Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 C-stainless steel composites using the improved MPS method
C-stainless steel composites using the improved MPS methodAhmed, Z.*; Wu, S.*; Sharma, A.*; Kumar, R.*; 山野 秀将; Pellegrini, M.*; 横山 諒*; 岡本 孝司*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 250, p.127343_1 - 127343_17, 2025/11
被引用回数:0The study aims to measure boron concentration through the unidirectional diffusion of boron within the stainless steel (SS) layers while evaluating the updated model ability to replicate melt relocation behavior and geometry. In the current MPS simulations, one scenario employed dummy walls as heat sources, while another scenario used SS surface particles as heat sources to avoid interference with the melt flow as it reached the bottom of the specimen.
Shi, W.*; 町田 昌彦; 山田 進; 岡本 孝司
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 184, p.105710_1 - 105710_10, 2025/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)最近、原子炉建屋内の少ない観測点で測定された空間線量値から放射線源分布を逆推定する方法としてLASSO(Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator)が提案された。しかし、空間線量値を測定する際には誤差が含まれるが、この誤差が逆推定結果の精度にどのように影響するかは解析されていなかった。そこで本論文では、LASSOに対する不確実性解析を行い、Candesの理論に基づく不確実性推定関数を提案した。実際に、モンテカルロ法の1つであるParticle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS)を使用して得られた不確実性を持つ数値を入力値として用いたテスト計算を実施し、計算結果の誤差が提案された推定関数に従うことを示した。これにより、LASSOは推定された不確実性の範囲内で放射線源分布を求めることができる方法であることが確認できた。
 C-SS eutectic melting and its relocation behaviour
C-SS eutectic melting and its relocation behaviourAhmed, Z.*; Sharma, A. K.*; Pellegrini, M.*; 山野 秀将; 岡本 孝司*
Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 50(5), p.3361 - 3371, 2025/03
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)This study pioneers the use of radiative heating for high-resolution visualisation and quantification of the eutectic melt composition, providing a novel approach to observing the melting and candling phenomena. Key findings include two distinct failure processes: SS cladding detachment forming molten droplets and fragmentation of B pellets, with sintering observed in B
pellets, with sintering observed in B powder.
powder.
相原 純; 植田 祥平; 本田 真樹*; 笠原 清司; 岡本 孝司*
JAEA-Research 2024-012, 98 Pages, 2025/02
Pu燃焼高温ガス炉とは、再処理Puの量を安全に減らすための高温ガス炉である。Pu燃焼高温ガス炉では、PuO -イットリア安定化ジルコニア(PuO
-イットリア安定化ジルコニア(PuO -YSZ)の微小球にZrC層を被覆し、更にSiC-TRISO被覆を施した核拡散抵抗性の高い被覆燃料粒子(CFP)を用いる計画である。ZrC層の役割は酸素ゲッターである。平成26-29年に行われたPu燃焼高温ガス炉研究プロジェクトでは、Puの模擬物質としてCeを用いて模擬CFPが製造され、更に、この模擬CFPがHTTR燃料と同様に黒鉛母材で焼き固められ模擬燃料コンパクトが製造された。本報告では、模擬燃料コンパクト製造までの各段階におけるCeO
