 meson production in
meson production in 
 Al,
Al, 
 Au,
Au, 
 Au, and
Au, and  He
He Au collisions at
Au collisions at  GeV
GeV
Acharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一 

 ; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之
; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之 

 ; 佐藤 進
; 佐藤 進 
 ; 谷田 聖
; 谷田 聖 

 ; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他365名*
; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他365名*
Acharya, U. A.*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Imai, Kenichi*; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Tanida, Kiyoshi; PHENIX Collaboration*; 365 of others*
Small nuclear collisions are mainly sensitive to cold-nuclear-matter effects; however, the collective behavior observed in these collisions shows a hint of hot-nuclear-matter effects. The identified-particle spectra, especially the  mesons which contain strange and antistrange quarks and have a relatively small hadronic-interaction cross section, are a good tool to study these effects. The PHENIX experiment has measured
mesons which contain strange and antistrange quarks and have a relatively small hadronic-interaction cross section, are a good tool to study these effects. The PHENIX experiment has measured  mesons in a specific set of small collision systems
mesons in a specific set of small collision systems 
 Al,
Al, 
 Au, and
Au, and  He
He Au, as well as
Au, as well as 
 Au, at
Au, at  GeV. The transverse-momentum spectra and nuclear-modification factors are presented and compared to theoretical-model predictions. The comparisons with different calculations suggest that quark-gluon plasma may be formed in these small collision systems at
GeV. The transverse-momentum spectra and nuclear-modification factors are presented and compared to theoretical-model predictions. The comparisons with different calculations suggest that quark-gluon plasma may be formed in these small collision systems at  GeV. However, the volume and the lifetime of the produced medium may be insufficient for observing strangeness-enhancement and jet-quenching effects. Comparison with calculations suggests that the main production mechanisms of
GeV. However, the volume and the lifetime of the produced medium may be insufficient for observing strangeness-enhancement and jet-quenching effects. Comparison with calculations suggests that the main production mechanisms of  mesons at midrapidity may be different in
mesons at midrapidity may be different in 
 Al versus
Al versus 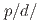
 He
He Au collisions at
Au collisions at  GeV. While thermal quark recombination seems to dominate in
GeV. While thermal quark recombination seems to dominate in 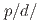
 He
He Au collisions, fragmentation seems to be the main production mechanism in
Au collisions, fragmentation seems to be the main production mechanism in 
 Al collisions.
Al collisions.