Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction study伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 287, p.120767_1 - 120767_16, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Incorporating solute hydrogen into Fe-Cr-Ni-based austenitic stainless steels enhances both strength and ductility, providing a promising solution to hydrogen embrittlement by causing solid-solution strengthening and assisting deformation twinning. However, its impacts on the relevant lattice defects evolution ( , dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using
, dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using  neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; 木村 勇次*; 山口 正剛; 海老原 健一; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 280, p.120288_1 - 120288_14, 2024/11
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The present study aimed at strengthening prior austenite grain boundary (PAGB) cohesive energy using carbon segregation and investigated the effect of carbon segregation at PAGB on the microscopic crack propagation behavior of hydrogen-related intergranular fractures in high-strength martensitic steels. At the low hydrogen content (below 0.2 wt. ppm), the fracture initiation toughness (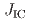 ) and tearing modulus (
) and tearing modulus (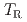 ), corresponding to crack growth resistance, were significantly improved by carbon segregation. In contrast,
), corresponding to crack growth resistance, were significantly improved by carbon segregation. In contrast, 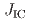 and
and 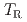 did not change by carbon segregation at the high hydrogen content (above 0.5 wt. ppm). Considering the non-linear relationship between the toughness properties and the PAGB cohesive energy, the experimentally evaluated toughness properties (
did not change by carbon segregation at the high hydrogen content (above 0.5 wt. ppm). Considering the non-linear relationship between the toughness properties and the PAGB cohesive energy, the experimentally evaluated toughness properties (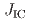 and
and 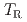 ) and the GB cohesive energy previously calculated by first-principles calculations were semi-quantitatively consistent even at the high hydrogen content. The microstructure observation confirmed that the plastic deformation associated with crack propagation, such as the local ductile fracture of uncracked ligaments and the formation of dislocation cell structures/nano-voids, played an important role in the non-linear relationship between the toughness properties and PAGB cohesive energy.
) and the GB cohesive energy previously calculated by first-principles calculations were semi-quantitatively consistent even at the high hydrogen content. The microstructure observation confirmed that the plastic deformation associated with crack propagation, such as the local ductile fracture of uncracked ligaments and the formation of dislocation cell structures/nano-voids, played an important role in the non-linear relationship between the toughness properties and PAGB cohesive energy.
 neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel
neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Steel Science (ISSS 2024), p.237 - 240, 2024/11
Hydrogen embrittlement has long been an obstacle to the development of safe infrastructure. However, in contrast to hydrogen's embrittling effect, recent research has revealed that the addition of hydrogen improves both the strength and uniform elongation of AISI Type 310S austenitic stainless steel. A detailed understanding of how hydrogen affects the deformation mechanism of this steel could pave the way for the development of more advanced materials with superior properties. In the present study,  neutron diffraction experiments were conducted on Type 310S steel with and without hydrogen-charged to investigate the effect of hydrogen on the deformation mechanism. In addition to the effect of solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen, the q-value, a parameter representing the proportion of edge and screw dislocations in the accumulated dislocations, was quantitatively evaluated using CMWP analysis on neutron diffraction patterns. The comparison of q-values between the hydrogen-charged and non-charged samples reveals that hydrogen has minimal effect on dislocation character in Type 310S steel.
neutron diffraction experiments were conducted on Type 310S steel with and without hydrogen-charged to investigate the effect of hydrogen on the deformation mechanism. In addition to the effect of solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen, the q-value, a parameter representing the proportion of edge and screw dislocations in the accumulated dislocations, was quantitatively evaluated using CMWP analysis on neutron diffraction patterns. The comparison of q-values between the hydrogen-charged and non-charged samples reveals that hydrogen has minimal effect on dislocation character in Type 310S steel.
上路 林太郎*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 柴田 曉伸*; 木村 勇次*; 井上 忠信*; 土田 紀之*
ISIJ International, 64(2), p.459 - 465, 2024/01
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:41.92(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT) during tensile or compressive deformations of the bainitic steels with various carbon content (0.15%C, 0.25%C, 0.62%C) was studied. In all of the bainitic steels, the tensile deformation exhibited larger work hardening than the compression. This difference indicates the suppression of the DIMT at the compression, and actually the measurements of electron back scattering diffraction (EBSD) confirmed the less reduction of retained austenite at the compression of all the bainitic steels. Additionally, the steel with the highest carbon content was examined by in situ neutron diffraction and clarified the difference similar to that obtained by the EBSD measurement. The regression of the relation between the fraction of austenite and applied strain with the conventional empirical equation revealed that the kinetic of DIMT is strongly dependent with the stress polarity, but not significantly changed by the carbon content.