-YSZ)の微小球にZrC層を被覆し、更にSiC-TRISO被覆を施した核拡散抵抗性の高い被覆燃料粒子(CFP)を用いる計画である。ZrC層の役割は酸素ゲッターである。平成26-29年に行われたPu燃焼高温ガス炉研究プロジェクトでは、Puの模擬物質としてCeを用いて模擬CFPが製造され、更に、この模擬CFPがHTTR燃料と同様に黒鉛母材で焼き固められ模擬燃料コンパクトが製造された。本報告では、模擬燃料コンパクト製造までの各段階におけるCeO -YSZ核及びZrC層の微細構造観察の結果を報告する。
-YSZ核及びZrC層の微細構造観察の結果を報告する。
Zhou, W.*; 三輪 修一郎*; 山下 晋; 岡本 孝司*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 177, p.105441_1 - 105441_17, 2024/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)原子力工学や水力工学の分野では、噴流によって引き起こされる空気の巻き込み現象を理解することが重要である。空気巻込みは、原子力システムの重要な安全設計パラメータの1つである。しかしながら、既存研究のほとんどは、気泡の侵入深さを推定するための経験的相関式やカーブフィッティングモデルに依存しており、様々なジェット条件に対する合意された計算原理は存在しない。この問題に対処するため、本研究では、2つの先進的なAIアプローチを開発した。すなわち、空気巻き込みをセグメント化するための改良型YOLOv5と、気泡侵入深さを予測するためのNSGA-III-BPNN法である。改良型YOLOv5は、多様な条件下での空気巻き込み運動とダイナミクスのリアルタイムなセグメンテーションと抽出を可能にし、高いスケーラビリティとロバスト性を実証した。改良型YOLOv5を用いて推定された侵入深度は、従来の経験的相関と比較して高い精度を示し、動的な空気巻き込みパターンに基づく形状レジームを分類するための従来の画像後処理技術よりも効率的である。一般的にビデオや画像データに依存する物体セグメンテーションの限界を克服するために、NSGA-III-BPNN法はYOLOv5よりも高い精度で最大侵入深度を予測する。YOLOv5よりも高い精度で最大侵入深度を予測し、空気巻き込み侵入深度のより効果的な予測モデルを提供する。高度なAI技術を活用することで、この研究は、数値流体力学(CFD)モデリングを改良するための貴重なセグメンテーションデータを提供するだけでなく、原子力工学と水力工学の両分野における重要な進歩への道を開くものである。
町田 昌彦; 山田 進; Kim, M.; 田中 伶詞*; 飛田 康弘*; 岩田 亜矢子*; 青木 勇斗; 青木 和久; 柳澤 憲一*; 山口 隆司; et al.
RIST News, (70), p.3 - 22, 2024/09
福島第一原子力発電所(1F)建屋内には、原子炉内から漏洩した放射性物質の汚染により高い放射線量を示す地点が多数存在し、廃炉作業を円滑に進める上での大きな障害となっている。日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)は、この課題解決に貢献するため、経済産業省の廃炉・汚染水対策事業費補助金「原子炉建屋内の環境改善のための技術開発(被ばく低減のための環境・線源分布のデジタル化技術の高機能化開発)」を受託し、令和(R)5年度4月より、廃炉屋内の放射線環境改善に係るデジタル技術の研究開発事業を進めている。本事業では、前期事業(R3 4年度実施)にて開発した3 D-ADRES-Indoor(プロトタイプ)を発展させ、現場で活用可能な高速デジタルツイン技術より成るFrontEnd、1F新事務本館等の居室で詳細解析を行うPro、そして、収集したデータ及び解析したデータを集中管理するデータベースの役割を果たすBackEndの3つの連携システムの開発を目標としている。本報告では、この3つの連携システムの中でも現場で活用するシステムとして、点群測定後、迅速に3Dメッシュモデルを作成し、線量率の計測結果から線源を逆推定し、その推定線源の位置や強度を更に高精度化する計算技術(再観測指示と再逆推定)を有するFrontEndを中心に、その開発状況について報告し、その検証結果として5号機での試験結果を示す。また、簡単に当該事業の今後の研究開発の計画も報告する。
4年度実施)にて開発した3 D-ADRES-Indoor(プロトタイプ)を発展させ、現場で活用可能な高速デジタルツイン技術より成るFrontEnd、1F新事務本館等の居室で詳細解析を行うPro、そして、収集したデータ及び解析したデータを集中管理するデータベースの役割を果たすBackEndの3つの連携システムの開発を目標としている。本報告では、この3つの連携システムの中でも現場で活用するシステムとして、点群測定後、迅速に3Dメッシュモデルを作成し、線量率の計測結果から線源を逆推定し、その推定線源の位置や強度を更に高精度化する計算技術(再観測指示と再逆推定)を有するFrontEndを中心に、その開発状況について報告し、その検証結果として5号機での試験結果を示す。また、簡単に当該事業の今後の研究開発の計画も報告する。
 C-stainless steel using the Moving Particle Semi-Implicit (MPS) Method
C-stainless steel using the Moving Particle Semi-Implicit (MPS) MethodAhmed, Z.*; Wu, S.*; Pellegrini, M.*; 岡本 孝司*; Sharma, A.*; 山野 秀将
Proceedings of 14th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation, and Safety (NTHOS-14) (Internet), 14 Pages, 2024/08
本解析では、いったん共晶反応が起こると、ステンレス鋼(SS)へボロンが拡散していくことを示す。単価ホウ素(B C)とSSの界面で溶融が開始し、融体はSS被覆管を伝って流下する。また、昇温するにつれて、融体内のボロン濃度が上昇することがわかった。炉心内のB
