分画分子量の異なるフミン酸の沈着速度と臨界沈着濃度
Deposition kinetics and critical deposition concentrations of humic acids with different molecular weight
山下 祐司; 田邊 洋祐*; 足立 泰久*
Yamashita, Yuji; Tanabe, Yosuke*; Adachi, Yasuhisa*
分画分子量30,000-100,000g/mol(SHA)、あるいは100,000-300,000g/mol(LHA)のフミン酸をさまざまなNaCl濃度で酸性条件下のガラスビーズ充填カラムへ流し入れ、その流出量の経時変化から破過曲線を得た。すべての条件において、破過曲線の立ち上がり後、相対濃度(流出濃度/流入濃度)は漸近的にある一定値へ収束し、NaCl濃度が増加するとともにその収束値は減少した。破過曲線で得られた相対濃度の収束値から、フミン酸の無次元沈着速度定数を算出し、さらに衝突係数を求めることで、フミン酸のコロイド安定性に対する分画分子量の影響を評価した。NaCl濃度と衝突係数の両対数プロット(安定度曲線)から、両フミン酸において急速沈着領域と緩速沈着領域の境である臨界沈着濃度(CDC)が明確に現れること、分画分子量の大きい方が緩速沈着領域における曲線の傾きは急峻であること、CDC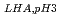 =0.73M, CDC
=0.73M, CDC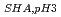 =1.46Mで分画分子量の小さなフミン酸のCDCが高いことが明らかとなった。
=1.46Mで分画分子量の小さなフミン酸のCDCが高いことが明らかとなった。
We obtained breakthrough curves of humic acids with different molecular weight through the column packed with glass beads with various NaCl concentrations. Each breakthrough curve of each humic acid reached almost a stable plateau at which the relative concentration was less than unity. The relative concentrations at each plateau decreased with an increase in the NaCl concentration. Dimensionless deposition rate constants and collision efficiencies of humic acids were calculated. Collision efficiencies were plotted as a function of NaCl concentration to draw a colloidal stability curve. In both humic acids, the obvious boundary points, which were known as the critical deposition concentration (CDC), were obtained from the colloidal stability curve. The value of CDC of smaller molecular weight fraction was higher than that of larger one. In the slow deposition condition, the slope of the stability curve of larger molecular weight fraction was steeper than that of smaller one.