Negative excursion of surface electric fields during gamma-ray glows in winter thunderstorms
冬季のガンマ線蛍光の間の地表面電場の負励起
和田 有希*; 鴨川 仁*; 久保 守*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 林 省吾*; 澤野 達也*; 米徳 大輔*; 土屋 晴文 
Wada, Yuki*; Kamogawa, Masashi*; Kubo, Mamoru*; Enoto, Teruaki*; Hayashi, Shugo*; Sawano, Tatsuya*; Yonetoku, Daisuke*; Tsuchiya, Harufumi
During the 2020-2021 winter season, we detected 6 gamma-ray glows at Kanazawa University, Japan. Negative surface electric fields (E-fields) were observed by a field mill during all the glow cases. In five of the six cases, the maximum E-field reached 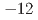 kV m
kV m , and the E-field during the glow detection was the strongest in 3 hours before and after the detection time. Therefore, negative charges should have been dominant in the thunderclouds that produced the gamma-ray glows, and electrons were probably accelerated and multiplied by the E-fields between a predominantly negative charge layer and a localized positive charge layer below. In addition, we extracted 8 non-detection cases in the 2020-2021 winter season, in which surface E-fields were stronger than
, and the E-field during the glow detection was the strongest in 3 hours before and after the detection time. Therefore, negative charges should have been dominant in the thunderclouds that produced the gamma-ray glows, and electrons were probably accelerated and multiplied by the E-fields between a predominantly negative charge layer and a localized positive charge layer below. In addition, we extracted 8 non-detection cases in the 2020-2021 winter season, in which surface E-fields were stronger than 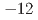 kV m
kV m . In 5 of the 8 cases, radar echoes were inadequately developed, suggesting insufficient charge accumulation. On the other hand, the remaining 3 cases had well-developed radar echoes, and there was no significant difference from the detection cases.
. In 5 of the 8 cases, radar echoes were inadequately developed, suggesting insufficient charge accumulation. On the other hand, the remaining 3 cases had well-developed radar echoes, and there was no significant difference from the detection cases.