Mao, W.; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Bai, Y.*; Harjo, S.; Park, M.-H.*; 柴田 曉伸*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 256, p.119139_1 - 119139_16, 2023/09
被引用回数:33 パーセンタイル:97.68(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)変形誘起塑性(TRIP)鋼は、変形誘起マルテンサイト変態(DIMT)に伴う加工硬化率の向上により、強度と延性の優れた組み合わせを示す。TRIP鋼や合金の加工硬化挙動におけるDIMTの役割を定量的に評価することは、強度と延性の両立を可能にする先進材料を設計するための指針を与えるが、変形中に相組成が変化し続け、応力と塑性ひずみの両方が構成相間で動的に分配されるため、その評価は困難である。本研究では、Fe-24Ni-0.3C(wt.%)TRIPオーステナイト鋼の引張変形とその場中性子回折測定を行った。中性子回折測定による応力分割と相分割に基づく解析手法を提案し、試験片の引張流動応力と加工硬化率を、オーステナイト母相,変形誘起マルテンサイト、DIMT変態速度に関連する因子に分解し、試料の加工硬化挙動における各因子の役割を考察した。さらに、回折プロファイル解析により測定した転位密度を用いてオーステナイトとマルテンサイト間の塑性ひずみ分配を間接的に推定し、材料中のオーステナイトとマルテンサイト間の応力・ひずみ分配の全体像を構築した。その結果、変形誘起マルテンサイト変態速度とマルテンサイトが負担する相応力の両方が、材料の全体的な引張特性に重要な役割を果たしていることが示唆された。提案した分解解析法は、TRIP現象を示す多相合金の機械的挙動を調べるために広く適用できる可能性がある。
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionGong, W.; Harjo, S.; 友田 陽*; 諸岡 聡; 川崎 卓郎; 柴田 曉伸*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 250, p.118860_1 - 118860_16, 2023/05
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:90.95(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Martensitic transformation is accompanied by the generation of microscale and macroscale internal stresses during cooling below the martensitic transformation start temperature. These internal stresses have been determined through X-ray or neutron diffraction, but the reported results are not consistent, probably because the measured lattice parameter is influenced not only by the internal stress but also by several factors, including solute elements and crystal defects. Therefore,  neutron diffraction combined with dilatometry measurements during martensitic transformation and subsequent cyclic tempering were performed for an Fe-18Ni alloy. The phase strains calculated by lattice parameter variations show that a hydrostatic compressive strain in austenite and a tensile strain in martensite arose as the martensitic transformation progressed during continuous cooling or isothermal holding. However, the phase stresses of austenite and martensite estimated from these strains failed to hold stress balance law when dense crystal defects involved in the processes. After these crystal defects were removed by appropriate tempering, the stress balance law held well. Meanwhile, the phase stresses of austenite and martensite were changed to opposite, revealing their true identity. Various crystal defects in austenite and martensite, introduced by plastic accommodation, were suggested to affect their lattice parameters and then their phase stresses.
neutron diffraction combined with dilatometry measurements during martensitic transformation and subsequent cyclic tempering were performed for an Fe-18Ni alloy. The phase strains calculated by lattice parameter variations show that a hydrostatic compressive strain in austenite and a tensile strain in martensite arose as the martensitic transformation progressed during continuous cooling or isothermal holding. However, the phase stresses of austenite and martensite estimated from these strains failed to hold stress balance law when dense crystal defects involved in the processes. After these crystal defects were removed by appropriate tempering, the stress balance law held well. Meanwhile, the phase stresses of austenite and martensite were changed to opposite, revealing their true identity. Various crystal defects in austenite and martensite, introduced by plastic accommodation, were suggested to affect their lattice parameters and then their phase stresses.
 phase to
phase to  phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformation
phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformationGuo, B.*; Mao, W.; Chong, Y.*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Chen, H.*; Jonas, J. J.*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 242, p.118427_1 - 118427_11, 2023/01
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:70.10(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dynamic transformation from alpha (HCP) to beta (BCC) phase in a zirconium alloy was revealed by the use of in-situ neutron diffraction during hot compression. The dynamic transformation was unexpectedly detected during isothermal compression at temperatures of 900 C and 950
C and 950 C (alpha + beta two-phase region) and strain rates of 0.01 s
C (alpha + beta two-phase region) and strain rates of 0.01 s and 0.001 s
and 0.001 s , even though equilibrium two-phase states were achieved prior to the hot compression. Dynamic transformation was accompanied by diffusion of Sn from beta to alpha phase, which resulted in changes of lattice parameters and a characteristic microstructure of alpha grains. The details of dynamic transformation are discussed using the evolution of lattice constants.
