Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Morishita, Yuki; Tomioka, Akifumi; Fujisawa, Makoto; Izaki, Kenji
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1065, p.169527_1 - 169527_5, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)It is important to differentiate between natural and artificial radioactive materials such as plutonium in nuclear facilities. In this study, a scintillator-based alpha-particle detector was developed using YAP:Ce scintillator and Multi-Anode PhotoMultiplier Tube. The detector was used to measure various naturally occurring radioactive materials (NORM) samples including radon progeny, lead plate, lantern mantle, and radium ceramic ball. The measurement results were compared with Monte Carlo simulation calculations and were found to be in agreement. The energy resolution of the detector is 8.6%FWHM. In the measurement results of radon progeny, peaks of 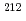 Bi (6.1 MeV),
Bi (6.1 MeV),  Po (7.7 MeV), and
Po (7.7 MeV), and 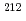 Po (8.8 MeV) can be observed. The lead plate contains
Po (8.8 MeV) can be observed. The lead plate contains  Po and emits 5.3 MeV alpha particle. The simulation with the same energy was able to reproduce the actual measurement. The results showed the energy and distribution of the alpha particles emitted by the NORM samples. The study successfully demonstrated the capability of the developed alpha-particle detector in identifying NORM.
Po and emits 5.3 MeV alpha particle. The simulation with the same energy was able to reproduce the actual measurement. The results showed the energy and distribution of the alpha particles emitted by the NORM samples. The study successfully demonstrated the capability of the developed alpha-particle detector in identifying NORM.
 Si
Si O
O (GPS) scintillator-based alpha imaging detector for rapid plutonium detection in high-radon environments
(GPS) scintillator-based alpha imaging detector for rapid plutonium detection in high-radon environmentsMorishita, Yuki; Izaki, Kenji; Kaneko, Junichi*; Yamamoto, Seiichi*; Higuchi, Mikio*; Torii, Tatsuo
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 67(10), p.2203 - 2208, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:68.22(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)We developed a Gd Si
Si O
O (GPS) scintillator-based alpha imaging detector and demonstrated its effectiveness by evaluating actual Pu particle and
(GPS) scintillator-based alpha imaging detector and demonstrated its effectiveness by evaluating actual Pu particle and  Rn progeny. The GPS scintillator plate was prepared by a sintering method. The outer dimensions of the GPS scintillator plate were 5
Rn progeny. The GPS scintillator plate was prepared by a sintering method. The outer dimensions of the GPS scintillator plate were 5  5 cm, and the scintillator layer was approximately 50
5 cm, and the scintillator layer was approximately 50  m on a 3-mm-thick high-transparency glass. The plate was optically coupled to a position-sensitive photomultiplier tube with silicone grease. The developed imaging detector exhibited good uniformity. Pu particle activities were accurately evaluated at 14 different positions, and the difference in activity was within 6%. Radon-222 (
m on a 3-mm-thick high-transparency glass. The plate was optically coupled to a position-sensitive photomultiplier tube with silicone grease. The developed imaging detector exhibited good uniformity. Pu particle activities were accurately evaluated at 14 different positions, and the difference in activity was within 6%. Radon-222 ( Rn) progeny counts were reduced by 65.3% by applying an energy window. Although the Pu/
Rn) progeny counts were reduced by 65.3% by applying an energy window. Although the Pu/ Rn progeny activity ratio was 1/51, the Pu particle was successfully identified among
Rn progeny activity ratio was 1/51, the Pu particle was successfully identified among  Rn progeny within the 5 min-measurement time. The imaging detector has an excellent ability for detecting Pu among
Rn progeny within the 5 min-measurement time. The imaging detector has an excellent ability for detecting Pu among  Rn progeny. Thus, this detector is useful for alpha contamination monitoring in high-radon-background environments.
Rn progeny. Thus, this detector is useful for alpha contamination monitoring in high-radon-background environments.
