Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction study伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 287, p.120767_1 - 120767_16, 2025/04
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:75.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Incorporating solute hydrogen into Fe-Cr-Ni-based austenitic stainless steels enhances both strength and ductility, providing a promising solution to hydrogen embrittlement by causing solid-solution strengthening and assisting deformation twinning. However, its impacts on the relevant lattice defects evolution ( , dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using
, dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using  neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
 neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel
neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Steel Science (ISSS 2024), p.237 - 240, 2024/11
Hydrogen embrittlement has long been an obstacle to the development of safe infrastructure. However, in contrast to hydrogen's embrittling effect, recent research has revealed that the addition of hydrogen improves both the strength and uniform elongation of AISI Type 310S austenitic stainless steel. A detailed understanding of how hydrogen affects the deformation mechanism of this steel could pave the way for the development of more advanced materials with superior properties. In the present study,  neutron diffraction experiments were conducted on Type 310S steel with and without hydrogen-charged to investigate the effect of hydrogen on the deformation mechanism. In addition to the effect of solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen, the q-value, a parameter representing the proportion of edge and screw dislocations in the accumulated dislocations, was quantitatively evaluated using CMWP analysis on neutron diffraction patterns. The comparison of q-values between the hydrogen-charged and non-charged samples reveals that hydrogen has minimal effect on dislocation character in Type 310S steel.
neutron diffraction experiments were conducted on Type 310S steel with and without hydrogen-charged to investigate the effect of hydrogen on the deformation mechanism. In addition to the effect of solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen, the q-value, a parameter representing the proportion of edge and screw dislocations in the accumulated dislocations, was quantitatively evaluated using CMWP analysis on neutron diffraction patterns. The comparison of q-values between the hydrogen-charged and non-charged samples reveals that hydrogen has minimal effect on dislocation character in Type 310S steel.
川崎 卓郎; 高橋 美和子*; 鬼柳 亮嗣; 大原 高志
Acta Crystallographica Section C; Structural Chemistry (Internet), 78(12), p.743 - 748, 2022/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Structural changes of the raffinose crystal on dehydration from the pentahydrate to the tetrahydrate were investigated by single-crystal time-of-flight neutron diffraction. It was revealed that during the dehydration, rearrangement occurs in the hydrogen bonds related to the lost water molecule, while the symmetry of the crystal structure is retained. The hydrogen-bonding status of raffinose pentahydrate and tetrahydrate were discussed comprehensively according to Jeffrey's hydrogen-bonding classification. It was shown that water molecules are hydrogen bonded to the surrounding molecules by 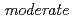 O-H...O hydrogen bonds and
O-H...O hydrogen bonds and 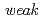 C-H...O hydrogen bonds, and the number of these two types of hydrogen bonds determines the water molecules that are removed by dehydration. The lattice constant c showed a significant decrease on dehydration and further dehydration leads to loss of crystallinity of the raffinose crystals.
C-H...O hydrogen bonds, and the number of these two types of hydrogen bonds determines the water molecules that are removed by dehydration. The lattice constant c showed a significant decrease on dehydration and further dehydration leads to loss of crystallinity of the raffinose crystals.