, even though equilibrium two-phase states were achieved prior to the hot compression. Dynamic transformation was accompanied by diffusion of Sn from beta to alpha phase, which resulted in changes of lattice parameters and a characteristic microstructure of alpha grains. The details of dynamic transformation are discussed using the evolution of lattice constants.
吉田 周平*; Fu, R.*; Gong, W.; 池内 琢人*; Bai, Y.*; Feng, Z.*; Wu, G.*; 柴田 曉伸*; Hansen, N.*; Huang, X.*; et al.
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 1249, p.012027_1 - 012027_6, 2022/08
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:80.61(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)This study revealed characteristics of the deformation behavior in high/medium entropy alloys (HEAs/MEAs) with face-centered cubic (FCC) structure. A Co Ni
Ni alloy and a Co
alloy and a Co Cr
Cr Ni
Ni MEA having low and high friction stresses (fundamental resistance to dislocation glide in solid solutions), respectively, but similar in other properties, including their stacking fault energy and grain sizes, were compared. The MEA exhibited a higher yield strength and work-hardening ability than those in the Co
MEA having low and high friction stresses (fundamental resistance to dislocation glide in solid solutions), respectively, but similar in other properties, including their stacking fault energy and grain sizes, were compared. The MEA exhibited a higher yield strength and work-hardening ability than those in the Co Ni
Ni alloy at room temperature. Deformation microstructures of the Co
alloy at room temperature. Deformation microstructures of the Co Ni
Ni alloy were composed of coarse dislocation cells (DCs) in most grains, and a few deformation twins (DTs) formed in grains with tensile axis (TA) nearly parallel to
alloy were composed of coarse dislocation cells (DCs) in most grains, and a few deformation twins (DTs) formed in grains with tensile axis (TA) nearly parallel to  111
111 . In the MEA, three microstructure types were found depending on the grain orientations: (1) fine DCs developed in TA
. In the MEA, three microstructure types were found depending on the grain orientations: (1) fine DCs developed in TA //
// 100
100 -oriented grains; (2) planar dislocation structures (PDSs) formed in grains with other orientations; and (3) dense DTs adding to the PDSs developed in TA
-oriented grains; (2) planar dislocation structures (PDSs) formed in grains with other orientations; and (3) dense DTs adding to the PDSs developed in TA //
// 111
111 -oriented grains. The results imply difficulty in cross-slip of screw dislocations and dynamic recovery in the MEA, leading to an increase in the dislocation density and work-hardening rate. Our results suggest that FCC high-alloy systems with high friction stress inherently develop characteristic deformation microstructures advantageous for achieving high strength and large ductility.
-oriented grains. The results imply difficulty in cross-slip of screw dislocations and dynamic recovery in the MEA, leading to an increase in the dislocation density and work-hardening rate. Our results suggest that FCC high-alloy systems with high friction stress inherently develop characteristic deformation microstructures advantageous for achieving high strength and large ductility.