C)とSSの界面で溶融が開始し、融体はSS被覆管を伝って流下する。また、昇温するにつれて、融体内のボロン濃度が上昇することがわかった。炉心内のB C侵入の効果を理解するため、更新されたMPS法によって、共晶反応モデルの計算能力がシビアアクシデントを模擬した制御棒の共晶反応及びその後の再配置を効果的に解析できることを示した。
C侵入の効果を理解するため、更新されたMPS法によって、共晶反応モデルの計算能力がシビアアクシデントを模擬した制御棒の共晶反応及びその後の再配置を効果的に解析できることを示した。
 C powder and B
C powder and B C pellet regarding the eutectic reaction with stainless steel
C pellet regarding the eutectic reaction with stainless steelHong, Z.*; Ahmed, Z.*; Pellegrini, M.*; 山野 秀将; Erkan, N.*; Sharma, A. K.*; 岡本 孝司*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 171, p.105160_1 - 105160_13, 2024/06
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:91.70(Nuclear Science & Technology)本研究では、B C粉末とステンレス鋼(SS)間との共晶反応はB
C粉末とステンレス鋼(SS)間との共晶反応はB C粉ペレットとSS間とのそれより相当に速いことが分かった。粉末及びペレットに対して導出された反応速度定数は参考文献値によく一致している。また、粉末とペレットの場合の詳細微細構造をSEM/EDSを用いて組成分析を行った。粉末の場合、(Fe,Cr)Bからなる反応層として厚肉層が見られた。一方、ペレットの場合、2つの反応層が見られた。
C粉ペレットとSS間とのそれより相当に速いことが分かった。粉末及びペレットに対して導出された反応速度定数は参考文献値によく一致している。また、粉末とペレットの場合の詳細微細構造をSEM/EDSを用いて組成分析を行った。粉末の場合、(Fe,Cr)Bからなる反応層として厚肉層が見られた。一方、ペレットの場合、2つの反応層が見られた。
 C pellet-stainless steel under radiative heating
C pellet-stainless steel under radiative heatingAhmed, Z.*; Sharma, A. K.*; Pellegrini, M.*; 山野 秀将; 叶野 翔*; 岡本 孝司*
Ceramics International, 50(10), p.17665 - 17680, 2024/05
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:51.99(Materials Science, Ceramics)本研究では、2つの独特な破損メカニズムを同定した。一つはB Cペレットからステンレス鋼が分離した後に溶融液滴が形成する。もう一つはおそらく熱応力によってB
Cペレットからステンレス鋼が分離した後に溶融液滴が形成する。もう一つはおそらく熱応力によってB Cペレットが複数個に破壊される。可視化技術と界面抵抗解析によって共晶温度を正確に捉えた。
Cペレットが複数個に破壊される。可視化技術と界面抵抗解析によって共晶温度を正確に捉えた。
 C-SS and its relocation behavior
C-SS and its relocation behaviorAhmed, Z.*; Sharma, A. K.*; Pellegrini, M.*; 山野 秀将; 岡本 孝司*
Proceedings of Saudi International Conference On Nuclear Power Engineering (SCOPE2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/11
本研究では、共晶反応とそれに続くボロン移動の融体構造について、輻射加熱を使って定量的な高解像度可視化手法によって観察した。実験は、1150 Cから1372
Cから1372 Cの温度範囲で実機の制御棒設計を模擬したステンレス鋼(SS)管と炭化ホウ素(B
Cの温度範囲で実機の制御棒設計を模擬したステンレス鋼(SS)管と炭化ホウ素(B C)ペレットを用いて実施した。正確な可視化技術によって、共晶溶融開始タイミングとその温度を同定し、ペレットとパウダーのケースで差異を指摘した。
C)ペレットを用いて実施した。正確な可視化技術によって、共晶溶融開始タイミングとその温度を同定し、ペレットとパウダーのケースで差異を指摘した。
町田 昌彦; 山田 進; Kim, M.; 奥村 雅彦; 宮村 浩子; 志風 義明; 佐藤 朋樹*; 沼田 良明*; 飛田 康弘*; 山口 隆司; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
福島第一原子力発電所(1F)建屋内には、原子炉内から漏洩した放射性物質の汚染により高い放射線量を示す地点が多数存在し、廃炉作業を円滑に進める上での大きな障害の一つとなっている。この課題解決に資するため、日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)は、経済産業省の廃炉・汚染水対策事業費補助金「原子炉建屋内の環境改善のための技術の開発(被ばく低減のための環境・線源分布のデジタル化技術の開発)」を受託し、令和3年度より2年間に渡り、放射線源の逆推定と推定線源に対する対策を仮想空間で実施可能とするためのデジタル技術の研究開発を実施してきた。本記事では、上記プロジェクトの成果(以下、前期プロジェクトと呼び、その2年間の研究開発の成果)を紹介する他、令和5年度4月より、新たに開始した継続プロジェクト(以下、後期プロジェクトと呼ぶ)の計画についても報告する。前期プロジェクトにて当初予定していた機械学習技術(LASSO)については、建屋内の複雑な構造情報と汚染源の性質を反映した一つの派生版手法へと結実させた成果を報告する他、実際の原子炉施設での検証結果を示す。更に、開発技術を集約したプラットフォームとしての機能を持つソフトウエア:3D-ADRES-Indoorを紹介し、継続して実施する予定の後期プロジェクトの研究開発計画も紹介する。