生田 大穣*; 大谷 栄治*; 佐野 亜沙美; 柴崎 裕樹*; 寺崎 英紀*; Yuan, L.*; 服部 高典
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9, p.7108_1 - 7108_8, 2019/05
被引用回数:52 パーセンタイル:92.41(Multidisciplinary Sciences)水素は地球の核にある軽元素のひとつである。その重要性にもかかわらず、高圧で鉄格子中の水素を直接観察することはなされていない。われわれは世界で初めて、その場中性子回折法を用いて、12GPaおよび1200Kまでの面心立方(fcc)鉄格子におけるサイト占有率および格子間水素の体積の決定を行った。体心立方晶および二重六方最密相からfcc相への転移温度は、以前に報告されたものよりも高かった。5GPa以下の圧力では、fcc水素化鉄格子(x)中の水素含有量はx 0.3で小さかったが、圧力の増加と共にx
0.3で小さかったが、圧力の増加と共にx 0.8まで増加した。水素原子は八面体(O)と四面体(T)の両方のサイトを占める。fcc格子は水素原子1個あたり2.22
0.8まで増加した。水素原子は八面体(O)と四面体(T)の両方のサイトを占める。fcc格子は水素原子1個あたり2.22 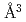 の割合でほぼ直線的に拡大した。これは以前に推定された値(1.9
の割合でほぼ直線的に拡大した。これは以前に推定された値(1.9 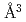 /H)よりも大きい。水素溶解による格子膨張は無視できるほど圧力に依存しない。格子間水素による大きな格子膨張は、コアの密度不足を説明する地球のコア内の推定水素含有量を減少させる。改訂された分析は、全コアが海洋質量の80倍の水素を含み、その内訳は外核と内核はそれぞれ79倍と0.8倍である。
/H)よりも大きい。水素溶解による格子膨張は無視できるほど圧力に依存しない。格子間水素による大きな格子膨張は、コアの密度不足を説明する地球のコア内の推定水素含有量を減少させる。改訂された分析は、全コアが海洋質量の80倍の水素を含み、その内訳は外核と内核はそれぞれ79倍と0.8倍である。
新村 信雄; 新井 栄揮; 栗原 和男; 茶竹 俊行*; 田中 伊知朗*; Bau, R.*
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 63(3), p.285 - 300, 2006/02
被引用回数:41 パーセンタイル:36.75(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)中性子回折は蛋白質やDNAの水素位置を直接的に決定する実験手法である。三つの異なったタイプの生体物質用高分解能中性子回折計が日本,フランス,アメリカに建設され、それらは近年、多くの蛋白質の結晶構造を決定するために頻繁に用いられてきた。本論文では、詳細な水素結合のジオメトリー,蛋白質及び核酸のH/D交換に関する情報,プロトンの正確な位置決定,酵素活性及び熱安定性における水素原子の役割,水和構造の動力学的挙動など、中性子構造解析から引出された成果を取り上げる。その他の重要な技術として開発された、結晶化相図による大型単結晶育成の最適化,完全重水素化蛋白質の調製,中性子蛋白質結晶学におけるクライオ技術の導入,生体水素水和水データベースの設立なども本論文中にて議論する。
本橋 治彦; 古田 照夫
JAERI-M 82-005, 14 Pages, 1982/03
軽水炉用燃料被覆管ジルカロイ-4を1000 Cおよび1050
Cおよび1050 Cで水蒸気-水素混合ガス気流中で酸化させ、表面に生成された酸化膜の特性について、X線回折法によって調べた。試料表面には混合ガスの組成によって、2種類の酸化膜、即ち単斜晶ZrO
Cで水蒸気-水素混合ガス気流中で酸化させ、表面に生成された酸化膜の特性について、X線回折法によって調べた。試料表面には混合ガスの組成によって、2種類の酸化膜、即ち単斜晶ZrO から成る単層および単斜晶・正方晶ZrO
から成る単層および単斜晶・正方晶ZrO とZrOからなる多層の酸化膜が生成される。単層の酸化膜が形成される場合の酸化速度は、放物線則に従っているが、多層酸化膜の場合は、酸化の初期において直線則に従っている。また多層酸化膜が形成される時、ジルカロイ中には多量の水素が吸収されている。多層酸化膜は、表面付近で単斜ZrO
とZrOからなる多層の酸化膜が生成される。単層の酸化膜が形成される場合の酸化速度は、放物線則に従っているが、多層酸化膜の場合は、酸化の初期において直線則に従っている。また多層酸化膜が形成される時、ジルカロイ中には多量の水素が吸収されている。多層酸化膜は、表面付近で単斜ZrO 、中間層では単斜晶と正方晶ZrO