Mao, W.; Gao, S.*; Bai, Y.*; Park, M.-H.*; 柴田 曉伸*; 辻 伸泰*
Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 17, p.2690 - 2700, 2022/03
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:81.39(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)超微細結晶粒(UFG)組織を有する準安定オーステナイト鋼は、冷間圧延中の変形誘起マルテンサイト変態と焼鈍時のオーステナイトへの逆変態を利用することにより、従来の冷間圧延および焼鈍プロセスで製造することができる。しかし、変形誘起マルテンサイト変態に対するオーステナイトの機械的安定性が高い場合には、冷間圧延中に十分な量のマルテンサイトが生成しないため、このようなプロセスは適用できない。本研究では、高い機械的安定性を有するFe-24Ni-0.3C準安定オーステナイト鋼に対して、冷間圧延と焼鈍の2段階プロセスを適用した。冷間圧延に先立ち、繰り返しサブゼロ処理と逆焼鈍処理を施した。このような処理により、オーステナイトの機械的安定性が劇的に低下し、その後の冷間圧延工程で変形誘起マルテンサイトの生成が大幅に促進された。その結果、結晶粒の微細化が著しく促進され、平均オーステナイト粒径0.5mmの完全再結晶試験片の作製に成功し、高強度と高延性を両立させた。
岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Gong, W.; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 225, p.117549_1 - 117549_13, 2022/02
被引用回数:29 パーセンタイル:91.89(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, the deformation microstructure of hydrogen-charged ferritic-pearlitic 2Mn-0.1C steel was characterized using SEM-BSE, SEM-EBSD, TEM, and neutron diffraction. The microscopic mechanism of hydrogen-related quasi-cleavage fracture along the 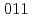 planes was also discussed. It was found that hydrogen increased the relative velocity of screw dislocations to edge dislocations, leading to a tangled dislocation morphology, even at the initial stage of deformation (strain = 0.03). In addition, the density of screw dislocations at the later stage of deformation (strain = 0.20) increased in the presence of hydrogen. Based on the experimental results, it is proposed that a high density of vacancies accumulated along
planes was also discussed. It was found that hydrogen increased the relative velocity of screw dislocations to edge dislocations, leading to a tangled dislocation morphology, even at the initial stage of deformation (strain = 0.03). In addition, the density of screw dislocations at the later stage of deformation (strain = 0.20) increased in the presence of hydrogen. Based on the experimental results, it is proposed that a high density of vacancies accumulated along 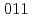 slip planes by jog-dragging of screw dislocations, and coalescence of the accumulated vacancies led to the hydrogen-related quasi-cleavage fracture along the {011} slip planes.
slip planes by jog-dragging of screw dislocations, and coalescence of the accumulated vacancies led to the hydrogen-related quasi-cleavage fracture along the {011} slip planes.
 neutron diffraction study on the deformation of a TRIP-assisted multi-phase steel composed of ferrite, austenite and martensite
neutron diffraction study on the deformation of a TRIP-assisted multi-phase steel composed of ferrite, austenite and martensiteLavakumar, A.*; Park, M. H.*; Gao, S.*; 柴田 曉伸*; 興津 貴隆*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 580, p.012036_1 - 012036_6, 2019/09
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:81.94(Engineering, Mechanical)Multi-phase steels showing transformation induced plasticity (TRIP), can exhibit an excellent combination of high strength and good ductility by the aid of martensitic transformation during deformation. Even though TRIP-assisted multi-phase steels have been widely used in industry, the role of each phase in the enhancement of mechanical properties is still unclear given their complicated microstructures. In order to understand better the nature of the TRIP effect, the mechanical interaction between different phases at the micro-scale should be clarified. In the present study, the mechanical behavior of a transformation induced plasticity (TRIP) assisted multi-phase steel, has been characterized by  neutron diffraction during tensile testing. The result of strain partitioning between the different phases obtained from the
neutron diffraction during tensile testing. The result of strain partitioning between the different phases obtained from the  neutron analysis revealed that the martensite phase took much more elastic strain than the ferrite and retained austenite phases, which suggests that the work hardening behavior in the present steel is affected by the higher load borne by deformation-induced martensite.
neutron analysis revealed that the martensite phase took much more elastic strain than the ferrite and retained austenite phases, which suggests that the work hardening behavior in the present steel is affected by the higher load borne by deformation-induced martensite.
 neutron diffraction analysis during thermomechanical processing
neutron diffraction analysis during thermomechanical processing柴田 曉伸*; 竹田 泰成*; Park, N.*; Zhao, L.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Gong, W.*; 辻 伸泰*
Scripta Materialia, 165, p.44 - 49, 2019/05
被引用回数:37 パーセンタイル:84.22(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Nowadays, a new concept of process utilizing dynamic ferrite transformation, which can achieve ultrafine-grained structure with a mean grain size of approximately 1 m, has been proposed. This paper reports transformation mode of dynamic ferrite transformation and formation mechanism of ultrafine-grained structure revealed by our novel technique of
m, has been proposed. This paper reports transformation mode of dynamic ferrite transformation and formation mechanism of ultrafine-grained structure revealed by our novel technique of  neutron diffraction analysis during thermomechanical processing. Dynamic ferrite transformation occurs in a diffusional manner, whose partitioning behavior changes from para- to ortho-equilibrium with the progress of transformation. Moreover, we propose that dynamic recrystallization of dynamically-transformed ferrite is the main mechanism for the formation of ultrafine-grained structure.
neutron diffraction analysis during thermomechanical processing. Dynamic ferrite transformation occurs in a diffusional manner, whose partitioning behavior changes from para- to ortho-equilibrium with the progress of transformation. Moreover, we propose that dynamic recrystallization of dynamically-transformed ferrite is the main mechanism for the formation of ultrafine-grained structure.
