High-energy spin and charge excitations in electron-doped copper oxide superconductors
電子ドープ銅酸化物超伝導体における高エネルギースピン・電荷励起
石井 賢司; 藤田 全基*; 佐々木 隆了*; Minola, M.*; Dellea, G.*; Mazzoli, C.*; Kummer, K.*; Ghiringhelli, G.*; Braicovich, L.*; 遠山 貴己*; 堤 健之*; 佐藤 研太朗*; 梶本 亮一 
 ; 池内 和彦*; 山田 和芳*; 吉田 雅洋*; 黒岡 雅仁*; 水木 純一郎
; 池内 和彦*; 山田 和芳*; 吉田 雅洋*; 黒岡 雅仁*; 水木 純一郎
Ishii, Kenji; Fujita, Masaki*; Sasaki, Takanori*; Minola, M.*; Dellea, G.*; Mazzoli, C.*; Kummer, K.*; Ghiringhelli, G.*; Braicovich, L.*; Toyama, Takami*; Tsutsumi, Kenji*; Sato, Kentaro*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Yoshida, Masahiro*; Kurooka, Masahito*; Mizuki, Junichiro
We combine X-ray and neutron inelastic scattering measurements to track the doping dependence of both spin and charge excitations in electron-doped materials. Copper 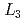 resonant inelastic X-ray scattering spectra show that magnetic excitations shift to higher energy upon doping. Their dispersion becomes steeper near the magnetic zone center and they deeply mix with charge excitations, indicating that electrons acquire a highly itinerant character in the doped metallic state. Moreover, above the magnetic excitations, an additional dispersing feature is observed near the
resonant inelastic X-ray scattering spectra show that magnetic excitations shift to higher energy upon doping. Their dispersion becomes steeper near the magnetic zone center and they deeply mix with charge excitations, indicating that electrons acquire a highly itinerant character in the doped metallic state. Moreover, above the magnetic excitations, an additional dispersing feature is observed near the  -point, and we ascribe it to particle-hole charge excitations. These properties are in stark contrast with the more localized spin-excitations (paramagnons) recently observed in hole-doped compounds even at high doping-levels.
-point, and we ascribe it to particle-hole charge excitations. These properties are in stark contrast with the more localized spin-excitations (paramagnons) recently observed in hole-doped compounds even at high doping-levels.