水中における重粒子線トラック構造の拡散モデルによる検討
Investigation on heavy-ion track structure in water using diffusion kinetic model simulation
山下 真一; 勝村 庸介; 前山 拓哉*; Lin, M.; 室屋 裕佐*; 村上 健*; Jay-Gerin, J.-P.*; Meesungnoen, J.*
Yamashita, Shinichi; Katsumura, Yosuke; Maeyama, Takuya*; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Jay-Gerin, J.-P.*; Meesungnoen, J.*
水は生体細胞主成分であり、その放射線との相互作用は重要と言えるものの、これまで生体に近い中性の条件下でがん治療に用いられるほど高エネルギーの重粒子線を用いた研究はほとんど報告されていない。そこで本研究ではこれまで放射線医学総合研究所のHIMACからのガン治療用GeV級重粒子線( He
He -
- Fe
Fe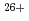 , 最大エネルギー500MeV/nucleon, LET 2
, 最大エネルギー500MeV/nucleon, LET 2 700keV/
700keV/ m)を用い、水の放射線分解主要生成物である水和電子(e
m)を用い、水の放射線分解主要生成物である水和電子(e
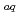 ), OHラジカル(
), OHラジカル( OH), 過酸化水素(H
OH), 過酸化水素(H O
O )のプライマリ収量を測定してきた。ここでプライマリ収量とは照射後約100ns後における収量である。照射後ps程度の間にトラックが形成され、トラックの中心部に水分解ラジカルは密集して生成されるが、その後水分解ラジカルは周囲へ拡散しつつも相互に反応する。このトラック内反応と拡散がほぼ落ち着く時間が約100nsと言えるため、プライマリ収量はトラック初期構造やトラック内における水分解ラジカルのダイナミクスを強く反映する量と言える。本研究ではこのプライマリ収量の測定だけでなく、測定値を元にシミュレーションを補完的に用い、より微視的な検討も実施している。
)のプライマリ収量を測定してきた。ここでプライマリ収量とは照射後約100ns後における収量である。照射後ps程度の間にトラックが形成され、トラックの中心部に水分解ラジカルは密集して生成されるが、その後水分解ラジカルは周囲へ拡散しつつも相互に反応する。このトラック内反応と拡散がほぼ落ち着く時間が約100nsと言えるため、プライマリ収量はトラック初期構造やトラック内における水分解ラジカルのダイナミクスを強く反映する量と言える。本研究ではこのプライマリ収量の測定だけでなく、測定値を元にシミュレーションを補完的に用い、より微視的な検討も実施している。
Although water is a main component of human cells and its interaction with ionizing radiations are of crucial importance, understanding of water radiolysis with heavy ions of energies comparable to those used in actual cancer treatments is not sufficient. Recently, such highly energetic heavy ions are available at the Heavy Ion Medical Accelerator in Chiba (HIMAC) of the National Institute of Radiological Sciences (NIRS), Chiba, Japan. We have carried out measurements of primary yields of main water decomposition products, hydrated electron (e
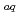 ), hydroxyl radical (
), hydroxyl radical ( OH) and hydrogen peroxide (H
OH) and hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) with heavy ions from
) with heavy ions from  He
He to
to  Fe
Fe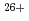 of energies up to 28 GeV (corresponding LET varies from 2 to 700 keV/
of energies up to 28 GeV (corresponding LET varies from 2 to 700 keV/ m) provided from the HIMAC. Note that primary yields are defined as the yields at 100 ns after irradiation, which can be regarded as a time scale when diffusions and intra-track reactions of initial products are almost terminated. Then, such yields are important because they inherently involve information of initial track structure and dynamics of water decomposition products during track expansion. In the present study, not only such measurements but also discussions based on the measured data were conducted by simulations.
m) provided from the HIMAC. Note that primary yields are defined as the yields at 100 ns after irradiation, which can be regarded as a time scale when diffusions and intra-track reactions of initial products are almost terminated. Then, such yields are important because they inherently involve information of initial track structure and dynamics of water decomposition products during track expansion. In the present study, not only such measurements but also discussions based on the measured data were conducted by simulations.