中村 良彦*; 柴田 曉伸*; Gong, W.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 伊東 篤志*; 辻 伸泰*
Proceedings of International Conference on Martensitic Transformations: Chicago, p.155 - 158, 2018/04
The microstructure evolution of medium manganese steel (Fe-5Mn-2Si-0.1C (wt%)) during thermo-mechanical processing in ferrite + austenite two-phase region was investigated by in situ neutron diffraction analysis and microstructure observations. When the specimens were isothermally held at a temperature of 700 C, the fraction of reversely transformed austenite increased gradually with an increase in the isothermal holding time. However, it did not reach the equilibrium fraction of austenite even after isothermal holding for 10 ks. On the other hand, the fraction of reversely transformed austenite increased rapidly after the compressive deformation at a strain rate of 1 s
C, the fraction of reversely transformed austenite increased gradually with an increase in the isothermal holding time. However, it did not reach the equilibrium fraction of austenite even after isothermal holding for 10 ks. On the other hand, the fraction of reversely transformed austenite increased rapidly after the compressive deformation at a strain rate of 1 s at 700
at 700 C and reached the equilibrium state during subsequent isothermal holding for around 3 ks.
C and reached the equilibrium state during subsequent isothermal holding for around 3 ks.
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Hydrogen is attracting attention as an alternative energy carrier to fossil fuels to establish a sustainable society. However, hydrogen is considered to cause embrittlement in steel, which has been a longstanding issue known as hydrogen embrittlement. In contrast to the embrittlement, recently, Ogawa  , reported that the addition of hydrogen improved both strength and ductility in SUS310S (Fe-24Cr-19Ni mass%) steel. This phenomenon is attributed to hydrogen-induced solid solution strengthening and the promotion of twinning deformation. These approaches are gaining attention as effective ways to utilize hydrogen, which has long been considered harmful. However, the impact of hydrogen on crystal defects (dislocations, stacking faults) and the mechanisms behind enhanced twinning in SUS310S steel remain unclear. In this work, we investigated the deformation mechanisms of hydrogen-charged SUS310S steel by
, reported that the addition of hydrogen improved both strength and ductility in SUS310S (Fe-24Cr-19Ni mass%) steel. This phenomenon is attributed to hydrogen-induced solid solution strengthening and the promotion of twinning deformation. These approaches are gaining attention as effective ways to utilize hydrogen, which has long been considered harmful. However, the impact of hydrogen on crystal defects (dislocations, stacking faults) and the mechanisms behind enhanced twinning in SUS310S steel remain unclear. In this work, we investigated the deformation mechanisms of hydrogen-charged SUS310S steel by  neutron diffraction measurement conducted by TAKUMI (MLF-BL19) of J-PARC.
neutron diffraction measurement conducted by TAKUMI (MLF-BL19) of J-PARC.
