Elemental substitution effects in multiferroic  Fe
Fe O
O (
( : rare earths)
: rare earths)
マルチフェロイック Fe
Fe O
O (
( : 希土類)の元素置換効果
: 希土類)の元素置換効果
吉井 賢資 
 ; 船江 岳史*; 水牧 仁一朗*; 江尻 宏紀*; 池田 直*; 齋藤 寛之; 松村 大樹
; 船江 岳史*; 水牧 仁一朗*; 江尻 宏紀*; 池田 直*; 齋藤 寛之; 松村 大樹 


Yoshii, Kenji; Funae, Takeshi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Ejiri, Hiroki*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Matsumura, Daiju
マルチフェロイック Fe
Fe O
O (
( : Y, Ho-Lu, In)の元素置換効果について調べた。これまでほとんど報告例のない、非磁性のGa
: Y, Ho-Lu, In)の元素置換効果について調べた。これまでほとんど報告例のない、非磁性のGa を鉄サイトに置換した場合は、磁気転移温度
を鉄サイトに置換した場合は、磁気転移温度 が減少した。これは過去、
が減少した。これは過去、 FeCoO
FeCoO などでも示した通り、鉄サイト間の磁気相互作用が弱まったためである。Ga
などでも示した通り、鉄サイト間の磁気相互作用が弱まったためである。Ga 置換した場合、室温の誘電率は母物質とほぼ変わらない1000-10000程度であった。また、誘電損失が減少することも判明した。この理由については現在不明であるが、損失の減少はエネルギー利用効率の上昇を示しており、応用に有利である。また
置換した場合、室温の誘電率は母物質とほぼ変わらない1000-10000程度であった。また、誘電損失が減少することも判明した。この理由については現在不明であるが、損失の減少はエネルギー利用効率の上昇を示しており、応用に有利である。また サイトの置換も行い、Dy
サイトの置換も行い、Dy のような大きな
のような大きな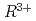 を10%程置換できることが、放射光吸収分光により判明した。なお、置換試料では
を10%程置換できることが、放射光吸収分光により判明した。なお、置換試料では が5-10K上昇した。この現象の起源についても現状では不明であるが、室温でマルチフェロイック状態を実現する一つの方向性を示しており、興味深い結果である。
が5-10K上昇した。この現象の起源についても現状では不明であるが、室温でマルチフェロイック状態を実現する一つの方向性を示しており、興味深い結果である。
We report the effects of elemental substitutions in multiferroic  Fe
Fe O
O (
( : Y, Ho-Lu, In). The substitution by nonmagnetic Ga
: Y, Ho-Lu, In). The substitution by nonmagnetic Ga at the Fe site, which has not been reported so far, shows a drastic decrease in the ferrimagnetic transition temperature (
at the Fe site, which has not been reported so far, shows a drastic decrease in the ferrimagnetic transition temperature ( ). This is plausibly owing to the suppression of magnetic interactions between Fe ions, based on our previous results of other substituted systems such as
). This is plausibly owing to the suppression of magnetic interactions between Fe ions, based on our previous results of other substituted systems such as  FeCoO
FeCoO . Dielectric constants near room temperature were comparable to those of
. Dielectric constants near room temperature were comparable to those of  Fe
Fe O
O . The suppression of dielectric loss in this system is suitable to application. The
. The suppression of dielectric loss in this system is suitable to application. The  -site substitution was also attempted by the large R
-site substitution was also attempted by the large R ions such as Dy
ions such as Dy . The solubility limit was up to about 10% of
. The solubility limit was up to about 10% of  ions, as confirmed by XRD and EXAFS measurements.
ions, as confirmed by XRD and EXAFS measurements.  was raised by 5-10 K for Dy
was raised by 5-10 K for Dy substitution.
substitution.