Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shibanuma, Tomohiro; Hirano, Hiroshi*; Kimura, Yasuhisa; Aita, Takahiro; Yoshida, Masato; Nagai, Yuya; Kitamura, Akihiro
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 58(2), p.91 - 98, 2023/08
We developed new containment tents that are more easily assembled and effectively functioned, by improving and refurbishing the shortcomings of the conventional tents. The new tents have been already tested in the real airborne contamination situation occurred at the plutonium fuel fabricating facility. The tents appropriately functioned for intended use but other shortcomings emerged and therefore we had modified the structure of the tents further.
Kitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 26(3), p.032802_1 - 032802_12, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)A bunch-shape monitor (BSM) is a useful device for performing longitudinal beam tuning using the pointwise longitudinal phase distribution measured at selected points in the beam transportation. To measure the longitudinal phase distribution of a low-energy negative hydrogen (H ) ion beam, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was adopted for the secondary-electron-emission target to mitigate the thermal damage due to the high-intensity beam loading. The HOPG target enabled the measurement of the longitudinal phase distribution at the center of a 3-MeV H
) ion beam, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was adopted for the secondary-electron-emission target to mitigate the thermal damage due to the high-intensity beam loading. The HOPG target enabled the measurement of the longitudinal phase distribution at the center of a 3-MeV H ion beam with a high peak current of about 50 mA. The longitudinal bunch width was measured using HOPG-BSM at the test stand, which was consistent with the beam simulation. The correlation measurement between the beam transverse and longitudinal planes was demonstrated using HOPG-BSM. The longitudinal Twiss and emittance measurement with the longitudinal Q-scan method was conducted using HOPG-BSM.
ion beam with a high peak current of about 50 mA. The longitudinal bunch width was measured using HOPG-BSM at the test stand, which was consistent with the beam simulation. The correlation measurement between the beam transverse and longitudinal planes was demonstrated using HOPG-BSM. The longitudinal Twiss and emittance measurement with the longitudinal Q-scan method was conducted using HOPG-BSM.
 beam
beamKitamura, Ryo; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Morishita, Takatoshi
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.330 - 332, 2023/01
In the J-PARC linac, a new bunch-shape monitor (BSM) is developed to stably measure the high-intensity and low-energy H beam by improving the strength of the target probe for the heat loading. The new target probe is made of the graphite. The first measurement of the longitudinal beam profile has been realized with the BSM at the core region of the high-intensity beam. Since the beam profile can be measured with the new BSM at any transverse position thanks to the new target probe, we propose the advanced application of the beam diagnostics with the BSM. In this presentation, some new approaches of the beam diagnostics with the BSM; the transverse profile measurement using the secondary electrons and the beam current evaluation from the transverse profile measurement, are discussed beyond the original usage of the BSM.
beam by improving the strength of the target probe for the heat loading. The new target probe is made of the graphite. The first measurement of the longitudinal beam profile has been realized with the BSM at the core region of the high-intensity beam. Since the beam profile can be measured with the new BSM at any transverse position thanks to the new target probe, we propose the advanced application of the beam diagnostics with the BSM. In this presentation, some new approaches of the beam diagnostics with the BSM; the transverse profile measurement using the secondary electrons and the beam current evaluation from the transverse profile measurement, are discussed beyond the original usage of the BSM.
Kitamura, Ryo; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Miura, Akihiko; Morishita, Takatoshi
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.212 - 214, 2023/01
In the J-PARC linac, the bunch-shape monitor (BSM) is developed to precisely and rapidly measure the longitudinal beam profile at the front-end, towards the improvement of the beam matching. The graphite target having the good strength to the high-power beam, has been introduced in order to resist the heat loading of the high-intensity beam. The resolution and other uncertainties were evaluated for the BSM. The longitudinal Twiss parameters and emittance were measured using the BSM and the IMPACT, which was the 3D particle-in-cell simulation code. The precision of the longitudinal emittance measurement was improved, by implementing uncertainties related to the BSM into the calculation. In this presentation, we will report a series of the measurement result, the method of the beam diagnostics with the BSM at the front-end, and the comparison between the measurement and the beam simulation.