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
持続可能な社会の構築に向け、国を挙げて水素社会の実現に向けた研究が行われている。水素インフラを構築するために、水素環境で強度・延性に優れる鉄鋼材料が求められているが、一般的に水素は脆化を引き起こすと考えられてきた。しかし近年、SUS310S (Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%))において、水素により強度・延性が共に向上することが報告され、注目を集めている。これには水素由来の固溶強化と双晶変形の促進が寄与していると考えられているが、転位密度や積層欠陥など、個々の因子に対する水素の影響の詳細は明らかとなっていない。そこで本研究では、MLFの工学材料回折装置 「匠」を利用した引張変形中その場中性子回折実験を行い、変形メカニズムに及ぼす水素の影響を定量的に評価した。
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
持続可能な社会の構築に向け、国を挙げて水素社会の実現を目指した研究が行われている。水素社会を実現するためには、安全性と信頼性を両立した水素インフラの構築が必要不可欠であり、そこで用いられる鉄鋼材料の変形メカニズムに対する水素の影響を明らかにすることは極めて重要である。多くの場合、水素は鉄鋼材料を脆化させ、機械特性を低下させると考えられてきた。しかし近年、小川らにより、SUS310S(Fe-24Cr-19Ni, mass%)に水素を均一に添加することで強度・延性が共に向上することが報告された)。これは、これまで材料特性を悪化させると考えられてきた水素を有効利用することが出来る手法として、注目を集めている。これには、水素由来の固溶強化と双晶変形の促進が寄与していると考えられている。しかし、転位密度や積層欠陥密度など、材料特性を司る個々の因子に対する水素の影響の詳細は明らかになっていない。そこで本研究では水素チャージを施したSUS310Sに対して「匠」を用いた引張試験中その場中性子回折実験を行い、変形メカニズムに及ぼす固溶水素の影響を調査した。
Mao, W.; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Park, M. H.*; Bai, Y.*; 柴田 曉伸*; 辻 伸泰*
no journal, ,
Deformation induced martensitic transformation (DIMT) during plastic deformation of metastable austenitic steels plays an important role in enhancing their strain hardening, leading to an outstanding combination of strength and tensile ductility. In this study, Fe-24Ni-0.3C metastable austenitic steel specimens having mean grain sizes ranging from 1.3 micrometer to 35 micrometers were fabricated by cold rolling and subsequent annealing processes. The effect of the grain size on the strain hardening behavior and DIMT in the material was investigated by tensile test at room temperature with in-situ neutron diffraction. Results obtained by the in-situ neutron diffraction showed that the enhanced strain-hardening rate was caused not only by the increase of the volume fraction of martensite but also by the rapid increase of the internal stress within martensite. When the grain size changed within the coarse grained region (35 micrometers to 4 micrometers) the influence of the grain size on the stress partitioning between austenite and martensite was relatively small, thus the work-hardening behavior was mainly determined by the increasing rate of the volume fraction of martensite. However, when the grain size decreased down to ultrafine grain regime (smaller than 2 micrometers), the internal stress in martensite significantly increased, which resulted in the increasing work-hardening rate. The increasing stress in martensite in the ultrafine grained specimens is explained by the enhanced elastic stress associated with the incompatibility between martensite and austenite phases.
Harjo, S.; 宮本 吾郎*; 柴田 曉伸*; 小山 元道*; 吉見 享祐*; Su, Y. H.; 高田 慎一; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎
no journal, ,
エネルギーミックスの最適化や地球温暖化の回避には、代替エネルギーキャリアの活用、高性能構造材の開発、そして熱効率の向上が求められる。しかし、その材料が使用環境で特性を発現するメカニズムについては、解明が不十分であることが課題である。これらの課題は、国内外の研究で取り組まれており、共通のキーワードである「欠陥」と「複相組織」を基盤に、課題横断的な研究が進められている。上記の耐疲労表面硬化材料、耐水素材料、及び超高温耐熱材料における複雑組織や破壊メカニズムを解明するため、MLFのBL19、BL15、BL22を用いたプロジェクト課題が2024年度より進行している。ポスター発表では、2024年度の進捗状況について報告する。
Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 友田 陽*; 諸岡 聡; 川崎 卓郎; 柴田 曉伸*; 辻 伸泰*
no journal, ,
Austenite to martensite transformation in steels is a volume expansion phase transformation. However, the puzzling results have still been reported that a hydrostatic compressive stress was observed in austenite as opposite to the Eshelby's inclusion theory. In present study, we carried out neutron diffraction experiments having higher penetration ability than above methods to investigate the lattice parameter changes in real time during martensitic transformation. A high-purity Fe-18Ni binary alloy was selected to avoid the chemical contribution from the interstitial element. Several measuring processes were carefully designed and performed by in-situ neutron diffraction. Thermal phase stresses in martensite and austenite phases were separated from those stemmed from the face-centered cubic to body-centered cubic transformation strains and lattice defects. As results, the plastic accommodation is suggested to affect the lattice parameter of austenite and then its phase stress.
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
近年、高圧ガス環境中で均一に水素を固溶させたオーステナイト系ステンレス鋼SUS310Sにおいて、強度・延性が共に向上することが報告された。これは水素による固溶強化と双晶変形の促進によると説明されているが、転位密度や積層欠陥など、個々の因子に対する水素の影響の詳細は明らかとなっていない。本研究では、J-PARCの工学材料回折装置「匠」での引張試験中その場中性子回折により、変形メカニズムを明らかにすることを試みた。得られた中性子回折パターンから、水素による体積変化や固溶強化の存在を確認した。更に、転位密度、積層欠陥密度、双晶変形開始ひずみ・応力を評価した。これらの解析により、水素が変形メカニズムに与える影響を明らかにした。