、中間層では単斜晶と正方晶ZrO がそして酸化膜と金属との界面ではZrOによって構成されている。正方晶ZrO
がそして酸化膜と金属との界面ではZrOによって構成されている。正方晶ZrO は酸化時間の増加と共に単斜晶ZrO
は酸化時間の増加と共に単斜晶ZrO へと変化していることも認められた。
へと変化していることも認められた。
古田 照夫; 川崎 了
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 105(2), p.119 - 131, 1982/00
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:87.06(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)冷却材喪失事故時の破裂被覆管内面で起こる反応挙動を明らかにするために、高温水蒸気-水素混合ガス中のジルカロイ-4管の反応挙動を調べた。全重量増加は混合ガス中の水素体積比によって変化し、反応温度と水蒸気流速に依存する臨界水素体積比が存在する。また、この臨界体積比で全重量増加は減少し、形成される酸化膜も緻密なものから多孔質なものへと変り、ジルカロイに多量の水素が吸収される。この水素吸収によってジルカロイの延性低下が起されることも判った。以上の結果から、混合ガス中の反応が水素体積比に影響されるという考え方は、破裂被覆管内面での反応挙動を十分説明できることを明らかにした。
古田 照夫; 本橋 治彦
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 95(3), p.303 - 306, 1980/00
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:94.05(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)軽水炉の冷却材喪失事故時に燃料棒が破裂すると、ジルカロイ被覆管は外面だけでなく内面も水蒸気と酸化反応を起こす。この時、内面の酸化膜は外面の稠蜜な被膜と異なった多孔質な被膜となる場合がある。ふたつの酸化膜について生成物の同定をX線回折によって行った。その結果、稠蜜な被膜は単斜晶ジルコニアであるのに対して、多孔質な被膜は単斜晶および正方晶ジルコニアの混合物であることが判った。さらに、多孔質被膜に認められる立方晶の回折線についても同定を行ない、従来あまり明確にされていないZrOであることを確認した。
古田 照夫; 上塚 寛; 川崎 了; 星野 昭; 磯 修一
JAERI-M 8497, 27 Pages, 1979/10
軽水炉冷却材過失事故時に生ずる内面酸化でジルカロイ被覆管に水素が吸収される。この水素吸収に関して、燃料棒の破裂/酸化試験およびジルカロイ管の滞留水蒸気あるいは水蒸気/水素混合雰囲気中の酸化試験によって検討を加えた。水素吸収は水蒸気/水素混合雰囲気中の水素の割合に依存して950 C以上の酸化で起る。そして、酸化時間が長くなるにつれて水素吸収量は増加する。このとき形成される酸化膜には単斜晶と混在した正方晶ジルコニアが比較的高い水素吸収量をもつ試料で認められる。燃料棒の水素吸収の場合、酸化の激しいところで発生した水素は水素吸収が容易に起る他の場所で吸収されるから、水素吸収は破裂開口の大きさや外側の水蒸気流速に影響される。
C以上の酸化で起る。そして、酸化時間が長くなるにつれて水素吸収量は増加する。このとき形成される酸化膜には単斜晶と混在した正方晶ジルコニアが比較的高い水素吸収量をもつ試料で認められる。燃料棒の水素吸収の場合、酸化の激しいところで発生した水素は水素吸収が容易に起る他の場所で吸収されるから、水素吸収は破裂開口の大きさや外側の水蒸気流速に影響される。
 -Radiation-induced crosslinking of polystyrene
-Radiation-induced crosslinking of polystyrene清水 雄一; 三井 光
Journal of Polymer Science; Polymer Chemistry Edition, 17(8), p.2307 - 2316, 1979/00
真空におけるポリスチレンの 線橋かけ反応を、30~100
線橋かけ反応を、30~100 Cの温度範囲において行った。線量率は635
Cの温度範囲において行った。線量率は635 10
10 rad/hrであった。水素の生成量は照射時間の増加および照射温度の上昇とともに増加するが、水素の生成速度は照射時間の増加に伴って低下する。ゲルの生成が初めて観測される限界時間以上照射すると、照射時間の増加とともにゲル分率は増加するが、ゲルの生成速度は照射時間の増加に伴って低下する。照射温度を上昇すると、ゲルの生成反応は抑制され、100
