放射光光電子分光による重水素イオン注入V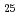 Cr
Cr Ti
Ti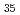 表面の熱変性分析
表面の熱変性分析
Thermal degradation analysis of deuterium-ion-implanted V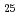 Cr
Cr Ti
Ti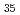 using synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy
using synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy
戸出 真由美; Harries, J.; 寺岡 有殿; 吉越 章隆 
Tode, Mayumi; Harries, J.; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
水素貯蔵合金の表面皮膜の熱変性過程と水素の脱離温度特性を、放射光光電子分光法で観測した。実験はSPring-8の原子力機構専用軟X線ビームライン(BL23SU)に設置した表面反応分析装置(SUREAC2000)を用いて行った。自然酸化膜付きのV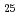 Cr
Cr Ti
Ti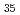 と、自然酸化膜上から重水素イオンを注入したV
と、自然酸化膜上から重水素イオンを注入したV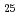 Cr
Cr Ti
Ti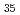 のSR-XPS測定を行った。非重水素化VCrTiでは373Kから473Kの間、重水素化では473Kから573Kの間で酸化膜が著しく変質した。重水素イオンを注入すると自然酸化膜の熱安定性が100度程度安定化することが観測された。
のSR-XPS測定を行った。非重水素化VCrTiでは373Kから473Kの間、重水素化では473Kから573Kの間で酸化膜が著しく変質した。重水素イオンを注入すると自然酸化膜の熱安定性が100度程度安定化することが観測された。
In order to study the thermal degradation process of the hydrogen storage materials surface layer and the thermal desorption of hydrogen property, we have used high-resolution synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The experiments were performed at the JAEA soft X-ray beamline BL23SU at SPring-8, using the "SUREAC2000" surface reaction analysis apparatus. Spectra were recorded for two samples (V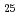 Cr
Cr Ti
Ti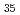 ) covered with native oxide layers, one of which was implanted with deuterium ions. For the un-implanted sample, the oxide layer changes dramatically between 373 K and 473 K, for the deuterium-implanted sample, the change occurs between 473 K and 573 K. The implantation of deuterium leads to a stabilization (of approximately 100 K) of the surface oxide layer.
) covered with native oxide layers, one of which was implanted with deuterium ions. For the un-implanted sample, the oxide layer changes dramatically between 373 K and 473 K, for the deuterium-implanted sample, the change occurs between 473 K and 573 K. The implantation of deuterium leads to a stabilization (of approximately 100 K) of the surface oxide layer.