Morishita, Yuki; Kaneko, Junichi*; Higuchi, Mikio*; Izaki, Kenji; Yajima, Tatsuo*; Matsuura, Mitsugu*; Tamura, Ken; Torii, Tatsuo
Radiation Measurements, 122, p.115 - 120, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:58.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)Morishita, Yuki; Yamamoto, Seiichi*; Izaki, Kenji; Kaneko, Junichi*; Hoshi, Katsuya; Torii, Tatsuo
Radiation Measurements, 112, p.1 - 5, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:87.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)To detect plutonium isotopes ( Pu,
Pu,  Pu, and
Pu, and  Pu) in a field of high beta and
Pu) in a field of high beta and  background, an alpha particle detector with low beta and
background, an alpha particle detector with low beta and  -ray sensitivity is required. Therefore, we optimized the thickness of the GAGG scintillator for alpha particle detection in a field of high beta and
-ray sensitivity is required. Therefore, we optimized the thickness of the GAGG scintillator for alpha particle detection in a field of high beta and  background. We prepared three GAGG scintillators with thicknesses of 0.05 mm, 0.07 mm, and 0.1 mm. Each of the GAGG scintillators was coupled optically to the SiPM array, which was used as the photodetector. Alpha, beta, and
background. We prepared three GAGG scintillators with thicknesses of 0.05 mm, 0.07 mm, and 0.1 mm. Each of the GAGG scintillators was coupled optically to the SiPM array, which was used as the photodetector. Alpha, beta, and  rays were irradiated onto the developed alpha particle detector, and their spectra were obtained. All GAGG scintillators used in this study were not sensitive to
rays were irradiated onto the developed alpha particle detector, and their spectra were obtained. All GAGG scintillators used in this study were not sensitive to  rays with a dose rate of 1 mSv/h. The beta count of the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG was only 1/100 that of the 0.1-mm-thick GAGG. Therefore, the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG scintillator is promising from the viewpoint of detecting plutonium contamination in a field with high beta and
rays with a dose rate of 1 mSv/h. The beta count of the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG was only 1/100 that of the 0.1-mm-thick GAGG. Therefore, the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG scintillator is promising from the viewpoint of detecting plutonium contamination in a field with high beta and  background.
background.
Morishita, Yuki; Yamamoto, Seiichi*; Izaki, Kenji; Kaneko, Junichi*; Nemoto, Norio
Radiation Measurements, 103, p.33 - 38, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nuclear fuel materials, such as uranium and plutonium (Pu), are handled at nuclear fuel facilities. There are a contamination source of Pu in tight spaces that cannot be directly measured by a ZnS(Ag) scintillation detector, such as interspace between a glovebox window and a platform, pipe flange, port cover of vinyl bag, and filter interspaces. Therefore, we developed a new imaging detector called a flexible alpha camera that enables to identify the Pu contamination for tight spaces at work sites. The thickness of the flexible alpha camera was only  1/5 of the ZnS(Ag) scintillation detector, and its efficiency for 4-pi direction was 42.7% for 5.5-MeV alpha particles. Minimal detectable activity (MDA) was 0.014 Bq. Four types of PuO
1/5 of the ZnS(Ag) scintillation detector, and its efficiency for 4-pi direction was 42.7% for 5.5-MeV alpha particles. Minimal detectable activity (MDA) was 0.014 Bq. Four types of PuO sample, removed from a duct, Bag-In/Bag-Out port, glovebox glove, and vinyl sheet, were measured by the flexible alpha camera and the PuO
sample, removed from a duct, Bag-In/Bag-Out port, glovebox glove, and vinyl sheet, were measured by the flexible alpha camera and the PuO particle was automatically identified. Using the flexible alpha camera, the Pu contamination source can be quickly detected, preventing the spread of contamination.
particle was automatically identified. Using the flexible alpha camera, the Pu contamination source can be quickly detected, preventing the spread of contamination.
Morishita, Yuki; Yamamoto, Seiichi*; Izaki, Kenji; Kaneko, Junichi*; Toi, Kohei*; Tsubota, Yoichi*; Higuchi, Mikio*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 764, p.383 - 386, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:96.55(Instruments & Instrumentation)Morishita, Yuki; Yamamoto, Seiichi*; Izaki, Kenji; Kaneko, Junichi*; Toi, Kohei*; Tsubota, Yoichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 747, p.81 - 86, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:94.35(Instruments & Instrumentation)Alpha particles are monitored for detecting nuclear fuel material (i.e., plutonium and uranium) at nuclear fuel facilities. In this study, we developed a new alpha-particle imaging system by combining an Si-PM array, which is insensitive to noise, with a Ce-doped Gd Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O (GAGG) scintillator, and evaluated our developed system's fundamental performance. The scintillator was 0.1-mm thick, and the light guide was 3.0 mm thick. An
(GAGG) scintillator, and evaluated our developed system's fundamental performance. The scintillator was 0.1-mm thick, and the light guide was 3.0 mm thick. An  Am source was used for all the measurements. We evaluated the spatial resolution by taking an image of a resolution chart. A 1.6 lp/mm slit was clearly resolved, and the spatial resolution was estimated to be less than 0.6-mm FWHM. The energy resolution was 13% FWHM. A slight distortion was observed in the image, and the uniformity near its center was within 24%. We conclude that our developed alpha-particle imaging system is promising for plutonium detection at nuclear fuel facilities.