rad/hrであった。水素の生成量は照射時間の増加および照射温度の上昇とともに増加するが、水素の生成速度は照射時間の増加に伴って低下する。ゲルの生成が初めて観測される限界時間以上照射すると、照射時間の増加とともにゲル分率は増加するが、ゲルの生成速度は照射時間の増加に伴って低下する。照射温度を上昇すると、ゲルの生成反応は抑制され、100 Cでは極く僅かなゲル分率しか観測されない。水素の生成および消失反応がそれぞれ水素の生成量のゼロ次および一次に比例すると仮定した速度式を導き、水素の生成量を解析した。ゲル分率はCharlesby-Pinnerの式を用いて解析した。解析結果に基づいて、ポリスチレンの
Cでは極く僅かなゲル分率しか観測されない。水素の生成および消失反応がそれぞれ水素の生成量のゼロ次および一次に比例すると仮定した速度式を導き、水素の生成量を解析した。ゲル分率はCharlesby-Pinnerの式を用いて解析した。解析結果に基づいて、ポリスチレンの 線橋かけ反応の機構を考察した。
線橋かけ反応の機構を考察した。
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
オーステナイト系ステンレス鋼のSUS316Lは、水素インフラで用いられている重要な材料である。本材料は、室温では優れた耐水素脆性を有することが知られているが、低温で変形を加えると、 (HCP)相や
(HCP)相や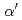 (BCC)相へと変形誘起マルテンサイト変態が生じる。これが水素脆化と密接に関連していることが知られており、水素がマルテンサイト変態に与える影響を明らかにすることは非常に重要である。本研究では、高圧ガスで均一に水素を添加したSUS316Lを使用し、引張試験中その場中性子回折実験を行うことで、低温変形中のマルテンサイト変態に対する固溶水素の影響を評価した。
(BCC)相へと変形誘起マルテンサイト変態が生じる。これが水素脆化と密接に関連していることが知られており、水素がマルテンサイト変態に与える影響を明らかにすることは非常に重要である。本研究では、高圧ガスで均一に水素を添加したSUS316Lを使用し、引張試験中その場中性子回折実験を行うことで、低温変形中のマルテンサイト変態に対する固溶水素の影響を評価した。
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Hydrogen is being considered as an alternative energy carrier to fossil fuels to achieve the goal of Carbon Neutrality. While hydrogen has historically been associated with causing steel embrittlement, Ogawa et al. reported that the introduction of hydrogen to a Fe-24Cr-19Ni-based (mass%) austenitic stainless steel (AISI Type 310S) enhances both strength and ductility, thus counteracts the embrittlement effect. Although this phenomenon was qualitatively explained by the hydrogen-induced solid-solution strengthening and the promotion of deformation twinning, the influence of hydrogen on the development of dislocations and stacking faults ( , twin nuclei) during deformation remains less understood. The aim of this work is to investigate the effects of hydrogen on the evolution of these crystal defects and overall deformation mechanisms by using
, twin nuclei) during deformation remains less understood. The aim of this work is to investigate the effects of hydrogen on the evolution of these crystal defects and overall deformation mechanisms by using  neutron diffraction measurements.
neutron diffraction measurements.