Shi, W.*; 町田 昌彦; 山田 進; 吉田 亨*; 長谷川 幸弘*; 岡本 孝司*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 162, p.104792_1 - 104792_19, 2023/08
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:59.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)空間線量率のモニタリングに基づいて原子炉建屋内の放射源分布を予測することは、原子力発電所の廃止措置に向けた最も重要なステップの一つである。しかし、この問題は、一般には数学的には計算を行うには条件が足りない不良設定問題になり、解くことが困難である。そこで、このような不良設定問題でも線源分布の逆推定を成功させるために、損失関数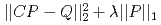 を最小化する機械学習手法であるLASSOの有効性を調査する。ここで、
を最小化する機械学習手法であるLASSOの有効性を調査する。ここで、 および
および はそれぞれ建屋の表面メッシュ上で定義された放射線源により構成されたベクトルおよび室内で観測された空間線量で構成されたベクトルである。また、
はそれぞれ建屋の表面メッシュ上で定義された放射線源により構成されたベクトルおよび室内で観測された空間線量で構成されたベクトルである。また、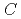 はPHITSを用いて計算された建屋の表面メッシュと観測点の寄与率で構成される行列である。CandesとTaoの理論に基づき、線源分布を正しく予測するための観測点の個数に関する条件を数学的に見出し、実際に、LASSOでは、観測点数がこの条件を満たす限り、実際に高い可能性で線源の分布を示すことができることを確認した。さらに、検出点数が基準値より少ない場合でも、線源分布の一部が示されることを見出した。さらに、現実的な実験モデルにおいても、放射線源が逆推定できることを確認する。最後に、逆推定における予測可能性を高めるために、観測点と線源間の距離のような影響因子を調査する。以上の実証結果から、LASSOスキームは福島第一原子力発電所のような損傷した原子力発電所で見られるホットスポットを探索するのに非常に有用な方法であることを示す。
はPHITSを用いて計算された建屋の表面メッシュと観測点の寄与率で構成される行列である。CandesとTaoの理論に基づき、線源分布を正しく予測するための観測点の個数に関する条件を数学的に見出し、実際に、LASSOでは、観測点数がこの条件を満たす限り、実際に高い可能性で線源の分布を示すことができることを確認した。さらに、検出点数が基準値より少ない場合でも、線源分布の一部が示されることを見出した。さらに、現実的な実験モデルにおいても、放射線源が逆推定できることを確認する。最後に、逆推定における予測可能性を高めるために、観測点と線源間の距離のような影響因子を調査する。以上の実証結果から、LASSOスキームは福島第一原子力発電所のような損傷した原子力発電所で見られるホットスポットを探索するのに非常に有用な方法であることを示す。
Li, C.-Y.; Wang, K.*; 内堀 昭寛; 岡野 靖; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; 高田 孝*; 岡本 孝司*
Applied Sciences (Internet), 13(13), p.7705_1 - 7705_29, 2023/07
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:36.16(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)For a sodium-cooled fast reactor, the capability for stable cooling and avoiding re-criticality on the debris bed is essential for achieving in-vessel retention when severe accidents occur. However, an unexploited uncertainty still existed regarding the compound effect of the heterogeneous configuration and dynamic particle redistribution for the debris bed's criticality and cooling safety assessment. Therefore, this research aims to develop a numerical tool for investigating the effects of the different transformations of the heterogeneous configurations on the debris bed's criticality/cooling assessment. Based on the newly