 Cs discharge from a forested catchment
Cs discharge from a forested catchmentSakuma, Kazuyuki; Hayashi, Seiji*; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Malins, A.; Funaki, Hironori; Tsuji, Hideki*; Kobayashi, Takamaru*; Kitamura, Akihiro; Iijima, Kazuki
Water Resources Research, 58(8), p.e2021WR031181_1 - e2021WR031181_16, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:34.88(Environmental Sciences) beam with 3 MeV by the bunch-shape monitor
beam with 3 MeV by the bunch-shape monitorKitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011012_1 - 011012_6, 2021/03
The new bunch shape monitor (BSM) is required to measure the bunch size of the high-intensity H beam with 3 MeV at the front-end section in the J-PARC linac. The carbon-nano tube wire and the graphene stick are good candidates for the target wire of the BSM, because these materials have the enough strength to detect the high-intensity beam. However, since the negative high voltage of more than a few kV should be applied to the wire in the BSM, the suppression of the discharge is the challenge to realize the new BSM. After the high-voltage test to investigate the effect of the discharge from the wire, the detection of the signal from the BSM was successful at the beam core with the peak current of 55 mA using the graphene stick. The preliminary result of the bunch-size measurement is reported in this presentation.
beam with 3 MeV at the front-end section in the J-PARC linac. The carbon-nano tube wire and the graphene stick are good candidates for the target wire of the BSM, because these materials have the enough strength to detect the high-intensity beam. However, since the negative high voltage of more than a few kV should be applied to the wire in the BSM, the suppression of the discharge is the challenge to realize the new BSM. After the high-voltage test to investigate the effect of the discharge from the wire, the detection of the signal from the BSM was successful at the beam core with the peak current of 55 mA using the graphene stick. The preliminary result of the bunch-size measurement is reported in this presentation.
Nagao, Fumiya; Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ito, Satomi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Dohi, Terumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Funaki, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Research 2020-007, 249 Pages, 2020/10
The accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. occurred due to the Great East Japan Earthquake, Sanriku offshore earthquake, of 9.0 magnitude and the accompanying tsunami. As a result, large amount of radioactive materials was released into the environment. Under these circumstances, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting "Long-term Assessment of Transport of Radioactive Contaminants in the Environment of Fukushima" concerning radioactive materials released in environment, especially migration behavior of radioactive cesium since November 2012. This report is a summary of the research results that have been obtained in environmental dynamics research conducted by JAEA in Fukushima Prefecture.
Kitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 17th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.251 - 253, 2020/09
A bunch-shape monitor (BSM) in the low-energy region is being developed in the J-PARC linac to accelerate the high-intensity proton beam with the low emittance. A highly-oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was introduced as the target of the BSM to mitigate the thermal loading. The stable measurement of the BSM was realized thanks to the HOPG target, while the tungsten target was broken by the thermal loading from the high-intensity beam. However, since the longitudinal distribution measured with the BSM using the HOPG target was wider than the expected one, the improvement of tuning parameters is necessary for the BSM. The BSM consists of an electron multiplier, a bending magnet, and a radio-frequency deflector, which should be tuned appropriately. Behavior of these components were investigated and tuned. The longitudinal distribution measured with the BSM after the tuning was consistent with the expected one.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hirano, Koichiro; Ito, Takashi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Shinto, Katsuhiro; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012077_1 - 012077_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.67(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have upgraded a 3-MeV linac at J-PARC. The ion source is same as the J-PARC linac's, and the old 30-mA RFQ is replaced by a spare 50-mA RFQ, therefore, the beam energy is 3 MeV and the nominal beam current is 50 mA. The main purpose of this system is to test the spare RFQ, but also used for testing of various components required in order to keep the stable operation of the J-PARC accelerator. The accelerator has been already commissioned, and measurement programs have been started. In this paper, present status of this 3-MeV linac is presented.