Am source was used for all the measurements. We evaluated the spatial resolution by taking an image of a resolution chart. A 1.6 lp/mm slit was clearly resolved, and the spatial resolution was estimated to be less than 0.6-mm FWHM. The energy resolution was 13% FWHM. A slight distortion was observed in the image, and the uniformity near its center was within 24%. We conclude that our developed alpha-particle imaging system is promising for plutonium detection at nuclear fuel facilities.
Sagawa, Naoki; Izaki, Kenji; Mizuniwa, Harumi*
JAEA-Technology 2013-029, 28 Pages, 2013/11
Developed in the Mixed Oxide fuel fabrication facility, Basic handling of IP, analysis method, detection of Pu and radioactivity quantification. These are the conditions that the exposure conditions and the analysis condition are constant. However, in the case of Contamination has occurred in the workplace, contaminated samples are not only Pu. It may contain a Pb or RnTn. Then, if other work is being carried out in a room that is the operation of IP, it's difficult to darken the room. PSL is reduced when light hits the IP. In this study, we have investigated in order to upgrade radiation protection, in the case of Containing the Pb or PSL reduction by light. Additionally, regarding change of analysis condition, the analysis method was examined when the resolution was changed to 50 micro, 100 micro and 200 micro.
Sagawa, Naoki; Yamazaki, Takumi; Kurosawa, Shigeyuki*; Izaki, Kenji; Mizuniwa, Harumi; Takasaki, Koji
JAEA-Technology 2010-051, 35 Pages, 2011/03
The image analysis method using a imaging plate (IP) is recent technique, and this method can get the information of radioactivity distribution by the unit of Photo Simulated Luminescence (PSL). We have investigated the PSL images obtained by measuring some plutonium samples which are radiation protection samples in order to apply imaging plate to the radiation protection at the MOX fuel facility. Plutonium spots were extracted from the PSL image extracted by the threshold, in which about 99% of the back ground was excluded, and identified by the additional requirement that the spot size is more than 40 pixels. The average background is subtracted from PSL strength of the spot area identified as Pu, and the radioactivity of the Pu spot was evaluated by multiplying the conversion calculation that is in consideration of fading.
Izaki, Kenji; Ino, Kazuo*; Mizuniwa, Harumi
JAEA-Research 2008-107, 46 Pages, 2009/03
The contamination control has been carried out by alpha-ray measurement in facilities where handling plutonium like the MOX fuel manufacturing facility and the reprocessing facility, etc. In the case of alpha-ray measurement, it is necessary to consider the influence of radon progeny that is natural radionuclide. The influence of radon progeny has been decreased by pulse height discrimination technique using the semiconductor detector as needed. However, the semiconductor detector has potentially significant problems such as the durability and noise susceptibility. Therefore the accuracy of pulse height discrimination by the ZnS(Ag) scintillation detector was confirmed as alternative to the semiconductor detector. This report shows the accuracy of pulse height discrimination technique using the ZnS(Ag) scintillation detector and evaluates the adaptability to contamination control equipments.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Tsujimura, Norio; Shimizu, Yoshio; Izaki, Kenji; Furuta, Sadaaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(Suppl.5), p.74 - 77, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)The purpose of this study is the establishment of the determination procedures for the placements of CAAS detectors in PCDF. The dose of detection point was evaluated the simple equation which was formulated in calculated factors by MCNP and ANISN. When the alarm trip point was 2.0 mGy/h, the detection area was covered 30 m distances from the equipment to the CAD and 100 cm concrete shielding. This result will be reflected in the determination of the CAD placements and three CADs were placed in PCDF.
