Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nagae, Daisuke*; Abe, Yasushi*; Okada, Shunsuke*; Omika, Shuichiro*; Wakayama, Kiyoshi*; Hosoi, Shun*; Suzuki, Shinji*; Moriguchi, Tetsuro*; Amano, Masamichi*; Kamioka, Daiki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 986, p.164713_1 - 164713_7, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:63.04(Instruments & Instrumentation) F from
F from  O
O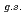 ?
?Tang, T. L.*; Uesaka, Tomohiro*; Kawase, Shoichiro; Beaumel, D.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Fujii, Toshihiko*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Fukunaga, Taku*; Galindo-Uribarri, A.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:72.90(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a neutron-rich  F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree (
F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree ( ) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of
) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of 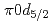 orbital is found to be 1.0
orbital is found to be 1.0  0.3. The result shows that the
0.3. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus, and the core consists of
O nucleus, and the core consists of  35%
35%  O
O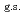 , and
, and  65% excited
65% excited  O. The result shows that the
O. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the
O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the  proton considerably changes the neutron structure in
proton considerably changes the neutron structure in  F from that in
F from that in  O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
Yanagisawa, Tsutomu*; Usami, Shin; Maeda, Seiichiro
Genshiryoku Nenkan 2018, p.90 - 95, 2017/10
no abstracts in English
; ; ; ; Sago, Hiromi*; ;
JNC TJ8400 2000-049, 161 Pages, 2000/02
In this study basic data on welds of overpack structures for HLW were acquired and a predictive destruction analysis was performed usig the data acquired, in order to examine the viability of weld design methods. The results are summarized as follows: (1)Investigation of Design and Welding Condition for Welded Joint Models. Three welding methods--EBW, TIG and MAG--were selected, and welding conditions were determined so that the welding quality almost equivalent to that of an actual over-pack was ensured. (2)Fabrication of Welded Joint Models. Three welded joint models, one for each of EBW, TIG and MAG, were fabricated. It was confirmed that these models satisfied the quality requirements for Class I specified in JIS Z3104. (3)Sampling and Machining of Strength Test Specimens. Test specimens were taken from each welded joint model, and models for corrosion tests were delivered to the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC). (4)Strength Test and Micro/macro Structure observation. Tensile tests were conducted at room temperature and at 150 C, and fracture toughness tests at 0
C, and fracture toughness tests at 0 C and 150
C and 150 C, in order to obtain stress-strain curves, J-R curves and Vickers hardness. In addition, an observation of micro and macro structures was performed. (5)Evaluation. Using the data on the welds obtained from the tests, a fracture prediction analysis and an evaluation of unstable fracture due to weld flaws were performed on the over-pack design described in the second progress report. The following conclusions were obtained: (a)For the overpack design examined, the effects of welds (material property and residual stress) and fabrication tolerance on fracture loading are negligible. (b)In addition, it was decided that even in a design with reduced wall thickness, welds have an insignificant effect on fracture loading because fracture initiates in the center of the shell of the overpack. (c)The size of flaws leading to unstable fracture is on ...
C, in order to obtain stress-strain curves, J-R curves and Vickers hardness. In addition, an observation of micro and macro structures was performed. (5)Evaluation. Using the data on the welds obtained from the tests, a fracture prediction analysis and an evaluation of unstable fracture due to weld flaws were performed on the over-pack design described in the second progress report. The following conclusions were obtained: (a)For the overpack design examined, the effects of welds (material property and residual stress) and fabrication tolerance on fracture loading are negligible. (b)In addition, it was decided that even in a design with reduced wall thickness, welds have an insignificant effect on fracture loading because fracture initiates in the center of the shell of the overpack. (c)The size of flaws leading to unstable fracture is on ...
