Neutron spin-echo studies of the structural relaxation of network liquid ZnCl at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak
at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak
ネットワーク液体ZnCl の第1およびプレピークにおける構造緩和の中性子スピンエコー研究
の第1およびプレピークにおける構造緩和の中性子スピンエコー研究
Luo, P.*; Zhai, Y.*; Leao, J. B.*; 古府 麻衣子 

 ; 中島 健次
; 中島 健次 

 ; Faraone, A.*; Zhang, Y.*
; Faraone, A.*; Zhang, Y.*
Luo, P.*; Zhai, Y.*; Leao, J. B.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Faraone, A.*; Zhang, Y.*
典型的なネットワークイオン性液体ZnCl の第1およびプレ回折ピークでの微視的な構造緩和を中性子スピンエコー分光により調べた。第1構造ピークの緩和はプレピークのものより速く、活性化エネルギーは約33%高い。融点より十分高温においても、伸長指数関数で記述される緩和が観測された。驚くべきことに、とくに第1ピークにおいて、非指数関数性パラメータは冷却とともに急激に増加し、
の第1およびプレ回折ピークでの微視的な構造緩和を中性子スピンエコー分光により調べた。第1構造ピークの緩和はプレピークのものより速く、活性化エネルギーは約33%高い。融点より十分高温においても、伸長指数関数で記述される緩和が観測された。驚くべきことに、とくに第1ピークにおいて、非指数関数性パラメータは冷却とともに急激に増加し、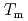 に向かって緩和は伸長指数型から指数型へと変わる。これらの結果は、過冷却状態の典型的なガラス的ダイナミクスが平衡液体で現れること、2つの異なる空間スケールの運動の活性化エネルギーが冷却に伴うネットワーク構造の形成と関連していることを示唆する。
に向かって緩和は伸長指数型から指数型へと変わる。これらの結果は、過冷却状態の典型的なガラス的ダイナミクスが平衡液体で現れること、2つの異なる空間スケールの運動の活性化エネルギーが冷却に伴うネットワーク構造の形成と関連していることを示唆する。
Using neutron spin-echo spectroscopy, we studied the microscopic structural relaxation of a prototypical network ionic liquid ZnCl at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak. The results show that the relaxation at the primary peak is faster than the prepeak and that the activation energy is
at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak. The results show that the relaxation at the primary peak is faster than the prepeak and that the activation energy is 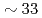 % higher. A stretched exponential relaxation is observed even at temperatures well-above the melting point
% higher. A stretched exponential relaxation is observed even at temperatures well-above the melting point 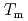 . Surprisingly, the stretching exponent shows a rapid increase upon cooling, especially at the primary peak, where it changes from a stretched exponential to a simple exponential on approaching the
. Surprisingly, the stretching exponent shows a rapid increase upon cooling, especially at the primary peak, where it changes from a stretched exponential to a simple exponential on approaching the 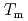 . These results suggest that the appearance of glassy dynamics typical of the supercooled state even in the equilibrium liquid state of ZnCl
. These results suggest that the appearance of glassy dynamics typical of the supercooled state even in the equilibrium liquid state of ZnCl as well as the difference of activation energy at the two investigated length scales are related to the formation of a network structure on cooling.
as well as the difference of activation energy at the two investigated length scales are related to the formation of a network structure on cooling.