった。また、銀河の化学進化のモデルにおいて、超新星で合成された
Bの量は三分の一になるなど、顕著な違いのあることもわかった。また、銀河の化学進化のモデルにおいて、超新星で合成された Bの量から、超新星爆発時に発生する各種のニュートリノの温度に対する制限が得られた。さらには新しい断面積を用いて、ニュートリノ振動による
Bの量から、超新星爆発時に発生する各種のニュートリノの温度に対する制限が得られた。さらには新しい断面積を用いて、ニュートリノ振動による Liと
Liと Bの増加がどの程度であるかを示した。
Bの増加がどの程度であるかを示した。
The neutrino-nucleus reaction cross sections of  He and
He and  C are evaluated using new shell model Hamiltonians. Branching ratios of various decay channels are calculated to evaluate the yields of Li, Be, and B produced through the
C are evaluated using new shell model Hamiltonians. Branching ratios of various decay channels are calculated to evaluate the yields of Li, Be, and B produced through the  -process in supernova explosions. The new cross sections enhance the yields of
-process in supernova explosions. The new cross sections enhance the yields of  Li and
Li and  B produced during the supernova explosion of a 16.2 M
B produced during the supernova explosion of a 16.2 M star model compared to our previous study by factors of 1.3 and 1.2, respectively. On the other hand, the yield of
star model compared to our previous study by factors of 1.3 and 1.2, respectively. On the other hand, the yield of  B decreases by a factor of three. The yields of
B decreases by a factor of three. The yields of  Li,
Li,  Be, and the radioactive nucleus
Be, and the radioactive nucleus  Be are found at a level of 10 to 11 M
Be are found at a level of 10 to 11 M . The temperature of
. The temperature of 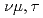 - and
- and 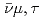 -neutrinos inferred from the supernova contribution of
-neutrinos inferred from the supernova contribution of  B in Galactic chemical evolution models is constrained to be in the range 4.5 MeV to 6.4 MeV. The increase in the
B in Galactic chemical evolution models is constrained to be in the range 4.5 MeV to 6.4 MeV. The increase in the  Li and
Li and  B yields due to neutrino oscillations is demonstrated with the new cross sections.
B yields due to neutrino oscillations is demonstrated with the new cross sections.