; ; ; ; Sago, Hiromi*; ;
JNC TJ8400 2000-048, 30 Pages, 2000/02
In this study basic data on welds of overpack structures for HLW were acquired and a predictive destruction analysis was performed using the data acquired, in order to examine the viability of weld design methods. The results are summarized as follows: (1)Investigation of Design and Welding Conditions for Welded Joint Models. Three welding methods--EBW, TIG and MAG-were selected, and welding conditions were determined so that the welding quality almost equivalent to that of an actual over-pack was ensured. (2)Fabrication of Welded Joint Models. Three welded joint models, one for each of EBW, TIG and MAG, were fabricated. It was confirmed that these models satisfied the quality requirements for Class I specified in JIS Z3104. (3)Sampling and Machining of Strength Test Specimens. Test specimens were taken from each welded joint model, and models for corrosion tests were delivered to the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC). (4)Strength Test and Micro/macro Structure observation. Tensile tests were conducted at room temperature and at 150 C, and fracture toughness tests at 0
C, and fracture toughness tests at 0 C and 150
C and 150 C, in order to obtain stress-strain curves, J-R curves and Vickers hardness. In addition, an observation of micro and macro structures was performed. (5)Evaluation. Using the data on the welds obtained from the tests, a fracture prediction analysis and an evaluation of unstable fracture due to weld flaws were performed on the over-pack design described in the second progress report. The following conclusions were obtained: (a)For the overpack design examined, the effects of welds (material property and residual stress) and fabrication tolerance on fracture loading are negligible. (b)In addition, it was decided that even in a design with reduced wall thickness, welds have an insignificant effect on fracture loading because fracture initiates in the center of the shell of the overpack. (c)The size of flaws leading to unstable fracture is on the ...
C, in order to obtain stress-strain curves, J-R curves and Vickers hardness. In addition, an observation of micro and macro structures was performed. (5)Evaluation. Using the data on the welds obtained from the tests, a fracture prediction analysis and an evaluation of unstable fracture due to weld flaws were performed on the over-pack design described in the second progress report. The following conclusions were obtained: (a)For the overpack design examined, the effects of welds (material property and residual stress) and fabrication tolerance on fracture loading are negligible. (b)In addition, it was decided that even in a design with reduced wall thickness, welds have an insignificant effect on fracture loading because fracture initiates in the center of the shell of the overpack. (c)The size of flaws leading to unstable fracture is on the ...
Yanagisawa, Ichiro*; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*; Izumi, Jun*; Saigusa, Moriyuki*; ; ; ; Ueta, Shinzo*
JNC TJ8400 2000-038, 202 Pages, 2000/02
(1)Sodalite and tourmaline are natural-occurring minerals, which can contain halide in their aluminosilicate lattices. Therefore, these materials have possibilities of immobilization of I-129. In this study, solubility measurements for these materials were carried out. It was confirmed from dissolution behaviors obtained for some kinds of sodalite and calculated results of solubilities based on thermodynamic data that dissolution of sodalite to aqueous solution could be limited by its solubility. Solubility of sodalite had tendencies of "synthesized one  natural one" and "chloride
natural one" and "chloride  iodide". Immobilized iodine in sodalite crystalline lattice was not replaced by chlolide ion in the solution. It was indicated that tourmaline has a possibility as a waste material containing I-129 from comparison of dissolution behavior of element with sodalite. (2)Leaching property of a multi-layered waste-form, that is composed of (1)iodine bearing material (zeolite), (2)coating layer (silica and apatite) and 3)low solubility matirx (apatite), was studied under reducing condition. The following results were obtained by the leaching experiments: (1)The coating layer of hidroxyapatite can reduce the iodine leaching rate by 4 order compared with that of bare iodine bearing material. (2)Ca and P concentration after one-month dipping reached the solubility estimated by the theoretical calculation using PHREEQE code. As a conclusion, it was indicated that this waste-form concept has potential to show low leaching rate.
iodide". Immobilized iodine in sodalite crystalline lattice was not replaced by chlolide ion in the solution. It was indicated that tourmaline has a possibility as a waste material containing I-129 from comparison of dissolution behavior of element with sodalite. (2)Leaching property of a multi-layered waste-form, that is composed of (1)iodine bearing material (zeolite), (2)coating layer (silica and apatite) and 3)low solubility matirx (apatite), was studied under reducing condition. The following results were obtained by the leaching experiments: (1)The coating layer of hidroxyapatite can reduce the iodine leaching rate by 4 order compared with that of bare iodine bearing material. (2)Ca and P concentration after one-month dipping reached the solubility estimated by the theoretical calculation using PHREEQE code. As a conclusion, it was indicated that this waste-form concept has potential to show low leaching rate.