Nagao, Fumiya; Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ito, Satomi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Dohi, Terumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Funaki, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-002, 235 Pages, 2019/08
The accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (hereinafter referred to 1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. occurred due to the Great East Japan Earthquake, Sanriku offshore earthquake, of 9.0 magnitude and the accompanying tsunami. As a result, large amount of radioactive materials was released into the environment. Under these circumstances, JAEA has been conducting Long-term Environmental Dynamics Research concerning radioactive materials released in environment, especially migration behavior of radioactive cesium since November 2012. This report is a summary of the research results that have been obtained in environmental dynamics research conducted by JAEA in Fukushima Prefecture.
 beam with 3 MeV using the carbon material
beam with 3 MeV using the carbon materialKitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.51 - 54, 2019/07
The longitudinal measurement and tuning at the beam transport after the RFQ are important to reduce the beam loss and the emittance growth in the J-PARC linac, when the high-intensity H beam of more than 60 mA is supplied. The new bunch shape monitor (BSM) using the carbon-nanotube (CNT) wire is necessary to measure the bunch shape of the high-intensity H
beam of more than 60 mA is supplied. The new bunch shape monitor (BSM) using the carbon-nanotube (CNT) wire is necessary to measure the bunch shape of the high-intensity H beam with 3 MeV, because the CNT wire has a high-temperature tolerance and a small energy deposit. However, when the high voltage was applied to the CNT wire to extract the secondary electron derived, the discharge prevents the power supply from applying the voltage. Therefore, the discharge should be suppressed to measure the bunch shape with stability. Considering the characteristics of the CNT as the emitter, when the length of the CNT wire was short, the high voltage of -10 kV was applied to the CNT wire. The current status and future prospects of the BSM using the CNT wire are reported in this presentation.
beam with 3 MeV, because the CNT wire has a high-temperature tolerance and a small energy deposit. However, when the high voltage was applied to the CNT wire to extract the secondary electron derived, the discharge prevents the power supply from applying the voltage. Therefore, the discharge should be suppressed to measure the bunch shape with stability. Considering the characteristics of the CNT as the emitter, when the length of the CNT wire was short, the high voltage of -10 kV was applied to the CNT wire. The current status and future prospects of the BSM using the CNT wire are reported in this presentation.
Kitamura, Ryo; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Otani, Masashi*; Kosaka, Satoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.2543 - 2546, 2019/06
A bunch shape monitor (BSM) is one of the important instruments to measure the longitudinal phase space distribution. For example in the J-PARC linac, three BSMs using the tungsten wire are installed at the ACS section to measure the bunch shapes between the accelerating cavities. However, this conventional BSM is hard to measure the bunch shape of H beam with 3 MeV at the beam transport between the RFQ and DTL sections, because the wire is broken around the center region of the beam. The new BSM using the carbon-nano-tube (CNT) wire is being developed to be able to measure the bunch shape of the H
beam with 3 MeV at the beam transport between the RFQ and DTL sections, because the wire is broken around the center region of the beam. The new BSM using the carbon-nano-tube (CNT) wire is being developed to be able to measure the bunch shape of the H beam with 3 MeV. The careful attention should be paid to apply the high voltage of
beam with 3 MeV. The careful attention should be paid to apply the high voltage of  10 kV to the CNT wire. The several measures are taken to suppress the discharge from the wire and operate the CNT-BSM. This presentation reports the current status of the development and future prospective for the CNT-BSM.
10 kV to the CNT wire. The several measures are taken to suppress the discharge from the wire and operate the CNT-BSM. This presentation reports the current status of the development and future prospective for the CNT-BSM.
 for modelling dissolved
for modelling dissolved  Cs concentrations in Fukushima river water; Case study of the upstream Ota River
Cs concentrations in Fukushima river water; Case study of the upstream Ota RiverSakuma, Kazuyuki; Tsuji, Hideki*; Hayashi, Seiji*; Funaki, Hironori; Malins, A.; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Kitamura, Akihiro; Iijima, Kazuki; Hosomi, Masaaki*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 184-185, p.53 - 62, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:7.01(Environmental Sciences)A study is presented on the applicability of the distribution coefficient ( ) absorption/desorption model to simulate dissolved
) absorption/desorption model to simulate dissolved  Cs concentrations in Fukushima river water. The simulation results were in good agreement with the observations on water and suspended sediment fluxes, and on particulate bound
Cs concentrations in Fukushima river water. The simulation results were in good agreement with the observations on water and suspended sediment fluxes, and on particulate bound  Cs concentrations under both ambient and high flow conditions. By contrast the measured concentrations of dissolved
Cs concentrations under both ambient and high flow conditions. By contrast the measured concentrations of dissolved  Cs in the river water were much harder to reproduce with the simulations. By tuning the
Cs in the river water were much harder to reproduce with the simulations. By tuning the  values for large particles, it was possible to reproduce the mean dissolved
values for large particles, it was possible to reproduce the mean dissolved  Cs concentrations during base flow periods (observation: 0.32 Bq/L, simulation: 0.36 Bq/L). However neither the seasonal variability in the base flow dissolved
Cs concentrations during base flow periods (observation: 0.32 Bq/L, simulation: 0.36 Bq/L). However neither the seasonal variability in the base flow dissolved  Cs concentrations (0.14-0.53 Bq/L), nor the peaks in concentration that occurred during storms (0.18-0.88 Bq/L, mean: 0.55 Bq/L), could be reproduced with realistic simulation parameters.
