Experimental investigation of particle pinch associated with turbulence in LHD heliotron and JT-60U tokamak plasmas
LHDヘリカル及びJT-60Uトカマクプラズマにおける密度揺動に関連した粒子ピンチに関する実験研究
田中 謙治*; 竹永 秀信; 村岡 克紀*; Michael, C.*; Vyacheslavov, L. N.*; 横山 雅之*; 山田 弘司*; 大山 直幸; 浦野 創; 鎌田 裕; 村上 定義*; 若狹 有光*; 徳沢 季彦*; 秋山 毅志*; 川端 一男*; 吉沼 幹朗*; 居田 克巳*; 山田 一博*; 成原 一途*; 田村 直樹*; LHD実験グループ*
Tanaka, Kenji*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Muraoka, Katsunori*; Michael, C.*; Vyacheslavov, L. N.*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Urano, Hajime; Kamada, Yutaka; Murakami, Sadayoshi*; Wakasa, Arimitsu*; Tokuzawa, Tokihiko*; Akiyama, Tsuyoshi*; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Ida, Katsumi*; Yamada, Ichihiro*; Narihara, Kazumichi*; Tamura, Naoki*; LHD Experimental Group*
トロイダルプラズマにおける密度分布を決定するパラメータを明らかにするために、LHDヘリカルプラズマとJT-60Uトカマクプラズマの比較研究を行った。両装置において異なる密度分布の衝突周波数依存性が観測された。LHDプラズマでは、衝突周波数が減少するにしたがって磁気軸位置R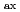 =3.6mでは密度分布のピーキング度が減少し、R
=3.6mでは密度分布のピーキング度が減少し、R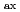 =3.5mではわずかに増加した。一方、JT-60Uでは衝突周波数が減少するにしたがって密度分布のピーキング度は増加した。LHDプラズマでのR
=3.5mではわずかに増加した。一方、JT-60Uでは衝突周波数が減少するにしたがって密度分布のピーキング度は増加した。LHDプラズマでのR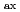 の違いによる衝突周波数依存性の違いは、乱流輸送の寄与の違いであると考えられる。R
の違いによる衝突周波数依存性の違いは、乱流輸送の寄与の違いであると考えられる。R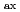 =3.5mのLHDプラズマでは、大きな乱流輸送がトカマクと同様な衝突周波数依存性を作り出している。両装置のコア領域において、密度分布が違う場合に揺動の変化が観測されている。JT-60Uでは、密度分布がピーキングした場合に径方向の相関が強くなることが観測された。このことから、粒子拡散と内向き対流速度が増大していることが示唆される。R
=3.5mのLHDプラズマでは、大きな乱流輸送がトカマクと同様な衝突周波数依存性を作り出している。両装置のコア領域において、密度分布が違う場合に揺動の変化が観測されている。JT-60Uでは、密度分布がピーキングした場合に径方向の相関が強くなることが観測された。このことから、粒子拡散と内向き対流速度が増大していることが示唆される。R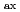 =3.6mのLHDプラズマでは、揺動レベルの増加がホローな密度分布を持つ高パワー加熱時に観測され、拡散の増加を示唆している。ピークした密度分布からホローな密度分布への変化は、新古典輸送の寄与増大による対流速度の内向きから外向きへの変化により引き起こされている。以上の結果よりLHDプラズマの密度分布の衝突周波数依存性は、新古典輸送と乱流輸送の両方によるものであることを明らかにした。
=3.6mのLHDプラズマでは、揺動レベルの増加がホローな密度分布を持つ高パワー加熱時に観測され、拡散の増加を示唆している。ピークした密度分布からホローな密度分布への変化は、新古典輸送の寄与増大による対流速度の内向きから外向きへの変化により引き起こされている。以上の結果よりLHDプラズマの密度分布の衝突周波数依存性は、新古典輸送と乱流輸送の両方によるものであることを明らかにした。
Comparative studies were carried out in LHD heliotron and JT-60U tokamak plasmas to elucidate the most essential parameter(s) for control of density profiles in toroidal systems. A difference in the collisionality dependence was found between the two devices. In LHD, the density peaking factor decreased with decrease of the collisionality at the magnetic axis position (R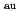 ) 3.6 m, while the density peaking factor gradually increased with a decreased of collisionality at R
) 3.6 m, while the density peaking factor gradually increased with a decreased of collisionality at R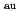 = 3.5 m. On the other hand, in JT-60U, the density peaking factor clearly increased with a decrease of the collisionality. The difference in the collisionality dependence between R
= 3.5 m. On the other hand, in JT-60U, the density peaking factor clearly increased with a decrease of the collisionality. The difference in the collisionality dependence between R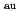 = 3.5 and R
= 3.5 and R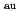 = 3.6 m is likely due to the contribution of the anomalous transport. At R
= 3.6 m is likely due to the contribution of the anomalous transport. At R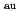 = 3.5 m, larger anomalous transport caused a similar collisionality dependence. Change of the fluctuation property was observed with different density profiles in the plasma core region on both devices. In JT-60U, the increase of the radial coherence was observed with higher density peaking profile suggesting enhanced diffusion and inward directed pinch. For a magnetic axis positions (R
= 3.5 m, larger anomalous transport caused a similar collisionality dependence. Change of the fluctuation property was observed with different density profiles in the plasma core region on both devices. In JT-60U, the increase of the radial coherence was observed with higher density peaking profile suggesting enhanced diffusion and inward directed pinch. For a magnetic axis positions (R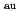 ) at 3.6 m in LHD, the increase of the fluctuation power with an increase in P
) at 3.6 m in LHD, the increase of the fluctuation power with an increase in P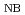 was observed for a hollow density profile suggesting an increase on diffusion due to anomalous processes. Change of density profiles from peaked to hollow indicates change in the convection direction. This is due to increase in neoclassical processes. The reduction of the density peaking factor with increase of P
was observed for a hollow density profile suggesting an increase on diffusion due to anomalous processes. Change of density profiles from peaked to hollow indicates change in the convection direction. This is due to increase in neoclassical processes. The reduction of the density peaking factor with increase of P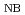 in LHD is partly due to the neoclassical effect and partly due to the anomalous effect.
in LHD is partly due to the neoclassical effect and partly due to the anomalous effect.