Yanagisawa, Ichiro*; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*; Izumi, Jun*; Saigusa, Moriyuki*; Kitao, Hideo*; Tsuzuki, Yasuo*; Neyama, Atsushi*; Kato, Hiroyasu*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Okada, Kenichi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-037, 61 Pages, 2000/02
no abstracts in English
Yanagisawa, Ichiro*; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*; Mukai, Satoru*;
JNC TJ8400 2000-028, 224 Pages, 2000/02
In this study, in-diffusion experiment was conducted under reducing condition to measure apparent diffusion coefficients and distribution coefficients of Uranium and Neptunium for bentonite materials as engineered barrier. The summary of this study is as follows: (1)Apparent diffusion coefficients of U and Np under reducing condition were one or two orders magnitude lower than those of the results obtained in the previous studies. From this result, the valence of U and Np was estimated to be +4 charge during diffusion experiment. (2)Distribution coefficients of U and Np for the system of equilibriated water with bentonite at density of 1.6 g/cm were a little lower than those for the other synthetic groundwater system. (3)Distribution coefficients of Cs and Sr decreased as ion strength of pore water in bentonite increased. Distribution coefficient of Sr increased for alternation of bentonite. (4)Distribution coefficients of Ni, Sn, Zr and Nb were little difference for any type of bentonite or synthetic groundwater. (5)Distribution coefficients or Am for Na-type of bentonite was higher than that of Ca-type of bentonite. But the difference of distribution coefficients for any synthetic groundwater was small. (6)Data base of apparent diffusion coefficients and distribution coefficients was renewed.
were a little lower than those for the other synthetic groundwater system. (3)Distribution coefficients of Cs and Sr decreased as ion strength of pore water in bentonite increased. Distribution coefficient of Sr increased for alternation of bentonite. (4)Distribution coefficients of Ni, Sn, Zr and Nb were little difference for any type of bentonite or synthetic groundwater. (5)Distribution coefficients or Am for Na-type of bentonite was higher than that of Ca-type of bentonite. But the difference of distribution coefficients for any synthetic groundwater was small. (6)Data base of apparent diffusion coefficients and distribution coefficients was renewed.
Yanagisawa, Ichiro*; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*; Mukai, Satoru*;
JNC TJ8400 2000-027, 28 Pages, 2000/02
no abstracts in English
; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*; Saigusa, Moriyuki*; ; Kitao, Hideo*; Tsuzuki, Yasuo*
JNC TJ8400 2000-012, 333 Pages, 2000/02
In this study, technical review, laboratory experiment and modeling calculations were implemented in order to reliability of geochemical assessment technique for the second progress report. The summary of this study is as follows: (1)We have implemented the technical review of the second progress backup report geochemical modeling and some data. We have extracted a subject about groundwater evolution modeling and thermodynamic data. (2)We have implemented multivariable analysis based on database of deep groundwater sampled in geoscientofic investigation in other countries. We have considered validity of peculiar model groundwater of SRLP, FRLP and MRNP. (3)We have researched on redox reaction of a coastal sedimentary layer, and was cleared geochemical mechanism of dedox reaction. (4)We have studied thermodynamic of Se in laboratory. We have confirmed condition, which SRB was not in experimental system, initial solid transformed to solid phase (FeSe). And we have clarified chemical species of Se in the liquid phase. (5)We have researched on degradation of the engineered barrier material. We have prepared natural analogue data set that related to the iron and cooper. And we have acquired basic property of buffer material (Kunipia-F) in laboratory. (6)We have studied on dissolution kinetic of UO in order to extract geochemistry technical factor for site selection. The dissolution rates in oxidized groundwater may be much slower than previously believed by most scientists. Therefore, oxidized environments, as well as reduced environments, may be considered as possible sites for underground repository sites.
in order to extract geochemistry technical factor for site selection. The dissolution rates in oxidized groundwater may be much slower than previously believed by most scientists. Therefore, oxidized environments, as well as reduced environments, may be considered as possible sites for underground repository sites.
; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*; Saigusa, Moriyuki*; ; Kitao, Hideo*; Tsuzuki, Yasuo*
JNC TJ8400 2000-011, 65 Pages, 2000/02
no abstracts in English
Tachikawa, Hirokazu*; Kitao, Hideo*; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*; Yanagisawa, Ichiro*; Shibata, Masahiro; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 99-068, 108 Pages, 1999/11
In an evaluation of high level waste (HLW) repository performance, Se-79 is one of important elements to be analyzed. Selenium solubility and solubility limiting solid phase is not clear. Then, we performed solubility measurement tests from over saturation direction under reducing conditions considering the repository conditions in deep underground. In some cases, bentonite (Kunigel V1) or pyrite coexisted in the experimental system to simulate the repository conditions. Se bearing solids were determined by XRD analysis, and solubility limiting solid phase was discussed. FeSe (Ferroselite) and Se (hexagonal) were identified in the simple condition test, in which Fe(II) solution and Se solution were mixed. SeS was also identified when S(-II) solution was added. The Se concentrations in aqueous phase were approximately 10
(Ferroselite) and Se (hexagonal) were identified in the simple condition test, in which Fe(II) solution and Se solution were mixed. SeS was also identified when S(-II) solution was added. The Se concentrations in aqueous phase were approximately 10 mol/l at neutral pH and approximately 10
mol/l at neutral pH and approximately 10 mol/l at pH9 in the bentonite coexisting tests and pyrite coexisting tests. The solid phases identified in the pyrite coexisting tests were mainly Se(hexagonal) and FeSe
mol/l at pH9 in the bentonite coexisting tests and pyrite coexisting tests. The solid phases identified in the pyrite coexisting tests were mainly Se(hexagonal) and FeSe (Ferroselite) in one of the samples. Further, the possibility of Fe(S,Se) solid solution formation was presumed on the pyrite surface dipping in the test solutions. In addition, we performed another selenium solubility measurement to accelerate the transformation of Se bearing solid phase at elevated temperature (80
(Ferroselite) in one of the samples. Further, the possibility of Fe(S,Se) solid solution formation was presumed on the pyrite surface dipping in the test solutions. In addition, we performed another selenium solubility measurement to accelerate the transformation of Se bearing solid phase at elevated temperature (80 C). The concentration of Se decreases with time and reached to the detection limit of ICP-MS (4
C). The concentration of Se decreases with time and reached to the detection limit of ICP-MS (4 10
10 mol/1) in 3 months. At first, Se(hexagonal) is dominant in the precipitation, however this solid phase was gradually transformed to Fe-Se solids (FeSe, FeSe
mol/1) in 3 months. At first, Se(hexagonal) is dominant in the precipitation, however this solid phase was gradually transformed to Fe-Se solids (FeSe, FeSe ) with time. Therefore it is strongly suggested that FeSe
) with time. Therefore it is strongly suggested that FeSe which is the thermodynamically most stable phase will be a solubility limiting solid phase under repository conditions in long term. As the experimental system was confirmed as sulfate reducing bacteria free, it should be noted that whole observed reactions ...
which is the thermodynamically most stable phase will be a solubility limiting solid phase under repository conditions in long term. As the experimental system was confirmed as sulfate reducing bacteria free, it should be noted that whole observed reactions ...