Cs concentrations (0.14-0.53 Bq/L), nor the peaks in concentration that occurred during storms (0.18-0.88 Bq/L, mean: 0.55 Bq/L), could be reproduced with realistic simulation parameters.
 Cs redistribution in the Oginosawa River catchment near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant using integrated watershed modeling
Cs redistribution in the Oginosawa River catchment near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant using integrated watershed modelingSakuma, Kazuyuki; Malins, A.; Funaki, Hironori; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Mori, Koji*; Tada, Kazuhiro*; Kobayashi, Takamaru*; Kitamura, Akihiro; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 182, p.44 - 51, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:36.73(Environmental Sciences)The Oginosawa River catchment lies 15 km south-west of the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear plant. The General-purpose Terrestrial Fluid-flow Simulator (GETFLOWS) code was used to study sediment and  Cs redistribution within the catchment. Cesium-137 input to watercourses came predominantly from land adjacent to river channels and forest gullies. Forested areas far from the channels only made a minor contribution to
Cs redistribution within the catchment. Cesium-137 input to watercourses came predominantly from land adjacent to river channels and forest gullies. Forested areas far from the channels only made a minor contribution to  Cs input to watercourses, total erosion of between 0.001-0.1 mm from May 2011 to December 2015. The 2.3-6.9% y
Cs input to watercourses, total erosion of between 0.001-0.1 mm from May 2011 to December 2015. The 2.3-6.9% y decrease in the amount of
decrease in the amount of  Cs in forest topsoil over the study period can be explained by radioactive decay (approximately 2.3% y
Cs in forest topsoil over the study period can be explained by radioactive decay (approximately 2.3% y ), along with a migration downwards into subsoil and a small amount of export. The amount of
), along with a migration downwards into subsoil and a small amount of export. The amount of  Cs available for release from land adjacent to rivers is expected to be lower in future than compared to this study period, as the simulations indicate a high depletion of inventory from these areas.
Cs available for release from land adjacent to rivers is expected to be lower in future than compared to this study period, as the simulations indicate a high depletion of inventory from these areas.
Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Niizato, Tadafumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Dohi, Terumi; Nakama, Shigeo; Funaki, Hironori; Misono, Toshiharu; Oyama, Takuya; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Hayashi, Seiji*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2017-018, 86 Pages, 2017/10
Since the accidents at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant following the Tohoku Region Pacific Coast Earthquake on March 11th, 2011, Fukushima Environmental Safety Center has carried out research on natural mobilization of radionuclide (especially radiocesium) and future forecast from forest to water system and surrounding residential areas. The report summarizes the latest results that have been accumulated from each study field, of our agency together with the other related research organizations. The contents of the report is to be used as evidence-based information for the QA-styled pages in the website of JAEA Sector of Fukushima Research and Development at the time of next renewal.
Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Kitamura, Seiji; Iwasaki, Akihisa*; Matsubara, Shinichiro*; Okamura, Shigeki*
Proceedings of 2017 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2017) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/07
To design fast reactor (FR) components, seismic response must be evaluated in order to ensure structural integrity. Therefore, a sophisticated analysis method has to be developed to study the seismic response of FR core. The fast reactors are made of several hundred core assemblies in hexagonal arrangement. When a big earthquake occurs, large horizontal displacement and impact force of each core assembly may cause a trouble for control rod insertability and core assembly intensity. Therefore, a seismic analysis method of fast reactor core considering horizontal nonlinear behavior, such as impact, fluid-structure interaction, etc. is needed. Validation of the core assembly vibration analysis code in three dimension (REVIAN-3D) was conducted by a full scale experiment. In this validation, the vertical behavior (raising displacement) and horizontal behavior (Impact force, horizontal response) of the analysis result agreed very well with the experiments.