proposed methodology in this research, via integrating the Discrete Element Method (DEM) with Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and Monte-Carlo-based Neutronics (MCN), the coupled CFD-DEM-MCN solver was constructed with the originally created interface to integrate two existing codes. The effects of the different bed configurations' transformations on the bed safety assessments were also quantitively confirmed, indicating that the effect of the particle-centralized fissile material had the dominant negative effect on the safety margin of avoiding re-criticality and particle re-melting accidents and had a more evident impact than the net bed-centralized effect. This coupled solver can serve to further assess the debris bed's safety via a multi-physics simulation approach, leading to safer SFR design concepts.
南上 光太郎; 塩津 弘之; 丸山 結; 杉山 智之; 岡本 孝司*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.816 - 823, 2023/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)For proper source term evaluation, we constructed the theoretical model to estimate the mass transfer coefficient of gaseous iodine species under two-phase flow conditions, which complicates the direct experimental measurements. The mass transfer speed is determined by the product of the overall mass transfer coefficient and the interfacial area. By using the ratio of two gas components, the interfacial area, which is an important parameter that is difficult to measure, can be canceled out and the ratio of their overall mass transfer coefficients can be obtained. This ratio is expected to be equal to the ratio of their diffusion coefficients. Therefore, the unknown mass transfer coefficient such as iodine species can be estimated using the diffusion coefficients of two gas components and the reference mass transfer coefficient such as O . We carried out the experiments using the bubble column to confirm this relationship. From the results in this study, we confirmed that the ratio of the overall mass transfer coefficient was in good agreement with the ratio of diffusion coefficient under the bubbly flow conditions. Using this relationship confirmed in this study, we estimated the mass transfer coefficient of I
. We carried out the experiments using the bubble column to confirm this relationship. From the results in this study, we confirmed that the ratio of the overall mass transfer coefficient was in good agreement with the ratio of diffusion coefficient under the bubbly flow conditions. Using this relationship confirmed in this study, we estimated the mass transfer coefficient of I , one of the iodine species.
