A Theoretical cell-killing model to evaluate oxygen enhancement ratios at DNA damage and cell survival endpoints in radiation therapy
放射線治療においてDNA損傷と細胞生存率をエンドポイントとして酸素増感比を評価する理論的細胞殺傷モデル
松谷 悠佑 
 ; 佐藤 達彦
; 佐藤 達彦 

 ; 中村 瑠委*; 内城 信吾*; 伊達 広行*
; 中村 瑠委*; 内城 信吾*; 伊達 広行*
Matsuya, Yusuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Nakamura, Rui*; Naijo, Shingo*; Date, Hiroyuki*
低酸素圧下で誘導される放射線抵抗性は、分割放射線療法の悪性進行において重要な役割を果たすことが知られている。低酸素圧下における細胞殺傷を予測する一般的なアプローチとして、細胞殺害モデル(例、線形二次モデルなど)を正常酸素圧下と低酸素圧下の両方の生存率データの実測値に適合させ、放射線抵抗性の程度を表現する酸素増感比(Oxygen enhancement ratio: OER)を取得する方法がある。しかしながら、そのような方法では、各酸素分圧条件に対応したモデルパラーメータが必要となり、放射線治療計画の立案で非効率となる。そこで本研究では、DNA二本鎖切断(double-strand break: DSB)をエンドポイントとしたOERと細胞周期を考慮した効率的なモデル(integrated microdosimetric-kinetic (IMK) model)を開発した。開発したモデルと実測の細胞周期データを用いることで、急性的ならびに慢性的に作り出される低酸素分圧条件に対する生存率の実測値の再現に成功した。また、細胞生存率の計算に使用されるOER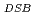 は、実験で報告されるDSB比とよく一致することも確認した。本研究は、不確実性を考慮した様々な酸素条件下に対する生物学的有効量(biological effective dose: BED)を提供し、多分割放射線治療計画の立案に貢献することができる。腫瘍内の酸素濃度を医療画像によって定量化することで、開発したモデルにより、より現実的な生体環境における低酸素圧下での細胞殺傷およびBEDの推定を可能とする。
は、実験で報告されるDSB比とよく一致することも確認した。本研究は、不確実性を考慮した様々な酸素条件下に対する生物学的有効量(biological effective dose: BED)を提供し、多分割放射線治療計画の立案に貢献することができる。腫瘍内の酸素濃度を医療画像によって定量化することで、開発したモデルにより、より現実的な生体環境における低酸素圧下での細胞殺傷およびBEDの推定を可能とする。
Radio-resistance induced under low oxygen pressure plays an important role in malignant progression in fractionated radiotherapy. For the general approach to predict cell killing under hypoxia, cell-killing models (e.g., the Linear-Quadratic model) have to be fitted to  experimental survival data for both normoxia and hypoxia to obtain the oxygen enhancement ratio (OER). However, model parameters for every oxygen condition needs to be considered by model-fitting approaches. This is inefficient for fractionated irradiation planning. Here, we present an efficient model for fractionated radiotherapy the integrated microdosimetric-kinetic model including cell-cycle distribution and the OER at DNA double-strand break endpoint. The cell survival curves described by this model can reproduce the
experimental survival data for both normoxia and hypoxia to obtain the oxygen enhancement ratio (OER). However, model parameters for every oxygen condition needs to be considered by model-fitting approaches. This is inefficient for fractionated irradiation planning. Here, we present an efficient model for fractionated radiotherapy the integrated microdosimetric-kinetic model including cell-cycle distribution and the OER at DNA double-strand break endpoint. The cell survival curves described by this model can reproduce the  experimental survival data for both acute and chronic low oxygen concentrations. The OER
experimental survival data for both acute and chronic low oxygen concentrations. The OER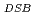 used for calculating cell survival agrees well with experimental DSB ratio of normoxia to hypoxia. This work provides biological effective dose (BED) under various oxygen conditions including its uncertainty, which can contribute to creating fractionated regimens for multi-fractionated radiotherapy. If the oxygen concentration in a tumor can be quantified by medical imaging, the present model will make it possible to estimate the cell-killing and BED under hypoxia in more realistic intravital situations.
used for calculating cell survival agrees well with experimental DSB ratio of normoxia to hypoxia. This work provides biological effective dose (BED) under various oxygen conditions including its uncertainty, which can contribute to creating fractionated regimens for multi-fractionated radiotherapy. If the oxygen concentration in a tumor can be quantified by medical imaging, the present model will make it possible to estimate the cell-killing and BED under hypoxia in more realistic intravital situations.