; ; Ida, Toshio*; Fusaeda, Shigeki*; ; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*
JNC TJ8400 99-039, 1926 Pages, 1999/02
This study has been carried out in order to increase the reliability of the performance assessment of geological isolation systems for high level wastes. We have been investigating a proper modeling of various phenomena, which would occur in the disposal environment and improving the reliability of geochemical data used in the performance assessment. The results are summarized as follows: (1)Quality assurance for geochemical data and modeling. We have compiled technical report, geochemical database (newest thermodynamic database), and calculation, conversion program for geochemical analysis, which supporting the second progress report. (2)Study on groundwater categorization and dominant reaction based on site data. We have carried out HCA/PCA analysis based on observed deep groundwater to support groundwater categorization of the second progress report. We concluded 3-type model groundwater categorized by analysis. (3)Experimental study on thermodynamic data of Se and Pd. It is confirmed that sulfate reduction bactelia do not exist in our experimental environment. (4)Planning on data acquisition for geochemical data of radioactive elements. Firstly we have pick up key radioactive elements and future studies based on the second progress report. Then we have draw up R&D plan for QUALITY. (5)Geochemical study on the long-term stability of backfill matelial. An extensive literature review was carried out about the effect of Iron on Bentonite stability. Experimental conditions are researched to develop thermodynamic and kinetic modeling. (6)Study on the technical geochemistry guideline of site selection for disposal. We have researched on the recommendation of sites for HLW (guideline of site selection) in foreign country and site selection from a view point of natural analogue. And we have summarized geochemistry technical guideline for site selection.
; ; Ida, Toshio*; Fusaeda, Shigeki*; ; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*
JNC TJ8400 99-038, 59 Pages, 1999/02
This study has been carried out in order to increase the reliability of the performance assessment of geological isolation systems for high level wastes. We have been investigating a proper modeling of various phenomena, which would occur in the disposal environment and improving the reliability of geochemical data used in the performance assessment. The results are summarized as follows: (1)Quality assurance for geochemical data and modeling. We have compiled technical report, geochemical database (newest thermodynamic database), and calculation, conversion program for geochemical analysis, which supporting the second progress report. (2)Study on groundwater categorization and dominant reaction based on site data. We have carried out HCA/PCA analysis based on observed deep groundwater to support groundwater categorization of the second progress report. We concluded 3-type model groundwater categorized by analysis. (3)Experimental study on thermodynamic data of Se and Pd. It is confirmed that sulfate reduction bacteria do not exist in our experimental environment. (4)Planning on data acquisition for geochemical data of radioactive elements. Firstly we have pick up key radioactive elements and future studies based on the second progress report. Then we have draw up R&D plan for QUALITY. (5)Geochemical study on the long-term stability of backfill material. An extensive literature review was carried out about the effect of Iron on Bentonite stability. Experimental conditions are researched to develop thermodynamic and kinetic modeling. (6)Study on the technical geochemistry guideline of site selection for disposal. We have researched on the recommendation of sites for HLW (guideline of site selection) in foreign country and site selection from a view point of natural analogue. And we have summarized geochemistry technical guideline for site selection.
Yanagisawa, Ichiro*; Naito, Taisei*; Kitao, Hideo*; Mukai, Satoru*; Doi, Hideo*
JNC TJ8400 99-020, 25 Pages, 1999/02
In this study, apparent diffusion coefficients and distribution coefficient of some nuclides were measured for bentonite materials as engineered barrier. The summary of this study is as follows: (1)Apparent diffusion coefficients of nuclides in compacted bentonite were measured. The data so far were summarized as database of apparent diffusion coefficients and distribution coefficients. (2)In diffusion tests for mixture of Ca-type altered bentonite and analcime, apparent diffusion coefficient of Sr was a little smaller than that for Ca-type altered bentonite. (3)In diffusion tests for Ca-type altered bentonite, apparent diffusion coefficients and distribution coefficients of nuclides showed no significant difference between bentonite-water system and bentonite-cementitious solution systems. (4)In Na-type bentonite-solution with nitrate system, apparent diffusion coefficients of Cs and Sr were smaller than that for other bentonite-solution systems. (5)Apparent diffusion coefficients of tritium showed no significant difference between Ca-type altered bentonite and Na-type bentonite in any solution systems.
Fusaeda, Shigeki*; Yanagisawa, Ichiro*; Kataoka, Shinichi*; Shimada, Takashi*; ; ;
PNC TJ1216 98-007, 46 Pages, 1998/02
None