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Hydrogen is attracting attention as an alternative energy carrier to fossil fuels to establish a sustainable society. However, hydrogen is considered to cause embrittlement in steel, which has been a longstanding issue known as hydrogen embrittlement. In contrast to the embrittlement, recently, Ogawa 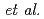 , reported that the addition of hydrogen improved both strength and ductility in SUS310S (Fe-24Cr-19Ni mass%) steel. This phenomenon is attributed to hydrogen-induced solid solution strengthening and the promotion of twinning deformation. These approaches are gaining attention as effective ways to utilize hydrogen, which has long been considered harmful. However, the impact of hydrogen on crystal defects (dislocations, stacking faults) and the mechanisms behind enhanced twinning in SUS310S steel remain unclear. In this work, we investigated the deformation mechanisms of hydrogen-charged SUS310S steel by
, reported that the addition of hydrogen improved both strength and ductility in SUS310S (Fe-24Cr-19Ni mass%) steel. This phenomenon is attributed to hydrogen-induced solid solution strengthening and the promotion of twinning deformation. These approaches are gaining attention as effective ways to utilize hydrogen, which has long been considered harmful. However, the impact of hydrogen on crystal defects (dislocations, stacking faults) and the mechanisms behind enhanced twinning in SUS310S steel remain unclear. In this work, we investigated the deformation mechanisms of hydrogen-charged SUS310S steel by  neutron diffraction measurement conducted by TAKUMI (MLF-BL19) of J-PARC.
neutron diffraction measurement conducted by TAKUMI (MLF-BL19) of J-PARC.
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
持続可能な社会の構築に向け、国を挙げて水素社会の実現に向けた研究が行われている。水素インフラを構築するために、水素環境で強度・延性に優れる鉄鋼材料が求められているが、一般的に水素は脆化を引き起こすと考えられてきた。しかし近年、SUS310S (Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%))において、水素により強度・延性が共に向上することが報告され、注目を集めている。これには水素由来の固溶強化と双晶変形の促進が寄与していると考えられているが、転位密度や積層欠陥など、個々の因子に対する水素の影響の詳細は明らかとなっていない。そこで本研究では、MLFの工学材料回折装置 「匠」を利用した引張変形中その場中性子回折実験を行い、変形メカニズムに及ぼす水素の影響を定量的に評価した。
大原 高志; 鬼柳 亮嗣; 中尾 朗子*; 宗像 孝司*; 石川 喜久*; 森山 健太郎*
no journal, ,
Hydrogen bonds in molecular crystals are one of the research areas extensively investigated by the single-crystal neutron diffraction technique. SENJU, a time-of-flight Laue-type single-crystal neutron diffractometer at J-PARC, is one of the world's limited single-crystal neutron diffractometer capable of measuring a sub-millimeter size molecular crystal. In this presentation, the authors will show what kind of structural research of hydrogen bonds in functional molecular crystals, e.g., proton transfers in temperature-induced spin-transfer metal complexes and a salt-cocrystal continuum formation in a photo-functional organic crystal, conducted at SENJU.
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
The mechanisms of hydrogen charging in a 310S-type austenitic stainless steel, which promote strengthening and twinning, were investigated, along with the evaluation of dislocation and stacking fault evolution using in situ neutron diffraction during deformation. The hydrogen-charged sample exhibited increased yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with previous studies. However, the effect of solute hydrogen on dislocation and stacking fault evolution was found to be minimal, in contrast to earlier reports suggesting that hydrogen promotes their formation to facilitate twinning. Further details will be presented and discussed.
