Evaluation of photonuclear reaction cross-section data for  Bi at 13 and 17 MeV photon energies
Bi at 13 and 17 MeV photon energies
13と17MeVガンマ線エネルギーでの Biに対する光核反応データの評価
Biに対する光核反応データの評価
Nguyen, T. T. H.*; 岩本 信之 
 ; 佐波 俊哉*
; 佐波 俊哉*
Nguyen, T. T. H.*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Sanami, Toshiya*
Photonuclear data are essential for electron accelerator shielding design and possibly nuclear transmutation. So far, photonuclear cross-sections of various target materials have been evaluated up to a photon energy of 200 MeV within the nuclear data libraries, such as JENDL-5. Almost all data in JENDL-5 have been evaluated based on the experimental reaction cross-section data. Unfortunately, the photonuclear cross-section cannot provide all information about the emitted secondary particles, for instance, their energy distributions. Recently, the photoneutron energy spectra on the  Bi target at 13 and 17 MeV photon energies have been measured. The 13 and 17 MeV photon beams are nearly monoenergetic and have high intensity. Given that
Bi target at 13 and 17 MeV photon energies have been measured. The 13 and 17 MeV photon beams are nearly monoenergetic and have high intensity. Given that  Bi is one of the standard target materials, we re-evaluated the photonuclear data of this target according to (
Bi is one of the standard target materials, we re-evaluated the photonuclear data of this target according to (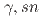 ), (
), (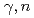 ), and (
), and (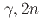 ) reaction cross-section data by I. Gheorghe et al. The evaluation procedure was conducted on the CCONE code system. The photo-absorption cross-sections were evaluated with the giant dipole resonance (GDR) and quasi-deuteron (QD) models. The emission of photoneutrons is described by the exciton model for the preequilibrium process and the statistical model for the compound process. The photoneutron energy spectra have been compared to the experimental data to find the connection between the theoretical reaction models and experiment.
) reaction cross-section data by I. Gheorghe et al. The evaluation procedure was conducted on the CCONE code system. The photo-absorption cross-sections were evaluated with the giant dipole resonance (GDR) and quasi-deuteron (QD) models. The emission of photoneutrons is described by the exciton model for the preequilibrium process and the statistical model for the compound process. The photoneutron energy spectra have been compared to the experimental data to find the connection between the theoretical reaction models and experiment.