Transverse single spin asymmetries of forward neutrons in 

 ,
, 
 Al, and
Al, and 
 Au collisions at
Au collisions at 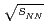 = 200 GeV as a function of transverse and longitudinal momenta
= 200 GeV as a function of transverse and longitudinal momenta
Acharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一 

 ; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之
; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之 

 ; 佐藤 進
; 佐藤 進 
 ; 谷田 聖
; 谷田 聖 

 ; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他305名*
; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他305名*
Acharya, U. A.*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Imai, Kenichi*; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Tanida, Kiyoshi; PHENIX Collaboration*; 305 of others*
In 2015 the PHENIX collaboration at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider recorded 

 ,
, 
 Al, and
Al, and 
 Au collision data at center of mass energies of
Au collision data at center of mass energies of  GeV with the proton beam(s) transversely polarized. At very forward rapidities
GeV with the proton beam(s) transversely polarized. At very forward rapidities 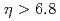 relative to the polarized proton beam, neutrons were detected either inclusively or in (anti)correlation with detector activity related to hard collisions. The resulting single spin asymmetries, that were previously reported, have now been extracted as a function of the transverse momentum of the neutron as well as its longitudinal momentum fraction
relative to the polarized proton beam, neutrons were detected either inclusively or in (anti)correlation with detector activity related to hard collisions. The resulting single spin asymmetries, that were previously reported, have now been extracted as a function of the transverse momentum of the neutron as well as its longitudinal momentum fraction 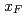 . The explicit kinematic dependence, combined with the correlation information allows for a closer look at the interplay of different mechanisms suggested to describe these asymmetries, such as hadronic interactions or electromagnetic interactions in ultra-peripheral collisions, UPC. Events that are correlated with a hard collision indeed display a mostly negative asymmetry that increases in magnitude as a function of transverse momentum with only little dependence on
. The explicit kinematic dependence, combined with the correlation information allows for a closer look at the interplay of different mechanisms suggested to describe these asymmetries, such as hadronic interactions or electromagnetic interactions in ultra-peripheral collisions, UPC. Events that are correlated with a hard collision indeed display a mostly negative asymmetry that increases in magnitude as a function of transverse momentum with only little dependence on 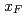 . In contrast, events that are not likely to have emerged from a hard collision display positive asymmetries for the nuclear collisions with a kinematic dependence that resembles that of a UPC based model. Because the UPC interaction depends strongly on the charge of the nucleus, those effects are very small for
. In contrast, events that are not likely to have emerged from a hard collision display positive asymmetries for the nuclear collisions with a kinematic dependence that resembles that of a UPC based model. Because the UPC interaction depends strongly on the charge of the nucleus, those effects are very small for 

 collisions, moderate for
collisions, moderate for 
 Al collisions, and large for
Al collisions, and large for 
 Au collisions.
Au collisions.