 neutron diffraction study of stacking fault energy in hydrogen-charged Type 310S austenitic steel at low temperatures
neutron diffraction study of stacking fault energy in hydrogen-charged Type 310S austenitic steel at low temperatures伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Stacking fault energy ( ) plays a crucial role in various deformation processes of austenitic steel, such as dislocation motion, deformation twinning, and martensitic transformation. Several previous studies have reported that hydrogen reduces
) plays a crucial role in various deformation processes of austenitic steel, such as dislocation motion, deformation twinning, and martensitic transformation. Several previous studies have reported that hydrogen reduces  . However, our recent in situ neutron diffraction experiment has shown that hydrogen has minimal effect on the
. However, our recent in situ neutron diffraction experiment has shown that hydrogen has minimal effect on the  of Fe-24Cr-19Ni (AISI Type 310S) steel during tensile deformation at room temperature, despite significant reductions in
of Fe-24Cr-19Ni (AISI Type 310S) steel during tensile deformation at room temperature, despite significant reductions in  due to hydrogen reported for a similar composition steel. Moreover, a recent study analyzing the work-hardening behavior of several hydrogen-charged austenitic stainless steels has suggested that hydrogen may have only a limited impact on
due to hydrogen reported for a similar composition steel. Moreover, a recent study analyzing the work-hardening behavior of several hydrogen-charged austenitic stainless steels has suggested that hydrogen may have only a limited impact on  . These findings indicate the need for further research to clarify the influence of hydrogen on
. These findings indicate the need for further research to clarify the influence of hydrogen on  . In this study, we investigated the effect of hydrogen on the
. In this study, we investigated the effect of hydrogen on the  of Type 310S austenitic steel at low temperatures using in situ neutron diffraction.
of Type 310S austenitic steel at low temperatures using in situ neutron diffraction.
 neutron diffraction study on the development of martensitic transformation in hydrogen-charged Type 316L steel at low temperature
neutron diffraction study on the development of martensitic transformation in hydrogen-charged Type 316L steel at low temperature伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Elucidating the influence of hydrogen on the deformation mechanisms of steel is essential for ensuring the reliability and safety of hydrogen infrastructure. In this study, we focused on Type 316L austenitic stainless steel (Fe-17Cr-12Ni, mass%), a material widely employed in hydrogen infrastructure applications. This alloy undergoes a martensitic transformation from  (FCC) to
(FCC) to  (HCP) and/or
(HCP) and/or  ' (BCC) phases when deformed at low temperatures. This transformation is closely associated with hydrogen embrittlement and is considered one of the key factors limiting the alloy's lower service temperature. Understanding the effect of hydrogen on this transformation is therefore crucial; however, it remains under debate whether hydrogen promotes or suppresses the transformation. To address this issue, we employed
' (BCC) phases when deformed at low temperatures. This transformation is closely associated with hydrogen embrittlement and is considered one of the key factors limiting the alloy's lower service temperature. Understanding the effect of hydrogen on this transformation is therefore crucial; however, it remains under debate whether hydrogen promotes or suppresses the transformation. To address this issue, we employed  neutron diffraction to investigate the evolution of martensite phase fractions during low-temperature deformation of hydrogen-charged Type 316L steel.
neutron diffraction to investigate the evolution of martensite phase fractions during low-temperature deformation of hydrogen-charged Type 316L steel.
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
近年、水素添加によりSUS310Sの強度と延性が共に向上することが報告され、注目を集めている。本講演では、J-PARCの「匠」を利用した引張試験中その場中性子回折実験により、そのメカニズムを明らかにした結果を報告する。
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
FCC構造を有するオーステナイト系Fe-Cr-Niステンレス鋼は、優れた耐水素脆性を示すことから、水素インフラ用材料として広く利用されている。これらの材料は、組成に応じて冷却や変形により (HCP)相や
(HCP)相や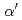 (BCC)相へとマルテンサイト変態を起こすことが知られているが、とくに
(BCC)相へとマルテンサイト変態を起こすことが知られているが、とくに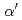 相は顕著な水素脆化を引き起こすことが報告されている。そのため、水素がマルテンサイト変態に与える影響を明らかにすることは、非常に重要である。本研究では、水素添加したステンレス鋼を対象に、J-PARC「匠」を用いた引張試験中その場中性子回折実験を行い、水素が積層欠陥の形成やマルテンサイト変態に及ぼす影響を評価した。
相は顕著な水素脆化を引き起こすことが報告されている。そのため、水素がマルテンサイト変態に与える影響を明らかにすることは、非常に重要である。本研究では、水素添加したステンレス鋼を対象に、J-PARC「匠」を用いた引張試験中その場中性子回折実験を行い、水素が積層欠陥の形成やマルテンサイト変態に及ぼす影響を評価した。