Izaki, Kenji; Suzuki, Hideki; Tsubaki, Hirohiko; Ozeki, Kiyoshi
JAEA-Research 2007-009, 40 Pages, 2007/03
Criticality Accident Alarm System (CAAS) has been used in Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories for about 20 years, and there is occurrence of the abnormal signal called "Single Detection", as an operational problem of CAAS. Radiation Protection Division has investigated the causes affecting "Single Detection", as well as reducing the influence of noises such as electromagnetic waves and power source variations. This report shows the result of the long-term observation with detectors of CAAS and describes that cosmic rays have high possibility to cause "Single Detection".
Izaki, Kenji
Hoken Butsuri, 41(2), p.64 - 66, 2006/06
no abstracts in English
Ishikawa, Hisashi; Nemoto, Norio; Izaki, Kenji; Kobayashi, Hirohide; Tanizawa, Teruaki*; Kanazawa, Yoshito*
JNC TN8400 2004-008, 124 Pages, 2004/05
In order to strengthen the functions of the self moving survey system, the design of the truck and the data transmission system, the investigation of the handling function and the durability test assumed under the disaster environment were executed.As the basic performance of the self moving survey system, it was demanded to have the functions in order to run on the bumpy road, go up and down the stairs and open and shut of the door. And the remote control by the PHS line or the SS wireless is adopted as an operational method. Moreover, as the function that can monitor the disaster situation in the facility, it was assumed the design that make modular the measurement equipments, which mainly measure alpha ray, gamma ray and neutron, and installed it.In consideration of the radiation monitoring under the environment that assumes the critical accident and a fire and the explosion etc. heat test, humidity test, radiation test, and aerosol (smoke) test for monitoring equipments were executed. As a result of the tests, it was confirmed that all equipment except the semiconductor detector operated normally.
Izaki, Kenji; Kobayashi, Hirohide
Ajia Oseania Hoshasen Bogo Kyogikai, 0 Pages, 2002/00
None
Ito, Yasuhisa; Noda, Kimio; ; Izaki, Kenji; Ebana, Minoru*
JNC TN8410 2001-007, 81 Pages, 2001/03
Dust Monitor is one of the equipments that measure the concentration of air-borne radioactive materials. This monitor generally collects the dusts in the air by the air pumps, but this system has several problems. Therefore we made the prototypes of Dust Monitor and Dust Sampler that adopted static electrical collecting system, and examined these prototypes. As the result of examination, we confirmed that the static electrical collecting system has the same collection efficiency with air suction system and it is possible to use these prototypes in controlled area.
Izaki, Kenji; Noda, Kimio; ; Kashimuta, Yoshio*
JNC TN8410 2001-005, 30 Pages, 2001/01
Stack monitoring is the most important work in radiation control works. Exhaust monitors used for stack monitoring have the background (which is the counts by natural radio-nuclides) on normal condition, and the values of the background vary with the facilities. Therefore, if the value of background is high, it is difficult to estimate rapidly the radioactive concentration in the exhaust. In order to estimate rapidly the radioactive concentration in exhaust, we analyzed the behavior of natural radioactivity in the facilities and examine the technique fo reducing the value of the background. As a result of the examination, we found that it is possible to estimate rapidly if we change over the monitoring point to immediately after the HEPA filters on the exhaust duct. In this reports, the analyzed results of behavior of natural radio-nuclides in the facilities and the technique for reducing the values of the background are described. To reduce the value of the background has a major effect on not only rapidly estimating the radioactive density in the exhaust but also finding the unusual things on stack monitoring.
Kobayashi, Hirohide; Kanamori, Masashi; Noda, Kimio; Izaki, Kenji; Miyabe, Kenjiro;
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, ,
None
井崎 賢二; 森下 祐樹; 山崎 巧
金子 純一*; 樋口 幹雄*; 坪田 陽一*; 山本 誠一*; 石橋 浩之*
【課題】環境中に管理対象放射性物質とそれ以外の放射性物質が混在する場合であっても、管理対象放射性物質に起因する放射能汚染を短時間に計測して評価する放射線計測方法を提供する。 【解決手段】測定試料に付着している放射性物質に感応して検出信号を発生する多数の検出ピクセルを平面状に並べて放射線検出面を構成した放射線検出器の多数の検出ピクセルから出力される検出信号を、放射線検出面を複数の領域に分割して各分割領域に該当する検出ピクセルから出力される検出信号を検出処理し、分割領域毎に検出される放射線検出結果を出力する信号処理装置を用いて測定試料中の放射性物質の放射線量を計測する。