Kurikami, Hiroshi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Kato, Tomoko; Kitamura, Akihiro; Kanno, Mitsuhiro*; Kurosawa, Naohiro*
JAEA-Research 2016-020, 50 Pages, 2017/01
In this report, we developed a compartment model of radionuclide migration in environment based on exposure pathways in a river basin scale and performed a preliminary calculation. The results showed good agreement with some measurement, although the comparison of bed sediment, transportation to outer sea and to agricultural products with the measurement was not enough. We continue to validate the model.
 Cs discharge out of reservoirs during various scale rainfall events
Cs discharge out of reservoirs during various scale rainfall eventsKurikami, Hiroshi; Funaki, Hironori; Malins, A.; Kitamura, Akihiro; Onishi, Yasuo*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 164, p.73 - 83, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:41.00(Environmental Sciences)We performed simulations using the three-dimensional finite volume code FLESCOT to understand sediment and radiocesium transport in generic models of reservoirs with parameters similar to those in Fukushima Prefecture. The simulations model turbulent water flows, transport of sediments with different grain sizes, and radiocesium migration both in dissolved and particulate forms. To demonstrate the validity of the modeling approach for the Fukushima environment, we performed a test simulation of the Ogaki Dam reservoir over a typhoon. We simulated a set of generic model reservoirs systematically varying features such as flood intensity, reservoir volume and the radiocesium distribution coefficient. The results ascertain how these features affect the amount of sediment or  Cs discharge downstream from the reservoirs, and the forms in which
Cs discharge downstream from the reservoirs, and the forms in which  Cs is discharged. Silt carries the majority of the radiocesium in the larger flood events, while the clay-sorbed followed by dissolved forms are dominant in smaller events. The results can be used to derive indicative values of discharges from Fukushima reservoirs under arbitrary flood events.
Cs is discharged. Silt carries the majority of the radiocesium in the larger flood events, while the clay-sorbed followed by dissolved forms are dominant in smaller events. The results can be used to derive indicative values of discharges from Fukushima reservoirs under arbitrary flood events.
Watakabe, Tomoyoshi; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki; Kitamura, Seiji; Morishita, Masaki
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 138(2), p.021801_1 - 021801_10, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:35.39(Engineering, Mechanical)With a purpose of identifying the failure mode and the associating ultimate strength of piping components against seismic integrity, many kinds of failure tests have been conducted for thick wall piping for Light Water Reactors (LWRs). However, there are little failure test data on thin wall piping for Sodium Cooled Fast Reactors (SFRs). In this paper, a series of failure tests on thin wall elbows for SFRs is presented. Based on the tests, the failure mode of a thin wall piping component under seismic loads was identified to be fatigue. The safety margin included in the current design methodology was clarified quantitatively.
 mutant
mutantKitamura, Satoshi; Ono, Yutaka; Narumi, Issey*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 64, 2016/02
Forward genetics approaches have helped elucidate the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in plants. We used the 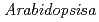 banyuls (ban) mutant, which accumulates anthocyanins, instead of colorless proanthocyanidin precursors, in immature seeds. In contrast to standard screens for mutants lacking anthocyanins in leaves/stems, we mutagenized ban plants and screened for mutants showing differences in pigmentation of immature seeds. The pale banyuls1 (pab1) mutation was found to show reduced levels of anthocyanins in immature seed coat. Here we characterize this mutant at the molecular level.
banyuls (ban) mutant, which accumulates anthocyanins, instead of colorless proanthocyanidin precursors, in immature seeds. In contrast to standard screens for mutants lacking anthocyanins in leaves/stems, we mutagenized ban plants and screened for mutants showing differences in pigmentation of immature seeds. The pale banyuls1 (pab1) mutation was found to show reduced levels of anthocyanins in immature seed coat. Here we characterize this mutant at the molecular level.