Neutron and X-ray crystallographic analysis of 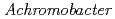 protease I at pD 8.0; Protonation states and hydration structure in the free-form
protease I at pD 8.0; Protonation states and hydration structure in the free-form
pD8.0におけるアクロモバクタープロテアーゼIの中性子/X線結晶構造解析; リガンド非結合型におけるプロトン化状態と水和構造
大西 裕季*; 山田 太郎*; 栗原 和男; 田中 伊知朗*; 崎山 文夫*; 正木 武治*; 新村 信雄*
Onishi, Yuki*; Yamada, Taro*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Sakiyama, Fumio*; Masaki, Takeharu*; Niimura, Nobuo*
セリンプロテアーゼの鍵となる触媒残基のプロトン化状態を調べるため、pD8.0におけるリガンド非結合型クロモバクタープロテアーゼI(API)の構造を単結晶X線と中性子回折データの同時使用によって精密化した。リガンド非結合型APIの活性部位における触媒三残基の占有率精密化により、H57のイミダゾール環の約30%、S197のヒドロキシル基の約70 が重水素化されていることが示された。この観察結果は、S197の多くが基質と結合していない状態でもプロトン化されていることを示す。API中の触媒三残基のプロトン化状態をウシ由来
が重水素化されていることが示された。この観察結果は、S197の多くが基質と結合していない状態でもプロトン化されていることを示す。API中の触媒三残基のプロトン化状態をウシ由来 -trypsin-BPTI複合体と比較することにより、基質のS197への近接はS197のヒドロキシル基の酸性を低下し得て、それによってH57はS194のヒドロキシル基から水素を引き抜くことができるという仮説が導かれた。また、APIに特異な残基であるH210は、触媒三残基D113と水素結合を形成していないが、代わりに、H210はS176、H177、一個の水和水と水素結合ネットワークを形成する。大きく疎水性な残基W169が近接することによりこの水素結合ネットワークを保護し、広範囲のpHに渡るAPIの機能を安定化しているかも知れない
-trypsin-BPTI複合体と比較することにより、基質のS197への近接はS197のヒドロキシル基の酸性を低下し得て、それによってH57はS194のヒドロキシル基から水素を引き抜くことができるという仮説が導かれた。また、APIに特異な残基であるH210は、触媒三残基D113と水素結合を形成していないが、代わりに、H210はS176、H177、一個の水和水と水素結合ネットワークを形成する。大きく疎水性な残基W169が近接することによりこの水素結合ネットワークを保護し、広範囲のpHに渡るAPIの機能を安定化しているかも知れない
The structure of the free-form of 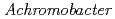 protease I (API) at pD 8.0 was refined by simultaneous use of single crystal X-ray and neutron diffraction data sets to investigate the protonation states of key catalytic residues of the serine protease. Occupancy refinement of the catalytic triad in the active site of API free-form showed that ca. 30% of the imidazole ring of H57 and ca. 70% of the hydroxyl group of S194 were deuterated. This observation indicates that a major fraction of S194 is protonated in the absence of a substrate. The protonation state of the catalytic triad in API was compared with the bovine
protease I (API) at pD 8.0 was refined by simultaneous use of single crystal X-ray and neutron diffraction data sets to investigate the protonation states of key catalytic residues of the serine protease. Occupancy refinement of the catalytic triad in the active site of API free-form showed that ca. 30% of the imidazole ring of H57 and ca. 70% of the hydroxyl group of S194 were deuterated. This observation indicates that a major fraction of S194 is protonated in the absence of a substrate. The protonation state of the catalytic triad in API was compared with the bovine  -trypsin-BPTI complex. The comparison led to the hypothesis that close contact of a substrate with S194 could lower the acidity of its hydroxyl group, thereby allowing H57 to extract the hydrogen from the hydroxyl group of S194. H210, which is a residue specific to API, does not form a hydrogen bond with the catalytic triad residue D113. Instead, H210 forms a hydrogen bond network with S176, H177 and a water molecule. The close proximity of the bulky, hydrophobic residue W169 may protect this hydrogen bond network, and this protection may stabilize the function of API over a wide pH range.
-trypsin-BPTI complex. The comparison led to the hypothesis that close contact of a substrate with S194 could lower the acidity of its hydroxyl group, thereby allowing H57 to extract the hydrogen from the hydroxyl group of S194. H210, which is a residue specific to API, does not form a hydrogen bond with the catalytic triad residue D113. Instead, H210 forms a hydrogen bond network with S176, H177 and a water molecule. The close proximity of the bulky, hydrophobic residue W169 may protect this hydrogen bond network, and this protection may stabilize the function of API over a wide pH range.