Heavy baryon spectrum with chiral multiplets of scalar and vector diquarks
スカラー及びベクトルダイクォークのカイラル多重項を用いたヘビーバリオンスペクトル
Kim, Y.*; Liu, Y.-R.*; 岡 眞 

 ; 鈴木 渓
; 鈴木 渓 


Kim, Y.*; Liu, Y.-R.*; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei
本論文では、スカラー及びベクトルダイクォークのカイラル有効理論を線形シグマ模型に基づいて構成する。有効理論の主な適用として、チャームまたはボトムクォークを1個含むシングルヘビーバリオンの基底状態と励起状態を記述する。ヘビークォーク(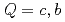 )とダイクォーク間の2体ポテンシャルを用いて、ヘビークォーク・ダイクォーク模型を構築し、
)とダイクォーク間の2体ポテンシャルを用いて、ヘビークォーク・ダイクォーク模型を構築し、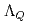 ,
, 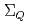 ,
, 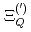 ,
, 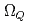 バリオンの正パリティ及び負パリティ状態のスペクトルを求める。ここで、有効理論に含まれる質量や相互作用パラメータは、格子QCDから得られたダイクォーク質量やヘビーバリオンの実験値を用いて決定される。結果として、擬スカラーダイクォーク質量の逆ヒエラルキーに起因して
バリオンの正パリティ及び負パリティ状態のスペクトルを求める。ここで、有効理論に含まれる質量や相互作用パラメータは、格子QCDから得られたダイクォーク質量やヘビーバリオンの実験値を用いて決定される。結果として、擬スカラーダイクォーク質量の逆ヒエラルキーに起因して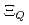 (フレーバー
(フレーバー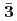 )の負パリティ励起状態のスペクトルが、
)の負パリティ励起状態のスペクトルが、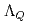 とは異なる振る舞いを示すことを示す。一方で、
とは異なる振る舞いを示すことを示す。一方で、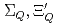 ,
, 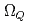 (フレーバー
(フレーバー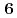 )のスペクトルは、
)のスペクトルは、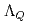 と同様である。さらに、我々のヘビークォーク・ダイクォーク模型による結果と実験値やクォーク模型による結果との比較を議論する。
と同様である。さらに、我々のヘビークォーク・ダイクォーク模型による結果と実験値やクォーク模型による結果との比較を議論する。
Chiral effective theory of scalar and vector diquarks is formulated according to the linear sigma model. The main application is to describe the ground and excited states of singly heavy baryons with a charm or bottom quark. Applying the potential quark model between the diquark and the heavy quark (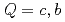 ), we construct a heavy-quark-diquark model. The spectra of the positive- and negative-parity states of
), we construct a heavy-quark-diquark model. The spectra of the positive- and negative-parity states of 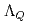 ,
, 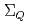 ,
, 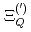 and
and 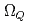 are obtained. The masses and interaction parameters of the effective theory are fixed partly from the lattice QCD data and also from fitting low-lying heavy baryon masses. We find that the negative parity excited states of
are obtained. The masses and interaction parameters of the effective theory are fixed partly from the lattice QCD data and also from fitting low-lying heavy baryon masses. We find that the negative parity excited states of 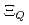 (flavor
(flavor 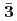 ) are different from those of
) are different from those of 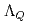 , because of the inverse hierarchy of the pseudoscalar diquark. On the other hand,
, because of the inverse hierarchy of the pseudoscalar diquark. On the other hand, 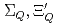 and
and 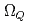 (flavor
(flavor 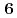 ) baryons have similar spectra. We compare our results of the heavy-quark-diquark model with experimental data as well as the quark model.
) baryons have similar spectra. We compare our results of the heavy-quark-diquark model with experimental data as well as the quark model.