, one of the iodine species.
Shi, W.*; 町田 昌彦; 山田 進; 吉田 亨*; 長谷川 幸弘*; 岡本 孝司*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 184, p.109686_1 - 109686_12, 2023/05
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:78.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)Clarification of radioactive source distributions is one of the most important steps in initial decommissioning of not only normally shutdown reactors but also damaged ones by accidents like Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants (FDNPP). Generally, since radioactive hot spots are restricted into specific areas in normal operating conditions, the clarification scheme can be mapped onto the inverse estimation in sparse source distributions. On the other hand, the fact that radioactive hot spots are largely spread in unknown manner as seen in FDNPP motivates to construct an inversion scheme in non-sparse source conditions. Thus, a reconstruction scheme applicable to both sparse and non-sparse radioactive distributions is highly in demand. In addition, a variety of radionuclides is produced in reactors. Thus, we also need a scheme to distinguish each source distribution in mixed multi radionuclides. In this paper, we confirm that the inverse estimation scheme using Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) method with spectral information commonly shows excellent performance in the above all situations. The proposed LASSO scheme with the spectral information enables to reduce the number of measurement points in sparse conditions, while information proliferation by sensing the spectrum makes it possible to directly reconstruct source distribution as almost solvable problems in non-sparse ones. Moreover, the LASSO scheme allows to reconstruct the source distribution of each potential radionuclide in multi-radionuclide coexisting situations. Consequently, we confirm that the LASSO scheme to reconstruct radioactive sources is promising for the future nuclear decommissioning projects widely from normally shutdown reactors to damaged ones like FDNPP.
沖田 将一朗; 水田 直紀; 高松 邦吉; 後藤 実; 吉田 克己*; 西村 洋亮*; 岡本 孝司*
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
Adoption of SiC-matrix fuel elements in future pin-in-block type HTGR designs will enhance oxidation resistance of the fuel element in the event of the air ingress accident, one of the most worrisome accidents in HTGRs. This would eliminate the need for the graphite sleeves used in the current pin-in-block type HTGR designs and enable high power density core designs with sleeveless and direct coolable fuel structure. Such a concept itself has been suggested by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in the past. However, JAEA has not yet demonstrated the feasibility for a core design with the SiC-matrix fuel elements. The present work is intended to demonstrate the feasibility for a new core design upgraded from an existing conceptual core design, called HTR50S, with 50 MW thermal power and reactor outlet temperature of 750 C. The new core design uses SiC-matrix fuel elements and increases the reactor power density to 1.2 times higher than the original HTR50S design. The feasibility is determined by whether the core satisfies the target values in nuclear and thermal-hydraulic designs by performing burn-up calculation with the whole core model and fuel temperature calculations. The calculation results showed that the new core design satisfied these target values on the reactor shutdown margin, the temperature coefficient of reactivity, and the maximum fuel temperature during normal operation.
C. The new core design uses SiC-matrix fuel elements and increases the reactor power density to 1.2 times higher than the original HTR50S design. The feasibility is determined by whether the core satisfies the target values in nuclear and thermal-hydraulic designs by performing burn-up calculation with the whole core model and fuel temperature calculations. The calculation results showed that the new core design satisfied these target values on the reactor shutdown margin, the temperature coefficient of reactivity, and the maximum fuel temperature during normal operation.
町田 昌彦; Shi, W.*; 山田 進; 宮村 浩子; 吉田 亨*; 長谷川 幸弘*; 岡本 孝司; 青木 勇斗; 伊藤 倫太郎; 山口 隆司; et al.
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2023/02
In order to find radioactive hot spots inside reactor building rooms from structural data together with air dose rate measurement data, Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) has been recently suggested as a promising scheme. The scheme has been examined in simplified room models and its high estimation feasibility has been confirmed by employing Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) as a radiation simulation code. In this paper, we apply the scheme to complex room models inside real reactor buildings. The target rooms are pool canal circulation system room and main circulation system room in Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) at Oarai area, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). In these real rooms, we create STL format structural data based on Computer Aided Design (CAD) models made directly from their point group data measured by laser scanning devices, and we notice that the total number of their surface meshes in these real rooms reaches to the order of 1 million. Then, this order of the mesh number clearly indicates that one needs a simplified radiation simulation code considering only direct transmission of gamma ray as a radiation calculation instead of PHITS demanding high computational costs. By developing such a simplified code and customizing it to perform LASSO scheme, we consequently confirm that LASSO scheme driven by the simplified simulation can also successfully predict unknown radioactive hot spots on real structural models.
Shi, W.*; 町田 昌彦; 山田 進; 吉田 亨*; 長谷川 幸弘*; 岡本 孝司*
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/02
Clarifying hot spots of radioactive sources inside reactor building rooms based on monitoring air dose rates is one of the most essential steps in decommissioning of nuclear power plants. However, the attempt is regarded as a rather difficult task, because information obtained by air dose rate measurements is generally not enough to inversely estimate contaminated distribution among a tremendous number of potential distributions inside complex reactor building rooms as far as one uses the conventional ways. Then, in order to successfully perform the inverse estimations on source distributions even in such ill-posed circumstances, we suggest that a machine learning method, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) is a promising scheme. Subsequently, we construct a simple room model and employ Monte Carlo simulation code, Particle and Heavy Ion Transport Systems (PHITS) to numerically test feasibility of LASSO inverse estimation scheme. Consequently, we confirm high reconstruction performance of the LASSO scheme in successfully predicting radioactive source distributions. In addition, we carry out uncertainty analysis for the inverse estimation and derive an error function describing uncertainty of the inverse estimation as a useful error estimator. Finally, we find that additional use of spectral information in the measurements can significantly decrease the number of measurement points for the present inverse estimation. In conclusion, LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore radioactive hot spots toward the future decommissioning of nuclear power plants.
Hong, Z.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; Liao, H.*; Yang, H.*; 山野 秀将; 岡本 孝司*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 180, p.109462_1 - 109462_9, 2023/01
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:41.50(Nuclear Science & Technology)実機制御棒の模擬材として、B C材とSUS304を用いて一連の実験を実施した。1450K-1500Kの温度範囲で共晶反応速度定数を得た結果、本研究で得られた反応速度定数は参照値と一致した。また、反応面の微細構造を観察し、組成分析を行った。
C材とSUS304を用いて一連の実験を実施した。1450K-1500Kの温度範囲で共晶反応速度定数を得た結果、本研究で得られた反応速度定数は参照値と一致した。また、反応面の微細構造を観察し、組成分析を行った。
南上 光太郎; 石川 淳; 杉山 智之; Pellegrini, M.*; 岡本 孝司*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1407 - 1416, 2022/11
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:73.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)To appropriately evaluate the amount of radioactive iodine released into the environment, we extended the current pool scrubbing model to consider revolatilization at bubble surfaces due to bubbly flow generated in the suppression pool, and the effect of revolatilization by bubbly flow was quantitatively evaluated using a station black out sequence in this work. Gaseous iodine species are produced in the suppression pool in an accident. They are gradually released from the pool surface, but when a large amount of gas flows from the drywell into the suppression pool, the revolatilization of gaseous iodine dissolved in the pool water is promoted by bubbly flow. The results of this study indicated that the release amount of iodine immediately after suppression chamber (S/C) vent operation increased by up to 134 times when considering the revolatilization effect associated with bubbly flow. These results were due to the increase in the gas-liquid interfacial area at bubble surfaces and the overall mass transfer coefficients under two-phase flow conditions due to bubbly flow. It was shown that caution is required for early S/C vent operation.